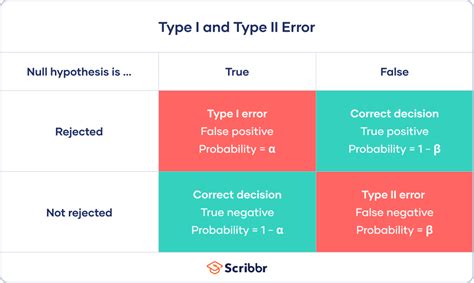
Type 2 errors, also known as false negatives, occur when a statistical test fails to detect a difference or relationship that actually exists. This type of error can have significant consequences, especially in fields like medicine, finance, and social sciences, where accurate conclusions are crucial for decision-making. Avoiding Type 2 errors is essential to ensure the validity and reliability of research findings. In this article, we will explore five ways to avoid Type 2 errors, providing researchers and practitioners with practical strategies to enhance the accuracy of their statistical analyses.
Key Points
- Understanding the concept of statistical power and its relationship to Type 2 errors
- Conducting thorough literature reviews to inform sample size calculations
- Implementing robust data collection methods to minimize variability
- Applying appropriate statistical tests and considering alternative hypotheses
- Interpreting results in the context of the research question and study limitations
Understanding Statistical Power

Statistical power refers to the probability that a test will correctly reject a false null hypothesis. In other words, it is the ability of a test to detect an effect if there is one. A common rule of thumb is to aim for a power of 0.8, which means that the test has an 80% chance of detecting a statistically significant effect if it exists. To avoid Type 2 errors, researchers should conduct power analyses to determine the required sample size. This involves specifying the expected effect size, the desired level of power, and the significance level (usually set at 0.05). By doing so, researchers can ensure that their study has sufficient statistical power to detect meaningful effects.
Conducting Thorough Literature Reviews
A comprehensive literature review is essential for understanding the context and scope of the research question. By examining previous studies, researchers can identify the expected effect size, which is critical for calculating the required sample size. A thorough review also helps to identify potential sources of variability, which can be controlled for in the study design. Furthermore, a literature review can inform the selection of appropriate statistical tests and the development of alternative hypotheses. For instance, if previous studies have found inconsistent results, a researcher may consider alternative explanations or moderators that could influence the outcome.
| Factor | Impact on Type 2 Error |
|---|---|
| Sample Size | Increasing sample size reduces Type 2 error rate |
| Effect Size | Larger effect sizes are easier to detect, reducing Type 2 error |
| Statistical Power | Higher power reduces Type 2 error rate |
| Significance Level | More stringent significance levels increase Type 2 error rate |
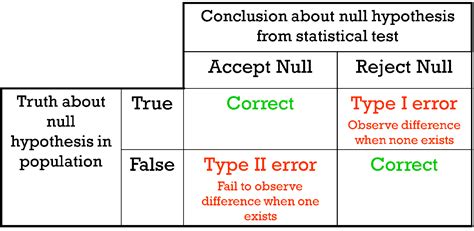
Implementing Robust Data Collection Methods
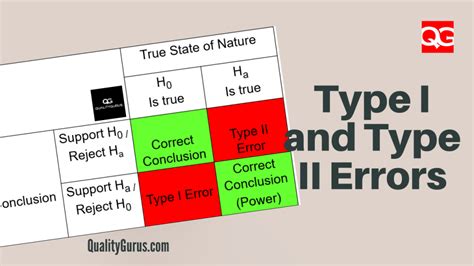
Data quality is crucial for avoiding Type 2 errors. Poor data quality can lead to increased variability, which reduces the statistical power of the test. To minimize variability, researchers should implement robust data collection methods, such as using validated instruments, training data collectors, and ensuring data are collected consistently. Additionally, researchers should consider using techniques like data imputation or sensitivity analysis to handle missing data or outliers. By doing so, researchers can increase the accuracy and reliability of their findings, reducing the risk of Type 2 errors.
Applying Appropriate Statistical Tests
The choice of statistical test depends on the research question, data type, and study design. Researchers should select tests that are appropriate for their data and research question, taking into account factors like normality, homoscedasticity, and independence of observations. Additionally, researchers should consider alternative hypotheses and potential sources of bias, such as confounding variables or selection bias. By applying appropriate statistical tests and considering alternative explanations, researchers can reduce the risk of Type 2 errors and increase the validity of their findings.
What is the relationship between sample size and Type 2 error?
+A larger sample size reduces the risk of Type 2 error, as it increases the statistical power of the test. However, increasing sample size is not always feasible or practical. In such cases, researchers can consider using more efficient study designs or alternative statistical tests.
How can I determine the required sample size for my study?
+To determine the required sample size, you should conduct a power analysis, specifying the expected effect size, desired level of power, and significance level. You can use software packages like G*Power or R to perform power analyses and determine the required sample size.
What are some common sources of variability that can increase the risk of Type 2 error?
+Common sources of variability include poor data quality, inadequate sample size, and inefficient study design. Additionally, factors like confounding variables, selection bias, and measurement error can increase the risk of Type 2 error.
In conclusion, avoiding Type 2 errors requires careful consideration of study design, data collection, and statistical analysis. By understanding the concept of statistical power, conducting thorough literature reviews, implementing robust data collection methods, applying appropriate statistical tests, and interpreting results in context, researchers can reduce the risk of Type 2 errors and increase the validity of their findings. Remember, a well-designed study with adequate statistical power is essential for detecting meaningful effects and avoiding false negatives.