Weathering, the process of breaking down rocks into smaller fragments, is a fundamental aspect of the Earth's geological cycle. It plays a crucial role in shaping our landscape, influencing the formation of soil, and affecting the environment. There are three primary types of weathering: mechanical, chemical, and biological. Each type has distinct characteristics and operates through different mechanisms, contributing to the complex and dynamic process of rock decomposition.
The study of weathering is essential for understanding various geological phenomena, such as erosion, sedimentation, and the formation of landforms. By examining the types of weathering and their effects, scientists can gain insights into the Earth's history, including climate changes, tectonic activities, and the evolution of life. Furthermore, understanding weathering processes is vital for addressing environmental concerns, such as soil degradation, landslide risks, and the impact of human activities on the geological landscape.
Key Points
- Weathering is the process of breaking down rocks into smaller fragments.
- There are three primary types of weathering: mechanical, chemical, and biological.
- Each type of weathering has distinct characteristics and operates through different mechanisms.
- Understanding weathering processes is essential for addressing environmental concerns and geological phenomena.
- The study of weathering provides insights into the Earth's history, including climate changes and the evolution of life.
Mechanical Weathering

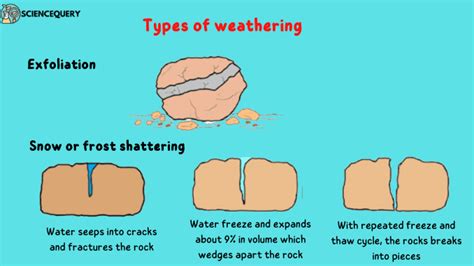
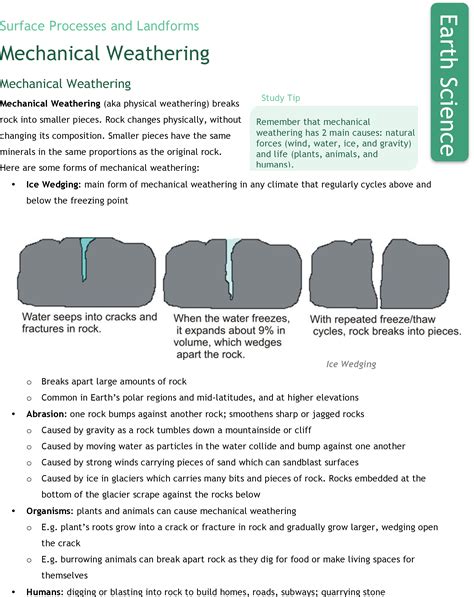
Mechanical weathering, also known as physical weathering, involves the breakdown of rocks into smaller pieces without altering their chemical composition. This process occurs through various mechanisms, including temperature fluctuations, freeze-thaw cycles, and physical forces such as wind, water, and ice. Mechanical weathering is a crucial process in shaping the Earth’s surface, particularly in regions with extreme climate conditions.
One of the most significant examples of mechanical weathering is the freeze-thaw process, which occurs when water seeps into rock fractures and expands upon freezing. This expansion creates pressure that can break the rock apart, leading to the formation of smaller fragments. Another example is the process of thermal expansion, where rocks expand and contract due to temperature changes, causing them to crack and break down over time.
Types of Mechanical Weathering
There are several types of mechanical weathering, including:
- Freeze-thaw weathering: occurs when water seeps into rock fractures and expands upon freezing.
- Thermal expansion: occurs when rocks expand and contract due to temperature changes.
- Hydraulic action: occurs when the force of water breaks rocks apart.
- Abrasion: occurs when rocks are worn away by the action of other rocks or sediment.
| Type of Mechanical Weathering | Description |
|---|---|
| Freeze-thaw weathering | Occurs when water seeps into rock fractures and expands upon freezing. |
| Thermal expansion | Occurs when rocks expand and contract due to temperature changes. |
| Hydraulic action | Occurs when the force of water breaks rocks apart. |
| Abrasion | Occurs when rocks are worn away by the action of other rocks or sediment. |

Chemical Weathering
Chemical weathering involves the breakdown of rocks through chemical reactions, which alter the rock’s composition. This process occurs when rocks come into contact with water, air, or other substances that contain chemicals such as acids, bases, or salts. Chemical weathering is a significant process in shaping the Earth’s surface, particularly in regions with high levels of rainfall or in areas with high concentrations of reactive chemicals.
One of the most common examples of chemical weathering is the reaction between rocks and acidic rainwater. Acidic rainwater, which contains high levels of sulfuric and nitric acid, can react with rocks to form new minerals and release ions such as calcium and magnesium. Another example is the process of oxidation, where rocks react with oxygen in the air to form new minerals such as iron oxide.
Types of Chemical Weathering
There are several types of chemical weathering, including:
- Hydrolysis: occurs when rocks react with water to form new minerals.
- Oxidation: occurs when rocks react with oxygen in the air to form new minerals.
- Carbonation: occurs when rocks react with carbon dioxide in the air to form new minerals.
- Dissolution: occurs when rocks are dissolved by water or other substances.
| Type of Chemical Weathering | Description |
|---|---|
| Hydrolysis | Occurs when rocks react with water to form new minerals. |
| Oxidation | Occurs when rocks react with oxygen in the air to form new minerals. |
| Carbonation | Occurs when rocks react with carbon dioxide in the air to form new minerals. |
| Dissolution | Occurs when rocks are dissolved by water or other substances. |
Biological Weathering
Biological weathering involves the breakdown of rocks through the action of living organisms such as plants, animals, and microorganisms. This process occurs when organisms such as roots, fungi, and bacteria interact with rocks, causing them to break down or alter their composition. Biological weathering is a significant process in shaping the Earth’s surface, particularly in regions with high levels of biological activity.
One of the most common examples of biological weathering is the action of plant roots, which can break rocks apart through physical force or alter their composition through chemical reactions. Another example is the action of microorganisms such as bacteria and fungi, which can break down rocks through enzymatic reactions or alter their composition through metabolic processes.
Types of Biological Weathering
There are several types of biological weathering, including:
- Root action: occurs when plant roots break rocks apart or alter their composition.
- Microbial action: occurs when microorganisms such as bacteria and fungi break down rocks through enzymatic reactions or alter their composition through metabolic processes.
- Burrowing action: occurs when animals such as worms and insects break rocks apart or alter their composition through physical force.
| Type of Biological Weathering | Description |
|---|---|
| Root action | Occurs when plant roots break rocks apart or alter their composition. |
| Microbial action | Occurs when microorganisms such as bacteria and fungi break down rocks through enzymatic reactions or alter their composition through metabolic processes. |
| Burrowing action | Occurs when animals such as worms and insects break rocks apart or alter their composition through physical force. |
What is the difference between mechanical and chemical weathering?
+Mechanical weathering involves the breakdown of rocks into smaller pieces without altering their chemical composition, while chemical weathering involves the breakdown of rocks through chemical reactions that alter their composition.
What are the types of biological weathering?
+The types of biological weathering include root action, microbial action, and burrowing action.
Why is understanding weathering important?
+Understanding weathering is important because it helps us predict and mitigate the effects of geological hazards such as landslides and rockfalls, as well as environmental hazards such as soil degradation and water pollution.