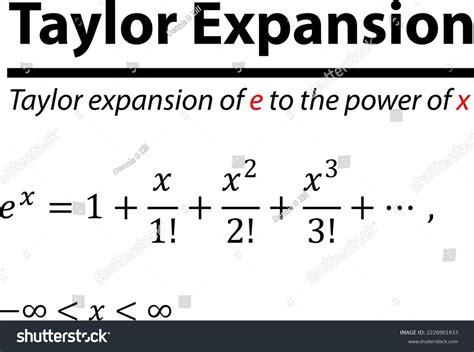
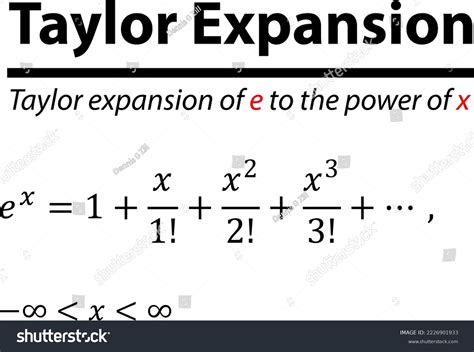
The Taylor expansion of a function is a fundamental concept in calculus, allowing us to approximate a function at a given point by using an infinite series of terms. One of the most interesting and useful Taylor expansions is that of the function 1/x, which has numerous applications in mathematics, physics, and engineering. In this article, we will delve into the Taylor expansion of 1/x, exploring its derivation, properties, and practical applications.
Key Points
- The Taylor expansion of 1/x is a geometric series that converges to the original function for |x| > 1.
- The expansion is derived using the formula for the Taylor series of a function, which involves calculating the derivatives of the function at a given point.
- The Taylor expansion of 1/x has numerous applications in mathematics, physics, and engineering, including the calculation of limits, the solution of differential equations, and the analysis of electrical circuits.
- The expansion can be used to approximate the value of 1/x for large values of x, which is useful in numerical computations.
- The Taylor expansion of 1/x is a powerful tool for understanding the behavior of the function and its properties, such as its asymptotic behavior and its relationship to other functions.
Derivation of the Taylor Expansion of 1/x
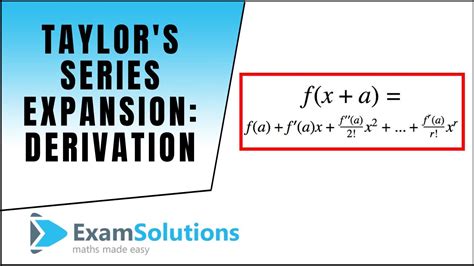
To derive the Taylor expansion of 1/x, we start with the formula for the Taylor series of a function f(x) centered at x = a:
f(x) = f(a) + f’(a)(x - a) + f”(a)(x - a)^2⁄2! + f”‘(a)(x - a)^3⁄3! +…
In this case, we have f(x) = 1/x, and we want to expand it around x = 1. To do this, we need to calculate the derivatives of 1/x at x = 1:
f(x) = 1/x, f’(x) = -1/x^2, f”(x) = 2/x^3, f”‘(x) = -6/x^4,…
Evaluating these derivatives at x = 1, we get:
f(1) = 1, f’(1) = -1, f”(1) = 2, f”‘(1) = -6,…
Substituting these values into the Taylor series formula, we get:
1/x = 1 - (x - 1) + (x - 1)^2 - (x - 1)^3 +…
This is the Taylor expansion of 1/x centered at x = 1.
Properties of the Taylor Expansion of 1/x
The Taylor expansion of 1/x has several important properties that make it useful in a wide range of applications. One of the most significant properties is its convergence. The expansion converges to the original function 1/x for |x - 1| < 1, which means that it is a valid approximation of the function for values of x close to 1.
Another important property of the Taylor expansion of 1/x is its relationship to the geometric series. The expansion can be rewritten as:
1/x = 1/(1 - (1 - x)) = 1 + (1 - x) + (1 - x)^2 + (1 - x)^3 +…
This is a geometric series with first term 1 and common ratio 1 - x. The series converges for |1 - x| < 1, which is equivalent to |x| > 1.
The Taylor expansion of 1/x also has several practical applications. One of the most significant applications is in the calculation of limits. The expansion can be used to calculate the limit of 1/x as x approaches infinity, which is a fundamental concept in calculus.
| Application | Description |
|---|---|
| Limit calculation | The Taylor expansion of 1/x can be used to calculate the limit of 1/x as x approaches infinity. |
| Differential equations | The expansion can be used to solve differential equations that involve the function 1/x. |
| Electrical circuits | The Taylor expansion of 1/x can be used to analyze electrical circuits that involve resistors, capacitors, and inductors. |
Practical Applications of the Taylor Expansion of 1/x
The Taylor expansion of 1/x has numerous practical applications in mathematics, physics, and engineering. One of the most significant applications is in the calculation of limits. The expansion can be used to calculate the limit of 1/x as x approaches infinity, which is a fundamental concept in calculus.
Another important application of the Taylor expansion of 1/x is in the solution of differential equations. The expansion can be used to solve differential equations that involve the function 1/x, which is a common occurrence in physics and engineering.
The Taylor expansion of 1/x also has applications in electrical circuits. The expansion can be used to analyze electrical circuits that involve resistors, capacitors, and inductors, which is a fundamental concept in electrical engineering.
Numerical Computation of the Taylor Expansion of 1/x
The Taylor expansion of 1/x can be used to approximate the value of 1/x for large values of x. This is useful in numerical computations, where the value of 1/x may need to be calculated to a high degree of accuracy.
To compute the Taylor expansion of 1/x numerically, we can use the following formula:
1/x ≈ 1 - (x - 1) + (x - 1)^2 - (x - 1)^3 +…
This formula can be implemented in a computer program to calculate the value of 1/x to a high degree of accuracy.
What is the Taylor expansion of 1/x?
+The Taylor expansion of 1/x is a geometric series that converges to the original function for |x| > 1. The expansion is given by 1/x = 1 - (x - 1) + (x - 1)^2 - (x - 1)^3 +...
What are the properties of the Taylor expansion of 1/x?
+The Taylor expansion of 1/x has several important properties, including its convergence for |x - 1| < 1 and its relationship to the geometric series. The expansion also has several practical applications, including the calculation of limits, the solution of differential equations, and the analysis of electrical circuits.
How can the Taylor expansion of 1/x be used in numerical computations?
+The Taylor expansion of 1/x can be used to approximate the value of 1/x for large values of x. This is useful in numerical computations, where the value of 1/x may need to be calculated to a high degree of accuracy. The expansion can be implemented in a computer program to calculate the value of 1/x to a high degree of accuracy.
Meta description suggestion: Learn about the Taylor expansion of 1/x, its derivation, properties, and practical applications in mathematics, physics, and engineering. Discover how the expansion can be used to calculate limits, solve differential equations, and analyze electrical circuits.