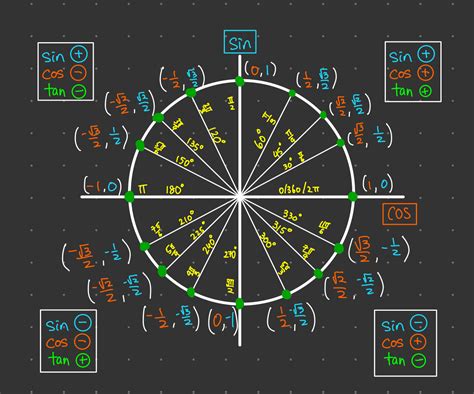
The unit circle is a fundamental concept in trigonometry, and understanding its properties is crucial for simplifying tan values. The unit circle is a circle with a radius of 1, centered at the origin of a coordinate plane. The equation of the unit circle is x^2 + y^2 = 1, where x and y are the coordinates of any point on the circle.
Trigonometric functions, such as tangent (tan), are defined as the ratio of the lengths of the sides of a right triangle. In the context of the unit circle, the tangent of an angle is defined as the ratio of the length of the side opposite the angle to the length of the side adjacent to the angle. This can be expressed as tan(θ) = y/x, where θ is the angle, and x and y are the coordinates of the point on the unit circle corresponding to the angle.
Key Points
- The unit circle has a radius of 1 and is centered at the origin of a coordinate plane.
- The equation of the unit circle is x^2 + y^2 = 1.
- The tangent of an angle in the unit circle is defined as tan(θ) = y/x.
- Common tan values can be simplified using the unit circle, such as tan(0) = 0, tan(π/4) = 1, and tan(π/2) = undefined.
- Knowledge of the unit circle and its properties is essential for simplifying tan values and working with trigonometric functions.
Unit Circle Properties and Tan Values

The unit circle has several key properties that are useful for simplifying tan values. The coordinates of the points on the unit circle can be used to determine the values of the trigonometric functions. For example, the point (1, 0) corresponds to an angle of 0 radians, and the point (0, 1) corresponds to an angle of π/2 radians. Using these coordinates, we can simplify common tan values, such as tan(0) = 0/1 = 0 and tan(π/4) = 1⁄1 = 1.
Common Tan Values and Simplification
Some common tan values can be simplified using the unit circle. For example, tan(π/4) = 1, because the point (1/√2, 1/√2) has coordinates that give a ratio of 1. Similarly, tan(π/3) = √3, because the point (1⁄2, √3/2) has coordinates that give a ratio of √3. These simplified values are essential for working with trigonometric functions and can be used to simplify more complex expressions.
| Angle (θ) | Tan Value |
|---|---|
| 0 | 0 |
| π/6 | 1/√3 |
| π/4 | 1 |
| π/3 | √3 |
| π/2 | undefined |
Applications and Implications

The unit circle and its properties have numerous applications in mathematics, physics, and engineering. Understanding the relationships between the coordinates of the points on the unit circle and the values of the trigonometric functions is essential for working with periodic phenomena, such as sound waves and light waves. The simplified tan values can be used to analyze and solve problems in these fields, and the knowledge of the unit circle is a fundamental building block for more advanced mathematical concepts.
Forward-Looking Implications
The unit circle and its properties will continue to play a vital role in the development of mathematical and scientific theories. As our understanding of the world and the universe evolves, the importance of the unit circle and its properties will only continue to grow. By mastering the concepts of the unit circle and its properties, we can unlock new insights and solve complex problems in a wide range of fields, from physics and engineering to computer science and mathematics.
What is the equation of the unit circle?
+The equation of the unit circle is x^2 + y^2 = 1, where x and y are the coordinates of any point on the circle.
What is the tangent of an angle in the unit circle?
+The tangent of an angle in the unit circle is defined as tan(θ) = y/x, where θ is the angle, and x and y are the coordinates of the point on the unit circle corresponding to the angle.
What are some common tan values that can be simplified using the unit circle?
+Some common tan values that can be simplified using the unit circle include tan(0) = 0, tan(π/4) = 1, and tan(π/3) = √3.