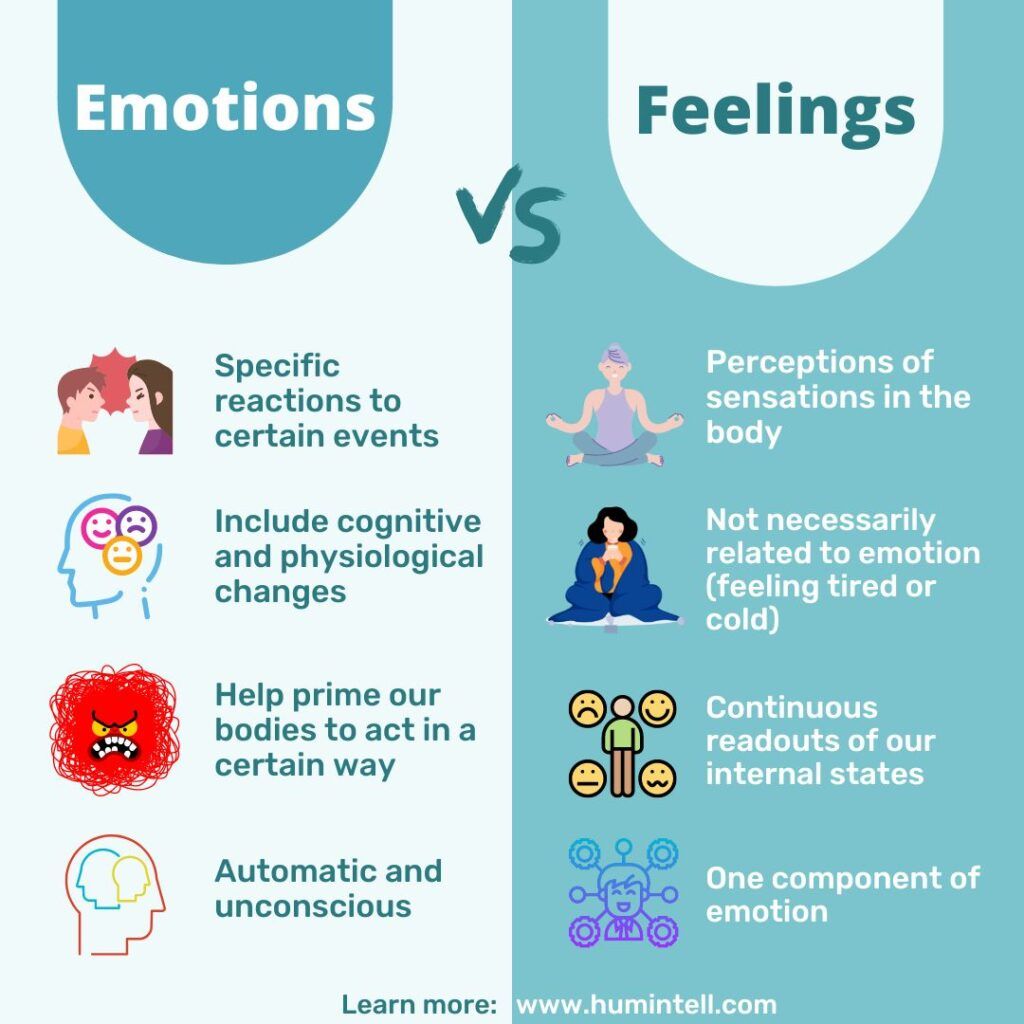
The emotions are a complex and multifaceted aspect of the human experience, influencing our thoughts, behaviors, and interactions with the world around us. Emotions are often described as intense mental states that are typically characterized by a combination of physiological, cognitive, and behavioral components. They can be understood as the body's way of responding to various stimuli, whether internal or external, and can range from simple feelings such as happiness or sadness to more complex emotional states like nostalgia or empathy. The study of emotions is a vast and interdisciplinary field, drawing from psychology, neuroscience, sociology, and philosophy, among other disciplines.
One of the key aspects of emotions is their ability to motivate and guide behavior. For instance, the emotion of fear can serve as a protective mechanism, prompting an individual to avoid potential dangers. Similarly, the emotion of joy can encourage social bonding and positive interactions with others. Emotions also play a crucial role in decision-making processes, often influencing choices in profound ways, even when such influences are not immediately apparent to the individual. Furthermore, emotions are closely linked to memory, with emotional experiences often being more vividly remembered than neutral ones. This is partly because the brain's emotional centers, such as the amygdala, are closely connected to memory formation processes.
Key Points
- Emotions are complex mental states that influence thoughts, behaviors, and interactions.
- They have physiological, cognitive, and behavioral components and can range from simple to complex states.
- Emotions motivate and guide behavior, influence decision-making, and are closely linked to memory.
- The study of emotions is an interdisciplinary field, drawing from psychology, neuroscience, sociology, and philosophy.
- Understanding emotions is crucial for developing emotional intelligence, which is vital for personal and professional relationships.
