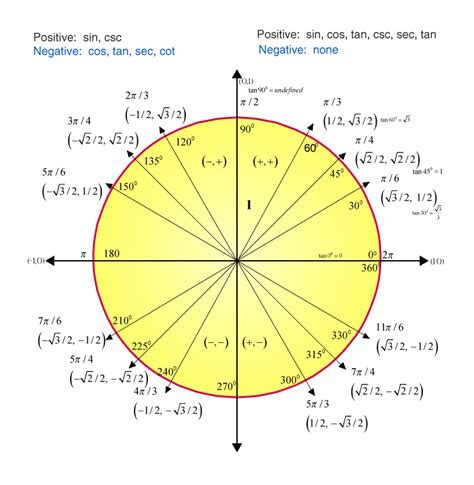
The unit circle is a fundamental concept in mathematics, particularly in trigonometry, and is used to define the trigonometric functions such as sine, cosine, and tangent. It is a circle with a radius of 1 unit, centered at the origin of a coordinate plane. The unit circle is often used to visualize and calculate the values of trigonometric functions for various angles. In this article, we will delve into the unit circle and the tangent function, exploring their definitions, properties, and applications.
Key Points
- The unit circle is a circle with a radius of 1 unit, centered at the origin of a coordinate plane.
- The tangent function, denoted as tan(x), is defined as the ratio of the sine and cosine functions.
- The unit circle is used to define the trigonometric functions and to calculate their values for various angles.
- The tangent function has a periodicity of π, meaning it repeats its values every π radians.
- The unit circle and tangent function have numerous applications in mathematics, physics, engineering, and other fields.
Unit Circle Definition and Properties
The unit circle is defined as the set of all points in a coordinate plane that are at a distance of 1 unit from the origin. This can be represented by the equation x^2 + y^2 = 1, where x and y are the coordinates of a point on the circle. The unit circle has several key properties, including its radius, center, and symmetry. The radius of the unit circle is 1 unit, and its center is at the origin (0, 0) of the coordinate plane.
The unit circle is also symmetric about the x-axis, y-axis, and the origin. This symmetry allows us to use the unit circle to define the trigonometric functions and to calculate their values for various angles. For example, the sine function can be defined as the y-coordinate of a point on the unit circle, while the cosine function can be defined as the x-coordinate of a point on the unit circle.
Tangent Function Definition and Properties
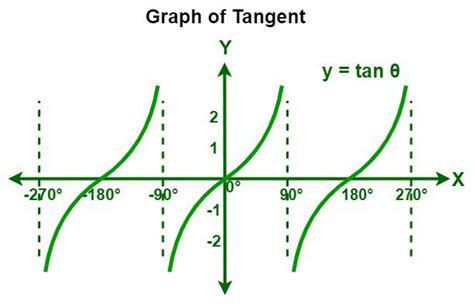
The tangent function, denoted as tan(x), is defined as the ratio of the sine and cosine functions. Mathematically, this can be represented as tan(x) = sin(x) / cos(x). The tangent function has several key properties, including its periodicity, range, and domain. The tangent function has a periodicity of π, meaning it repeats its values every π radians. This periodicity allows us to use the tangent function to model periodic phenomena, such as the motion of a pendulum or the vibration of a string.
The range of the tangent function is all real numbers, while its domain is all real numbers except for odd multiples of π/2. The tangent function is also an odd function, meaning that tan(-x) = -tan(x). This property allows us to use the tangent function to model phenomena that have rotational symmetry, such as the motion of a wheel or the vibration of a spring.
| Angle (radians) | Tangent Value |
|---|---|
| 0 | 0 |
| π/4 | 1 |
| π/2 | undefined |
| 3π/4 | -1 |
| π | 0 |
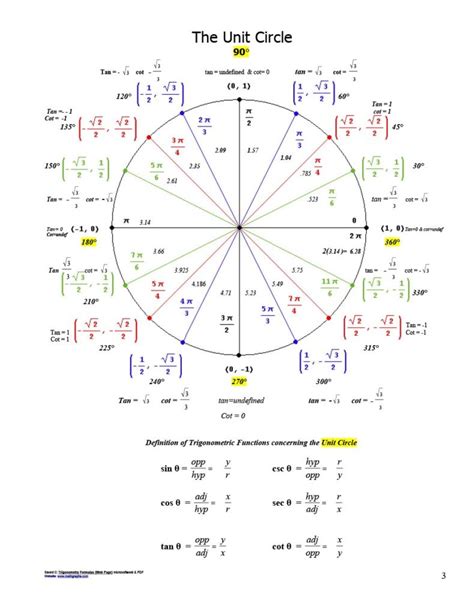
Applications of the Unit Circle and Tangent Function
The unit circle and tangent function have numerous applications in mathematics, physics, engineering, and other fields. In mathematics, the unit circle is used to define the trigonometric functions and to calculate their values for various angles. The tangent function is used to model periodic phenomena, such as the motion of a pendulum or the vibration of a string.
In physics, the unit circle and tangent function are used to model the motion of objects, such as the trajectory of a projectile or the vibration of a spring. The tangent function is also used to model the behavior of waves, such as sound waves or light waves. In engineering, the unit circle and tangent function are used to design and analyze systems, such as electrical circuits or mechanical systems.
Conclusion and Future Directions
In conclusion, the unit circle and tangent function are fundamental concepts in mathematics and have numerous applications in physics, engineering, and other fields. The unit circle is used to define the trigonometric functions and to calculate their values for various angles, while the tangent function is used to model periodic phenomena and phenomena with rotational symmetry. As mathematics and science continue to evolve, the unit circle and tangent function will remain essential tools for understanding and modeling the world around us.
What is the definition of the unit circle?
+The unit circle is a circle with a radius of 1 unit, centered at the origin of a coordinate plane. It is defined by the equation x^2 + y^2 = 1, where x and y are the coordinates of a point on the circle.
What is the definition of the tangent function?
+The tangent function, denoted as tan(x), is defined as the ratio of the sine and cosine functions. Mathematically, this can be represented as tan(x) = sin(x) / cos(x).
What are some applications of the unit circle and tangent function?
+The unit circle and tangent function have numerous applications in mathematics, physics, engineering, and other fields. They are used to model periodic phenomena, such as the motion of a pendulum or the vibration of a string, and to design and analyze systems, such as electrical circuits or mechanical systems.