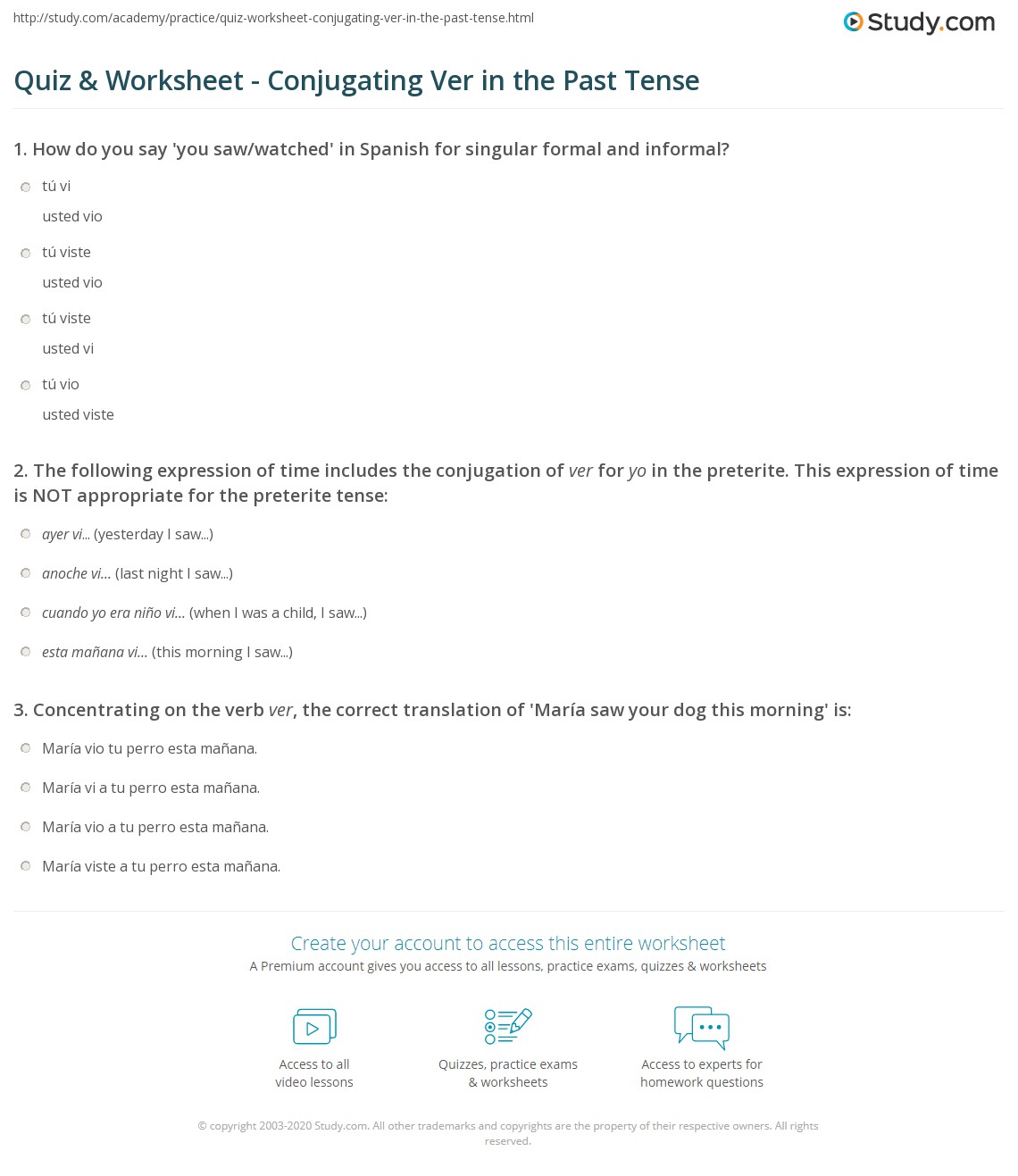
The Spanish verb "ver" (to see) is a crucial part of the language, and mastering its conjugation in different tenses is essential for effective communication. The preterite tense, in particular, is used to describe completed actions in the past. In this article, we will delve into the conjugation of "ver" in the preterite tense, exploring its various forms and providing examples of how it is used in context.
