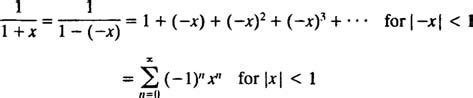The Taylor series is a fundamental concept in mathematics, particularly in the field of calculus. It is a way to represent a function as an infinite sum of terms, each term being a power of the variable. The Taylor series is named after James Gregory and Brook Taylor, who introduced it in the 17th century. In this article, we will explore 5 ways the Taylor series is used in mathematics and other fields.
Key Points
- The Taylor series is used to approximate functions, especially when the function is difficult to compute directly.
- It is used in calculus to find the derivatives and integrals of functions.
- The Taylor series is used in numerical analysis to solve equations and optimize functions.
- It is used in physics and engineering to model real-world phenomena, such as the motion of objects and the behavior of electrical circuits.
- The Taylor series is used in computer science to develop algorithms for solving mathematical problems.
Approximation of Functions
The Taylor series is often used to approximate functions, especially when the function is difficult to compute directly. For example, the function e^x can be approximated using the Taylor series: e^x = 1 + x + \frac{x^2}{2!} + \frac{x^3}{3!} + \ldots. This approximation is useful when x is small, and the higher-order terms can be neglected.
Truncation Error
The Taylor series approximation is not exact, and the error is known as the truncation error. The truncation error can be estimated using the remainder term, which is the difference between the exact function and the approximated function. For example, the remainder term for the Taylor series approximation of e^x is given by: R_n(x) = \frac{f^{(n+1)}(c)}{(n+1)!}x^{n+1}, where c is a constant between 0 and x.
| Function | Taylor Series Approximation | Truncation Error |
|---|---|---|
| $e^x$ | $1 + x + \frac{x^2}{2!} + \frac{x^3}{3!} + \ldots$ | $R_n(x) = \frac{f^{(n+1)}(c)}{(n+1)!}x^{n+1}$ |
| $\sin x$ | $x - \frac{x^3}{3!} + \frac{x^5}{5!} - \ldots$ | $R_n(x) = \frac{f^{(n+1)}(c)}{(n+1)!}x^{n+1}$ |

Calculus Applications

The Taylor series is used in calculus to find the derivatives and integrals of functions. For example, the derivative of e^x can be found using the Taylor series: \frac{d}{dx}e^x = \frac{d}{dx}(1 + x + \frac{x^2}{2!} + \frac{x^3}{3!} + \ldots) = 1 + x + \frac{x^2}{2!} + \ldots. Similarly, the integral of e^x can be found using the Taylor series: \int e^x dx = \int (1 + x + \frac{x^2}{2!} + \frac{x^3}{3!} + \ldots) dx = x + \frac{x^2}{2} + \frac{x^3}{3!} + \ldots.
Derivatives and Integrals
The Taylor series can be used to find the derivatives and integrals of functions, even when the function is difficult to compute directly. For example, the derivative of \sin x can be found using the Taylor series: \frac{d}{dx}\sin x = \frac{d}{dx}(x - \frac{x^3}{3!} + \frac{x^5}{5!} - \ldots) = 1 - \frac{x^2}{2!} + \frac{x^4}{4!} - \ldots.
Numerical Analysis Applications
The Taylor series is used in numerical analysis to solve equations and optimize functions. For example, the Taylor series can be used to solve the equation x^2 + 2x + 1 = 0 by approximating the function f(x) = x^2 + 2x + 1 using the Taylor series: f(x) = f(0) + f'(0)x + \frac{f''(0)}{2!}x^2 + \ldots. The roots of the equation can be found by setting the approximated function equal to zero and solving for x.
Optimization
The Taylor series can be used to optimize functions by approximating the function using the Taylor series and then finding the maximum or minimum of the approximated function. For example, the function f(x) = x^2 + 2x + 1 can be optimized using the Taylor series: f(x) = f(0) + f'(0)x + \frac{f''(0)}{2!}x^2 + \ldots. The maximum or minimum of the function can be found by setting the derivative of the approximated function equal to zero and solving for x.
Physics and Engineering Applications
The Taylor series is used in physics and engineering to model real-world phenomena, such as the motion of objects and the behavior of electrical circuits. For example, the motion of an object under the influence of gravity can be modeled using the Taylor series: y(t) = y(0) + v(0)t + \frac{a(0)}{2!}t^2 + \ldots, where y(t) is the position of the object at time t, v(0) is the initial velocity, and a(0) is the initial acceleration.
Electrical Circuits
The Taylor series can be used to model the behavior of electrical circuits, such as the voltage and current in a circuit. For example, the voltage in a circuit can be modeled using the Taylor series: V(t) = V(0) + \frac{dV}{dt}(0)t + \frac{d^2V}{dt^2}(0)\frac{t^2}{2!} + \ldots, where V(t) is the voltage at time t, and \frac{dV}{dt}(0) and \frac{d^2V}{dt^2}(0) are the initial voltage and current, respectively.
Computer Science Applications

The Taylor series is used in computer science to develop algorithms for solving mathematical problems. For example, the Taylor series can be used to develop algorithms for solving equations and optimizing functions. The Taylor series can also be used to model the behavior of complex systems, such as the motion of objects and the behavior of electrical circuits.
Algorithms
The Taylor series can be used to develop algorithms for solving mathematical problems, such as finding the roots of equations and optimizing functions. For example, the Taylor series can be used to develop an algorithm for finding the roots of the equation x^2 + 2x + 1 = 0 by approximating the function f(x) = x^2 + 2x + 1 using the Taylor series: f(x) = f(0) + f'(0)x + \frac{f''(0)}{2!}x^2 + \ldots. The roots of the equation can be found by setting the approximated function equal to zero and solving for x.
What is the Taylor series?
+The Taylor series is a way to represent a function as an infinite sum of terms, each term being a power of the variable.
What are the applications of the Taylor series?
+The Taylor series has many applications in mathematics, physics, engineering, and computer science, including approximating functions, finding derivatives and integrals, solving equations, and optimizing functions.
How is the Taylor series used in calculus?
+The Taylor series is used in calculus to find the derivatives and integrals of functions, even when the function is difficult to compute directly.
What is the truncation error in the Taylor series?
+The truncation error is the error that occurs when the Taylor series is truncated, or cut off, at a finite number of terms.
How is the Taylor series used in numerical analysis?
+The Taylor series is used in numerical analysis to solve equations and optimize functions by approximating the function using the Taylor series and then finding the maximum or minimum of the approximated function.