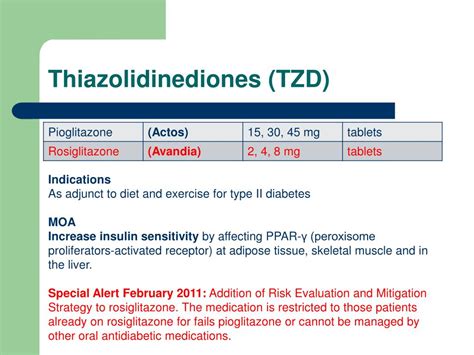
Tzd medications, also known as thiazolidinediones, are a class of prescription drugs used in the treatment of type 2 diabetes. These medications work by increasing the body's sensitivity to insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas that regulates blood sugar levels. The primary mechanism of action of tzd medications involves the activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPAR-γ), which plays a crucial role in glucose and lipid metabolism. By enhancing the body's response to insulin, tzd medications help to lower blood sugar levels, reducing the risk of complications associated with diabetes, such as heart disease, kidney damage, and nerve damage.
Primary Tzd Medications
There are several tzd medications available, each with its unique characteristics and side effect profiles. The most commonly prescribed tzd medications include pioglitazone (Actos) and rosiglitazone (Avandia). Pioglitazone is often used in combination with other diabetes medications, such as metformin or sulfonylureas, to improve blood sugar control. Rosiglitazone, on the other hand, has been associated with an increased risk of heart attacks and strokes, leading to restricted use in certain patient populations. Despite these differences, both medications have been shown to be effective in reducing hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) levels, a measure of average blood sugar control over time.
Benefits and Risks of Tzd Medications
Tzd medications offer several benefits for patients with type 2 diabetes, including improved insulin sensitivity, enhanced glucose uptake in the muscles, and increased glucose excretion in the urine. However, these medications are not without risks. Common side effects of tzd medications include weight gain, fluid retention, and increased risk of heart failure. Additionally, tzd medications have been linked to an increased risk of bone fractures, particularly in older adults. To minimize these risks, patients should be carefully selected and monitored, with regular assessments of their kidney function, liver function, and overall cardiovascular health.
| Medication | Indication | Common Side Effects |
|---|---|---|
| Pioglitazone (Actos) | Type 2 diabetes | Weight gain, fluid retention, increased risk of heart failure |
| Rosiglitazone (Avandia) | Type 2 diabetes | Increased risk of heart attacks and strokes, weight gain, fluid retention |

Key Points
- Tzd medications increase the body's sensitivity to insulin, reducing blood sugar levels and the risk of diabetes-related complications.
- Pioglitazone and rosiglitazone are the most commonly prescribed tzd medications, each with unique characteristics and side effect profiles.
- Common side effects of tzd medications include weight gain, fluid retention, and increased risk of heart failure.
- Regular monitoring of kidney function, liver function, and cardiovascular health is essential to minimize the risks associated with tzd medications.
- Tzd medications should be used in combination with lifestyle modifications, such as a healthy diet and regular exercise, to achieve optimal blood sugar control.
Mechanism of Action and Pharmacokinetics
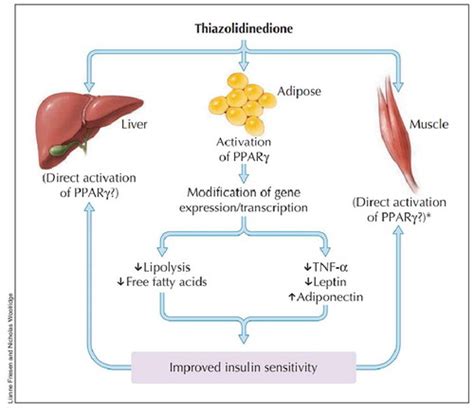
The mechanism of action of tzd medications involves the activation of PPAR-γ, a nuclear receptor that regulates gene expression in various tissues, including adipose tissue, skeletal muscle, and the liver. By binding to PPAR-γ, tzd medications increase the expression of genes involved in glucose and lipid metabolism, leading to improved insulin sensitivity and reduced glucose production in the liver. The pharmacokinetics of tzd medications vary depending on the specific medication, with pioglitazone having a longer half-life (approximately 24 hours) compared to rosiglitazone (approximately 3-4 hours).
Combination Therapy with Tzd Medications
Tzd medications are often used in combination with other diabetes medications, such as metformin, sulfonylureas, or dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors, to achieve optimal blood sugar control. Combination therapy can help to improve glycemic control, reduce the risk of diabetes-related complications, and minimize the side effects associated with individual medications. However, combination therapy requires careful monitoring and adjustment of medication dosages to avoid hypoglycemia and other adverse effects.
What are the primary benefits of tzd medications in the treatment of type 2 diabetes?
+Tzd medications offer several benefits, including improved insulin sensitivity, enhanced glucose uptake in the muscles, and increased glucose excretion in the urine, leading to reduced blood sugar levels and a lower risk of diabetes-related complications.
What are the common side effects of tzd medications, and how can they be minimized?
+Common side effects of tzd medications include weight gain, fluid retention, and increased risk of heart failure. These risks can be minimized by careful patient selection, regular monitoring of kidney function, liver function, and cardiovascular health, and adjusting medication dosages as needed.
Can tzd medications be used in combination with other diabetes medications, and what are the benefits and risks of combination therapy?
+Tzd medications can be used in combination with other diabetes medications, such as metformin or sulfonylureas, to achieve optimal blood sugar control. Combination therapy can help to improve glycemic control, reduce the risk of diabetes-related complications, and minimize the side effects associated with individual medications. However, combination therapy requires careful monitoring and adjustment of medication dosages to avoid hypoglycemia and other adverse effects.
In conclusion, tzd medications are a valuable addition to the treatment armamentarium for type 2 diabetes, offering improved insulin sensitivity, enhanced glucose uptake in the muscles, and increased glucose excretion in the urine. While these medications are associated with several benefits, they also carry risks, including weight gain, fluid retention, and increased risk of heart failure. By carefully selecting patients, monitoring their response to treatment, and adjusting medication dosages as needed, healthcare providers can optimize the benefits of tzd medications while minimizing their risks. As the prevalence of type 2 diabetes continues to rise, the development of new and effective treatments, such as tzd medications, remains a critical public health priority.