Key Points
- The verb "ver" is conjugated differently in the preterite tense depending on the subject pronoun.
- The preterite tense of "ver" is used to describe completed actions in the past.
- Understanding the conjugation of "ver" in the preterite tense is essential for effective communication in Spanish.
- The verb "ver" has different forms for each subject pronoun in the preterite tense, including yo, tú, él/ella/usted, nosotros/as, vosotros/as, and ellos/as.
- Mastering the conjugation of "ver" in the preterite tense requires practice and exposure to different contexts and scenarios.
Conjugation of Ver in Preterite Tense
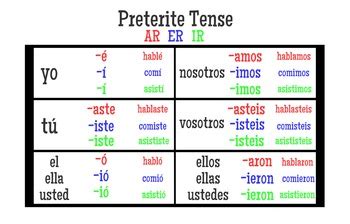
The conjugation of “ver” in the preterite tense is as follows:
| Subject Pronoun | Preterite Tense Conjugation |
|---|---|
| Yo | Vi |
| Tú | Viste |
| Él/Ella/Usted | Vio |
| Nosotros/Nosotras | Vimos |
| Vosotros/Vosotras | Visisteis |
| Ellos/Elas | Vieron |
As shown in the table above, the conjugation of “ver” in the preterite tense varies depending on the subject pronoun. For example, “yo vi” means “I saw,” while “tú viste” means “you saw.” It’s essential to understand these different forms to communicate effectively in Spanish.
Using Ver in Preterite Tense in Context
The preterite tense of “ver” is used to describe completed actions in the past. For instance:
Ayer, vi una película en el cine. (Yesterday, I saw a movie at the cinema.)
Él vio el partido de fútbol en la televisión. (He saw the soccer game on TV.)
Nosotros vimos un concierto de música en vivo. (We saw a live music concert.)
These examples demonstrate how the preterite tense of “ver” is used to describe completed actions in the past. The verb conjugation changes depending on the subject pronoun, and understanding these different forms is crucial for effective communication.
Common Mistakes and Tips

One common mistake when using the preterite tense of “ver” is to confuse it with the imperfect tense. The imperfect tense is used to describe ongoing or repeated actions in the past, whereas the preterite tense is used for completed actions. For example:
Yo veía la televisión todos los días (I used to watch TV every day) - imperfect tense
Yo vi la película ayer (I saw the movie yesterday) - preterite tense
To avoid this mistake, it’s essential to understand the context and the intended meaning of the sentence. Additionally, practicing the conjugation of “ver” in the preterite tense and exposure to different scenarios and contexts can help improve your skills and confidence.
What is the difference between the preterite and imperfect tenses of ver?
+The preterite tense of ver is used to describe completed actions in the past, whereas the imperfect tense is used to describe ongoing or repeated actions in the past.
How do I know which form of ver to use in the preterite tense?
+The form of ver used in the preterite tense depends on the subject pronoun. For example, "yo vi" means "I saw," while "tú viste" means "you saw." It's essential to understand these different forms to communicate effectively in Spanish.
Can I use the preterite tense of ver to describe actions that are still ongoing?
+No, the preterite tense of ver is used to describe completed actions in the past. If the action is still ongoing, you should use the imperfect or present tense instead.
In conclusion, mastering the conjugation of “ver” in the preterite tense is essential for effective communication in Spanish. By understanding the different forms of the verb and how to use them in context, you can improve your language skills and confidence. Remember to practice the conjugation of “ver” in the preterite tense and expose yourself to different scenarios and contexts to become more proficient in using this verb correctly.