The Spanish language is known for its complex verb conjugation system, and the preterite tense is no exception. The preterite tense, also known as the simple past, is used to describe completed actions that occurred at a specific point in the past. In this article, we will delve into the world of verb conjugation, focusing on the preterite tense of the verb "ver," which means "to see." We will explore the conjugation patterns, provide examples, and offer tips for mastering this essential aspect of Spanish grammar.
Key Points
- The preterite tense is used to describe completed actions that occurred at a specific point in the past.
- The verb "ver" is a regular -er verb, and its preterite conjugation follows a predictable pattern.
- The preterite conjugation of "ver" is used to describe actions such as seeing, watching, or observing something in the past.
- Mastering the preterite conjugation of "ver" is essential for effective communication in Spanish.
- Practice and context are key to understanding and using the preterite tense correctly.
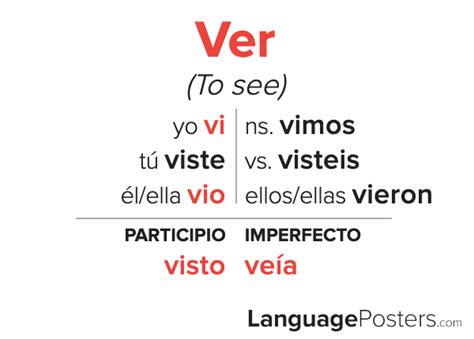
Preterite Conjugation of Ver

The verb “ver” is a regular -er verb, and its preterite conjugation follows a predictable pattern. The conjugation is as follows:
| Subject | Preterite Conjugation |
|---|---|
| Yo | vi |
| Tú | viste |
| Él/ella/usted | vio |
| Nosotros/as | vimos |
| Vosotros/as | visisteis |
| Ellos/as | vieron |

As you can see, the preterite conjugation of "ver" is relatively straightforward. The verb endings are added to the root "vi-" to form the conjugated verb. For example, "yo vi" means "I saw," and "ella vio" means "she saw."
Using the Preterite Conjugation of Ver in Context
The preterite conjugation of “ver” is used to describe actions that occurred at a specific point in the past. For example:
Ayer, yo vi una película en el cine. (Yesterday, I saw a movie at the cinema.)
Mi hermano vio un concierto de rock la semana pasada. (My brother saw a rock concert last week.)
Nosotros vimos un documental sobre la historia de España. (We saw a documentary about the history of Spain.)
As you can see, the preterite conjugation of "ver" is used to describe a wide range of actions, from seeing a movie to watching a concert or observing a historical event.
Common Mistakes and Tips

One common mistake when using the preterite conjugation of “ver” is to confuse it with the present tense. For example, “yo veo” means “I see,” whereas “yo vi” means “I saw.” To avoid this mistake, make sure to use the correct verb ending for the subject and tense.
Another tip is to practice the preterite conjugation of "ver" in different contexts. Try using it to describe actions that occurred at different times in the past, such as yesterday, last week, or last year. This will help you get a feel for how the preterite tense is used in everyday conversation.
Irregularities and Exceptions
While the preterite conjugation of “ver” is relatively regular, there are some irregularities and exceptions to be aware of. For example, the verb “ver” can be used in the imperfect tense to describe ongoing or repeated actions in the past. In this case, the conjugation is different from the preterite tense.
Additionally, the verb "ver" can be used in the present perfect tense to describe actions that started in the past and continue up to the present. This tense is formed using the present tense of the verb "haber" (to have) and the past participle of "ver," which is "visto."
| Subject | Present Perfect Conjugation |
|---|---|
| Yo | he visto |
| Tú | has visto |
| Él/ella/usted | ha visto |
| Nosotros/as | hemos visto |
| Vosotros/as | habéis visto |
| Ellos/as | han visto |
As you can see, the present perfect tense is used to describe actions that have a connection to the present, such as "yo he visto una película esta semana" (I have seen a movie this week).
What is the difference between the preterite and imperfect tenses in Spanish?
+The preterite tense is used to describe completed actions that occurred at a specific point in the past, whereas the imperfect tense is used to describe ongoing or repeated actions in the past.
How do I know when to use the preterite or present perfect tense in Spanish?
+The preterite tense is used to describe actions that occurred at a specific point in the past, whereas the present perfect tense is used to describe actions that started in the past and continue up to the present.
Can I use the preterite conjugation of "ver" to describe actions that occurred in the present?
+No, the preterite conjugation of "ver" is used to describe actions that occurred in the past, not in the present. To describe actions that occurred in the present, you would use the present tense of "ver," which is "veo."
In conclusion, the preterite conjugation of “ver” is a fundamental aspect of Spanish grammar, and mastering it is essential for effective communication. By practicing the conjugation in context and understanding the nuances of the preterite tense, you can improve your Spanish skills and become a more confident speaker. Remember to use the correct verb ending for the subject and tense, and don’t be afraid to practice and make mistakes. With time and effort, you’ll become proficient in using the preterite conjugation of “ver” to describe a wide range of actions in the past.