The Psychology of Emotions

The psychological study of emotions focuses on understanding their causes, consequences, and functions within the individual and their social environment. One of the foundational theories in the psychology of emotions is the James-Lange theory, which posits that emotions result from physiological responses to external stimuli. For example, when an individual encounters a threatening stimulus, their body’s “fight or flight” response is triggered, leading to the sensation of fear. Other theories, such as the two-factor theory, suggest that emotions are the result of a combination of physiological arousal and cognitive appraisal of the situation. This means that the same physiological state can lead to different emotional experiences depending on how the individual interprets their situation.
Emotional Intelligence and Well-being
Emotional intelligence (EI) refers to the ability to recognize and understand emotions in oneself and others, and to use this awareness to guide thought and behavior. Developing emotional intelligence is considered crucial for maintaining good mental health, building strong relationships, and achieving personal and professional success. Individuals with high emotional intelligence are better equipped to manage their emotions, empathize with others, and develop effective coping strategies for dealing with stress and adversity. Furthermore, emotional intelligence is linked to better decision-making, as it allows individuals to consider the emotional implications of their choices and to navigate complex social situations more effectively.
| Aspect of Emotional Intelligence | Description |
|---|---|
| Self-Awareness | The ability to recognize and understand one's own emotions and how they impact behavior. |
| Self-Regulation | The ability to control and regulate one's own emotions and impulses. |
| Motivation | The ability to use emotions to drive motivation and achieve goals. |
| Empathy | The ability to understand and recognize emotions in others. |
| Social Skills | The ability to effectively communicate and interact with others based on awareness of their emotions. |
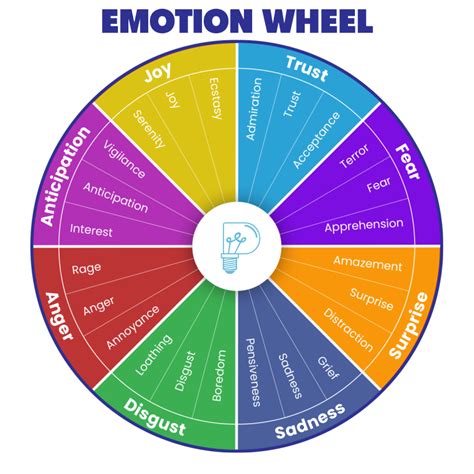
Neuroscience of Emotions

The neuroscience of emotions explores the neural mechanisms underlying emotional experiences. Research has identified several key brain regions involved in emotional processing, including the amygdala, which is crucial for detecting and responding to emotional stimuli, and the prefrontal cortex, which plays a role in the regulation and management of emotions. Neuroscientific studies have also shed light on the neurotransmitters involved in emotional states, such as serotonin and dopamine, which are associated with mood regulation and reward processing, respectively. Furthermore, advances in neuroimaging techniques have allowed for the detailed mapping of brain activity during emotional experiences, providing insights into how emotions are processed and integrated into conscious awareness.
The study of emotions also extends to the realm of emotional disorders, where an imbalance or dysfunction in emotional processing can lead to conditions such as depression, anxiety disorders, and bipolar disorder. Understanding the neural underpinnings of these disorders is critical for the development of effective treatments, which may include pharmacological interventions, psychotherapy, or a combination of both. Additionally, neuroscientific research into emotions informs our understanding of the impact of emotional experiences on physical health, highlighting the intricate mind-body connection and the potential for emotional states to influence susceptibility to disease and overall well-being.
Cultural and Social Aspects of Emotions
Emotions are not only personal experiences but are also shaped by cultural and social contexts. Different cultures may have unique emotional norms, values, and expressions, influencing how emotions are perceived, experienced, and communicated. For instance, some cultures may emphasize the importance of emotional restraint, while others encourage open emotional expression. Social norms also play a significant role in shaping emotional experiences, as individuals learn what emotions are appropriate to express in different social situations and how to manage their emotions to conform to social expectations. Understanding these cultural and social aspects of emotions is essential for navigating diverse social environments effectively and for developing empathy and understanding towards individuals from different backgrounds.
What is the role of emotions in decision-making?
+Emotions play a significant role in decision-making, often influencing choices by weighing the potential emotional outcomes of different options. They can guide decisions towards outcomes that are anticipated to result in positive emotional states and away from those likely to lead to negative emotional states.
How can emotional intelligence be developed?
+Emotional intelligence can be developed through practices such as self-reflection, mindfulness, and social skills training. Engaging in activities that promote emotional awareness, empathy, and effective emotional regulation can also contribute to the development of emotional intelligence.
What are some strategies for managing negative emotions?
+Strategies for managing negative emotions include cognitive reappraisal, where the individual changes their interpretation of the situation to reduce its emotional impact, and expressive suppression, where the individual inhibits the outward expression of the emotion. Other strategies include mindfulness, physical exercise, and seeking social support.
In conclusion, emotions are a fundamental aspect of human experience, influencing behavior, decision-making, and overall well-being. Understanding emotions, whether through the lens of psychology, neuroscience, or sociology, provides valuable insights into the human condition and offers pathways for personal growth, improved relationships, and enhanced emotional intelligence. As research into emotions continues to evolve, it is likely to uncover even more complex and nuanced aspects of emotional experiences, further highlighting the importance of emotions in shaping our lives and interactions with the world around us.