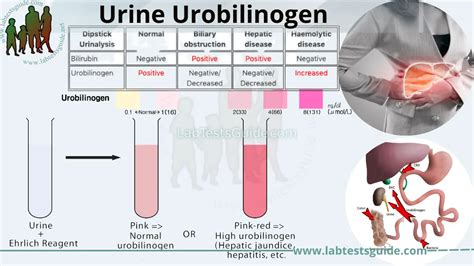
The urobilinogen semi-quantitative test, often abbreviated as Urobilinogen Semi Qn, is a diagnostic tool used in clinical settings to assess the levels of urobilinogen in urine. Urobilinogen is a colorless product of bilirubin reduction, produced during the breakdown of hemoglobin in the intestines. A portion of urobilinogen is absorbed into the bloodstream and then excreted by the kidneys into the urine. The presence and concentration of urobilinogen in urine can provide valuable information about the liver's ability to process bilirubin and the overall health of the gastrointestinal and urinary systems.
Understanding Urobilinogen

Urobilinogen is produced when intestinal bacteria act on bilirubin, which has been excreted into the bile and then into the intestines. Normally, most of the urobilinogen is converted back into urobilin and excreted in the feces, giving stool its characteristic brown color. However, a small amount is absorbed back into the bloodstream and eventually ends up in the urine. The level of urobilinogen in urine can be an indicator of how well the liver and the intestines are functioning. For instance, elevated levels of urobilinogen in urine can suggest liver dysfunction or an increased breakdown of red blood cells, while decreased levels might indicate obstructive jaundice or severe liver disease.
Clinical Significance of Urobilinogen Semi Qn
The urobilinogen semi-quantitative test is a simple and effective method to estimate the amount of urobilinogen in urine. It involves the use of a reagent strip or tablet that changes color in the presence of urobilinogen, with the intensity of the color change being roughly proportional to the concentration of urobilinogen present. This test can help in the diagnosis and monitoring of various conditions, including hemolytic anemia, liver cirrhosis, and hepatitis. For example, in cases of hemolytic anemia, where red blood cells are destroyed faster than they can be made, the liver may be overwhelmed by the amount of bilirubin it needs to process, leading to an increase in urobilinogen production and, consequently, its excretion in urine.
| Urobilinogen Levels | Clinical Interpretation |
|---|---|
| Normal (0.5-2.0 mg/dL) | Indicates normal liver function and bilirubin metabolism |
| Elevated (2.0-4.0 mg/dL) | Suggests increased hemolysis or liver dysfunction |
| Highly Elevated (>4.0 mg/dL) | May indicate severe hemolytic disease or significant liver impairment |
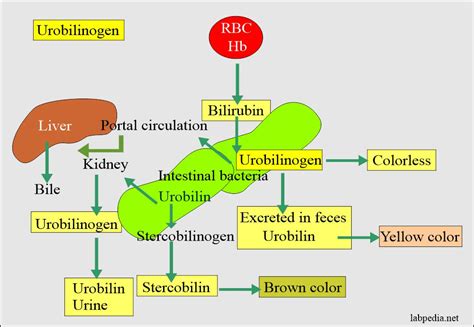
Methodology and Limitations

The urobilinogen semi-quantitative test is relatively straightforward to perform. A urine sample is required, and the test can be conducted using either a dipstick or a tablet that reacts with urobilinogen. The reaction produces a color change that is compared to a reference chart to estimate the concentration of urobilinogen. However, the accuracy of the test can be affected by several factors, including the concentration of the urine, the presence of certain drugs, and the timing of the sample collection. For instance, it is recommended to collect a morning urine sample when possible, as urobilinogen levels can vary throughout the day.
Practical Applications and Considerations
In clinical practice, the urobilinogen semi-quantitative test serves as a useful screening tool for detecting abnormalities in bilirubin metabolism and liver function. However, it should be used in conjunction with other diagnostic tests, such as liver function tests (e.g., ALT, AST, bilirubin levels) and complete blood counts, to obtain a comprehensive understanding of the patient’s condition. Furthermore, the test’s simplicity and non-invasive nature make it an attractive option for initial assessments and monitoring in both outpatient and inpatient settings.
Key Points
- The urobilinogen semi-quantitative test is used to assess liver function and detect abnormalities in bilirubin metabolism.
- Elevated levels of urobilinogen in urine can indicate increased hemolysis or liver dysfunction.
- The test should be interpreted in the context of the patient's overall clinical picture and in conjunction with other diagnostic tests.
- Factors such as diet, medications, and the timing of sample collection can influence the accuracy of the test.
- The urobilinogen semi-quantitative test is a useful screening tool but may require follow-up with more specific diagnostic tests for definitive diagnoses.
In conclusion, the urobilinogen semi-quantitative test provides valuable insights into the metabolism of bilirubin and the functional status of the liver. While it is a useful diagnostic tool, its results must be considered in the broader clinical context, taking into account the patient's medical history, physical examination findings, and the results of other diagnostic tests.
What does an elevated urobilinogen level indicate?
+An elevated level of urobilinogen in urine can suggest increased breakdown of red blood cells or liver dysfunction, among other conditions. It is essential to interpret these results in the context of the patient’s overall health status and other diagnostic findings.
How is the urobilinogen semi-quantitative test performed?
+The test involves using a reagent strip or tablet that reacts with urobilinogen in a urine sample, resulting in a color change. The intensity of the color change is correlated with the concentration of urobilinogen present.
What factors can influence the accuracy of the urobilinogen semi-quantitative test?
+Several factors can affect the test’s accuracy, including the concentration of the urine, certain medications, and the timing of the sample collection. Therefore, it’s crucial to follow proper sampling and testing procedures and to consider these factors when interpreting the results.