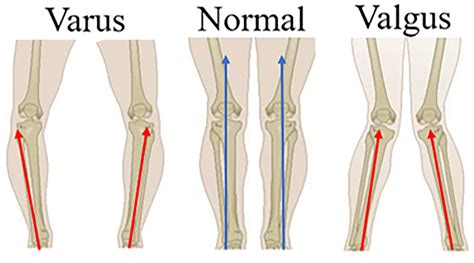
The terms varus and valgus are frequently used in the medical field, particularly in orthopedics and sports medicine, to describe the alignment of bones and joints in the human body. Understanding the difference between these two terms is crucial for accurately diagnosing and treating various musculoskeletal conditions. In this article, we will delve into the definitions, causes, and implications of varus and valgus deformities, as well as explore their differences and similarities.
Key Points
- Varus and valgus refer to the inward and outward angulation of bones or joints, respectively.
- Varus deformities are often associated with conditions such as bowlegs, while valgus deformities are linked to conditions like knock-knees.
- The causes of varus and valgus deformities can be congenital, developmental, or acquired due to injury or disease.
- Treatment options vary depending on the severity and location of the deformity, ranging from conservative management to surgical intervention.
- Accurate diagnosis and timely treatment are essential to prevent long-term complications and improve patient outcomes.
Varus Deformity
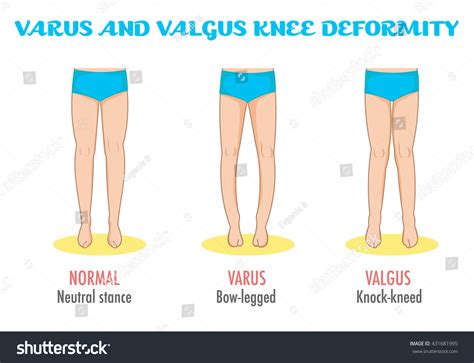
A varus deformity occurs when the distal segment of a bone or joint is angled inward, relative to the proximal segment. This can result in an abnormal gait, reduced range of motion, and increased risk of osteoarthritis. Varus deformities can affect various joints, including the knee, ankle, and hip. For instance, a varus deformity of the knee, also known as genu varum, is characterized by an inward bowing of the knee joint, which can lead to uneven wear and tear on the joint cartilage.
Causes of Varus Deformity
The causes of varus deformity can be divided into three main categories: congenital, developmental, and acquired. Congenital varus deformities are present at birth and may be due to genetic factors or prenatal conditions. Developmental varus deformities occur during childhood and adolescence, often as a result of abnormal bone growth or muscle imbalances. Acquired varus deformities, on the other hand, can arise from injuries, infections, or diseases that affect the bones and joints.
| Type of Varus Deformity | Description |
|---|---|
| Congenital | Present at birth, often due to genetic factors or prenatal conditions |
| Developmental | Occurs during childhood and adolescence, often due to abnormal bone growth or muscle imbalances |
| Acquired | Arises from injuries, infections, or diseases that affect the bones and joints |
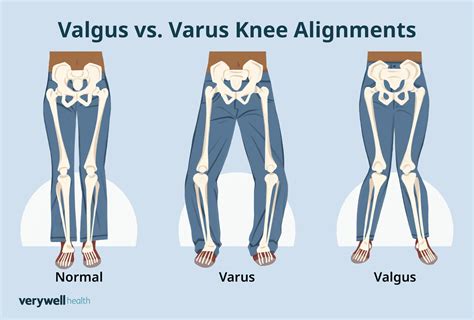
Valgus Deformity

A valgus deformity, in contrast, occurs when the distal segment of a bone or joint is angled outward, relative to the proximal segment. This can result in an abnormal gait, reduced range of motion, and increased risk of osteoarthritis. Valgus deformities can also affect various joints, including the knee, ankle, and hip. For example, a valgus deformity of the knee, also known as genu valgum, is characterized by an outward bowing of the knee joint, which can lead to uneven wear and tear on the joint cartilage.
Causes of Valgus Deformity
The causes of valgus deformity are similar to those of varus deformity, including congenital, developmental, and acquired factors. However, valgus deformities are more commonly associated with conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, which can cause joint instability and deformity.
| Type of Valgus Deformity | Description |
|---|---|
| Congenital | Present at birth, often due to genetic factors or prenatal conditions |
| Developmental | Occurs during childhood and adolescence, often due to abnormal bone growth or muscle imbalances |
| Acquired | Arises from injuries, infections, or diseases that affect the bones and joints |
Comparison of Varus and Valgus Deformities
While both varus and valgus deformities can result in abnormal joint alignment and function, there are distinct differences between the two. Varus deformities tend to be more common in the knee and ankle joints, whereas valgus deformities are more commonly seen in the hip and knee joints. Additionally, varus deformities are often associated with a more pronounced inward angulation of the joint, whereas valgus deformities are characterized by a more pronounced outward angulation.
What is the main difference between varus and valgus deformities?
+The main difference between varus and valgus deformities is the direction of the angulation of the joint. Varus deformities are characterized by an inward angulation, whereas valgus deformities are characterized by an outward angulation.
What are the common causes of varus and valgus deformities?
+The common causes of varus and valgus deformities include congenital factors, developmental abnormalities, and acquired conditions such as injuries, infections, or diseases.
How are varus and valgus deformities treated?
+Treatment options for varus and valgus deformities vary depending on the severity and location of the deformity, and may include conservative management, physical therapy, or surgical intervention.
In conclusion, varus and valgus deformities are two distinct types of joint misalignments that can result in abnormal function and increased risk of osteoarthritis. Understanding the differences and similarities between these two conditions is essential for accurate diagnosis and treatment. By recognizing the causes and implications of varus and valgus deformities, healthcare professionals can provide effective management and prevention strategies to improve patient outcomes.