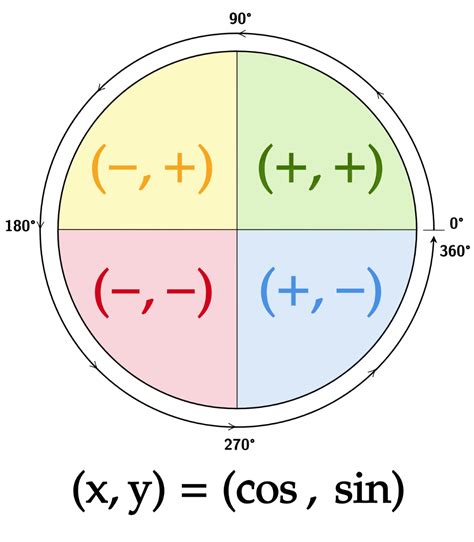
The unit circle is a fundamental concept in mathematics, particularly in trigonometry, and is used to define the sine and cosine functions. Understanding the unit circle can be a challenging task for many students, but with the right approach, it can be made easy. In this article, we will explore the unit circle and its relationship with sine and cosine, providing a comprehensive guide on how to master these concepts.
Key Points
- The unit circle is a circle with a radius of 1 unit, centered at the origin (0,0) of a coordinate plane.
- The sine and cosine functions can be defined as the ratios of the lengths of the sides of a right triangle formed within the unit circle.
- The unit circle can be used to find the values of sine and cosine for any angle, using the coordinates of a point on the circle.
- There are several key angles in the unit circle, including 0°, 30°, 45°, 60°, and 90°, which have well-known values for sine and cosine.
- Understanding the unit circle and its relationship with sine and cosine is crucial for solving problems in trigonometry, physics, and engineering.
What is the Unit Circle?
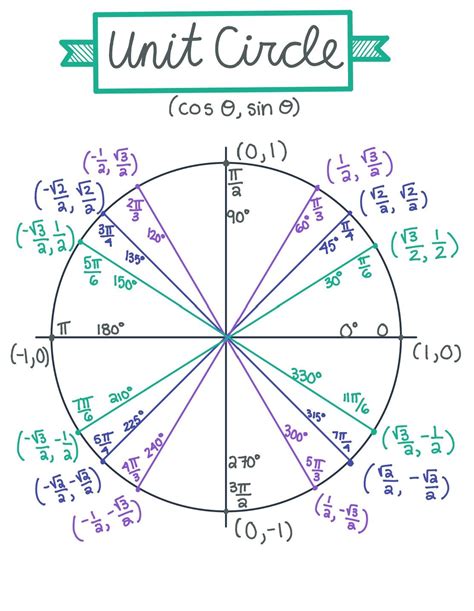
The unit circle is a circle with a radius of 1 unit, centered at the origin (0,0) of a coordinate plane. It is called the “unit” circle because its radius is 1 unit, which makes it a convenient and simple shape to work with. The unit circle is often used to define the sine and cosine functions, as well as other trigonometric functions.
Defining Sine and Cosine using the Unit Circle
The sine and cosine functions can be defined as the ratios of the lengths of the sides of a right triangle formed within the unit circle. Let’s consider a point P on the unit circle, with coordinates (x,y). We can draw a line from the origin to point P, which forms a right triangle with the x-axis and the line segment from the origin to point P. The sine of the angle θ formed by this triangle is defined as the ratio of the length of the side opposite the angle (y) to the length of the hypotenuse (1), or sin(θ) = y/1 = y. Similarly, the cosine of the angle θ is defined as the ratio of the length of the side adjacent to the angle (x) to the length of the hypotenuse (1), or cos(θ) = x/1 = x.
