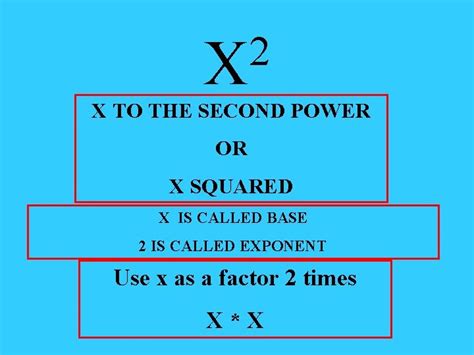
Squaring numbers to the second power is a fundamental mathematical operation that has numerous applications in various fields, including algebra, geometry, physics, and engineering. At its core, squaring a number involves multiplying the number by itself, which can be represented mathematically as $x^2$, where $x$ is the number being squared. For instance, the square of 5 is $5^2 = 5 \times 5 = 25$. This operation is essential for solving equations, calculating distances, and determining areas, among other uses.
One of the key characteristics of squaring numbers is that the result is always positive, regardless of whether the original number is positive or negative. This is because multiplying two negative numbers yields a positive result. For example, $(-3)^2 = (-3) \times (-3) = 9$, which is positive. Understanding this property is crucial for applications in physics, where negative numbers can represent directions or orientations in space.
Key Points
- The square of a number is obtained by multiplying the number by itself.
- Squaring a number always results in a positive value, regardless of the original number's sign.
- The operation is fundamental in various mathematical and scientific disciplines.
- It is used in calculating areas, solving quadratic equations, and determining distances.
- Squaring numbers has practical applications in physics, engineering, and computer science.
Mathematical Representation and Properties

The mathematical representation of squaring a number is straightforward, involving the exponentiation of the number to the power of 2, denoted as x^2. This operation can be applied to any real number, including integers, fractions, and decimals. A notable property of squaring numbers is that it is a monotonic increasing function for positive numbers but has a minimum at zero, indicating a change in the direction of the function.
From a geometric perspective, squaring a number can be visualized as finding the area of a square with a side length equal to the number. For example, if we have a square with sides of length 4, its area would be $4^2 = 16$ square units. This geometric interpretation underlines the significance of squaring numbers in calculating areas and volumes of various shapes.
Algebraic and Geometric Applications
In algebra, squaring numbers plays a critical role in solving quadratic equations, which are equations of the form ax^2 + bx + c = 0. The process of squaring is also integral to completing the square, a method used to solve these equations by transforming them into a perfect square trinomial. Furthermore, in geometry, the concept of squaring numbers is used to calculate distances and lengths, applying the Pythagorean theorem, which states that in a right-angled triangle, the square of the length of the hypotenuse (the side opposite the right angle) is equal to the sum of the squares of the lengths of the other two sides.
| Mathematical Operation | Example | Result |
|---|---|---|
| Squaring a Positive Number | $5^2$ | $25$ |
| Squaring a Negative Number | $(-3)^2$ | $9$ |
| Squaring a Fraction | $(1/2)^2$ | $1/4$ |

Practical Applications and Future Implications

Beyond the theoretical realm, squaring numbers has numerous practical applications. In physics, the square of the velocity of an object is directly proportional to its kinetic energy, highlighting the importance of this operation in understanding and predicting physical phenomena. In computer science, algorithms often rely on squaring numbers to perform tasks such as encryption, data compression, and image processing.
As technology continues to advance, the role of squaring numbers in developing new technologies and solving complex problems will only become more pronounced. For instance, in the field of artificial intelligence, squaring numbers is used in neural network algorithms to optimize performance and in machine learning models to improve prediction accuracy. The future of computing and scientific discovery will undoubtedly be shaped by our ability to efficiently and accurately perform mathematical operations, including squaring numbers.
What is the result of squaring a negative number?
+The result of squaring a negative number is always positive. For example, (-4)^2 = 16.
How is squaring numbers applied in physics?
+Squaring numbers is used in physics to calculate kinetic energy, where the energy is proportional to the square of the velocity of an object. It is also used in the Pythagorean theorem to calculate distances and lengths in right-angled triangles.
What is the geometric interpretation of squaring a number?
+The geometric interpretation of squaring a number is finding the area of a square with a side length equal to the number. For instance, the area of a square with sides of length 5 is 5^2 = 25 square units.