| Angle (θ) | Sine (sin(θ)) | Cosine (cos(θ)) |
|---|---|---|
| 0° | 0 | 1 |
| 30° | 1/2 | √3/2 |
| 45° | √2/2 | √2/2 |
| 60° | √3/2 | 1/2 |
| 90° | 1 | 0 |
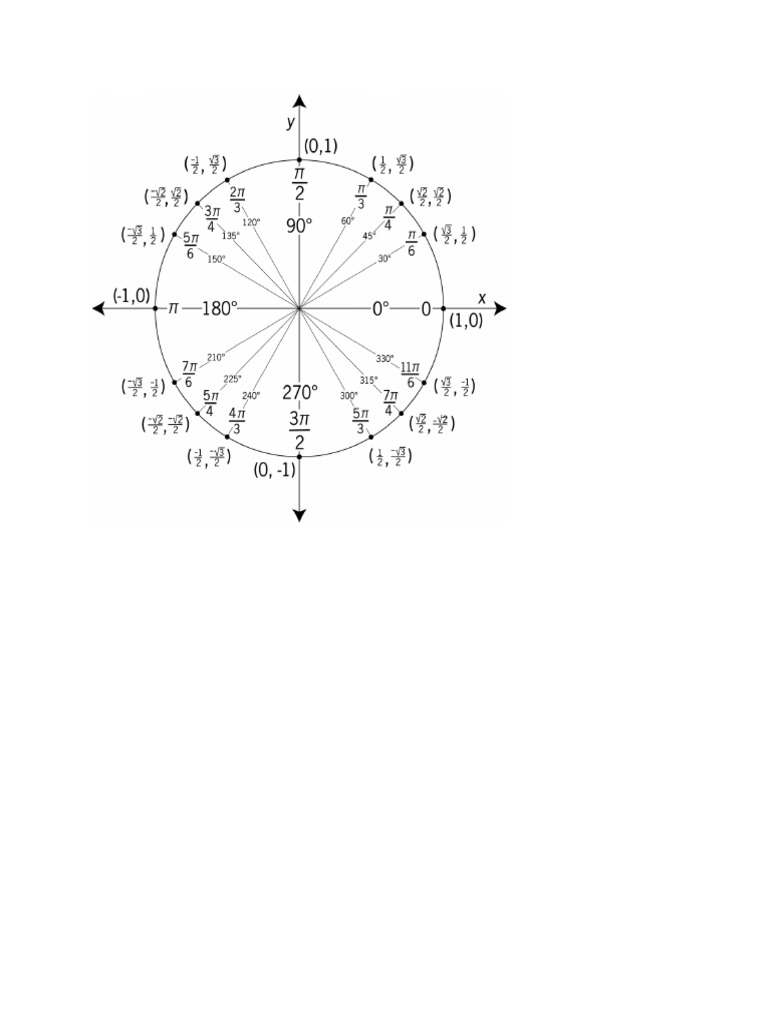
Key Angles in the Unit Circle
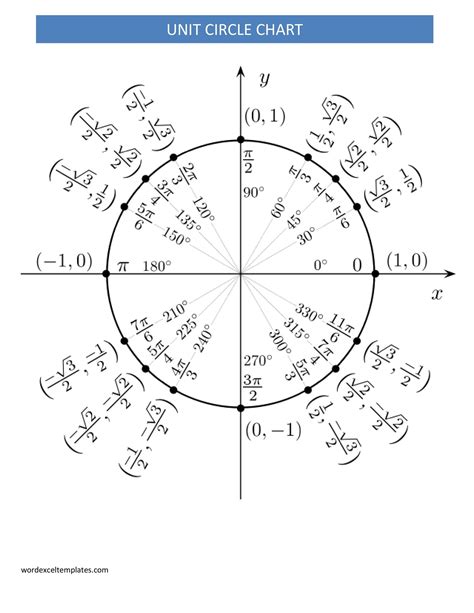
There are several key angles in the unit circle, including 0°, 30°, 45°, 60°, and 90°, which have well-known values for sine and cosine. These angles are often referred to as the “special angles” of the unit circle. By memorizing the values of sine and cosine for these angles, you can easily find the values for other angles using the unit circle.
Using the Unit Circle to Find Sine and Cosine Values
The unit circle can be used to find the values of sine and cosine for any angle, using the coordinates of a point on the circle. Let’s say we want to find the value of sin(75°). We can start by drawing a diagram of the unit circle and locating the point on the circle that corresponds to an angle of 75°. We can then use the coordinates of this point to find the value of sin(75°). For example, if the point has coordinates (x,y), then sin(75°) = y.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the unit circle is a powerful tool for understanding the sine and cosine functions. By mastering the unit circle, you can easily find the values of sine and cosine for any angle, and solve problems in trigonometry, physics, and engineering. Remember to memorize the values of sine and cosine for the special angles, and use the unit circle to find the values for other angles. With practice and patience, you can become proficient in using the unit circle to solve problems and unlock the secrets of trigonometry.
What is the unit circle, and why is it important in mathematics?
+The unit circle is a circle with a radius of 1 unit, centered at the origin (0,0) of a coordinate plane. It is important in mathematics because it is used to define the sine and cosine functions, as well as other trigonometric functions. The unit circle is also used to solve problems in trigonometry, physics, and engineering.
How do I find the values of sine and cosine for a given angle using the unit circle?
+To find the values of sine and cosine for a given angle using the unit circle, start by drawing a diagram of the unit circle and locating the point on the circle that corresponds to the given angle. Then, use the coordinates of this point to find the values of sine and cosine. For example, if the point has coordinates (x,y), then sin(θ) = y and cos(θ) = x.
What are the special angles in the unit circle, and why are they important?
+The special angles in the unit circle are 0°, 30°, 45°, 60°, and 90°. These angles are important because they have well-known values for sine and cosine, which can be used to find the values of sine and cosine for other angles. By memorizing the values of sine and cosine for the special angles, you can easily find the values for other angles using the unit circle.