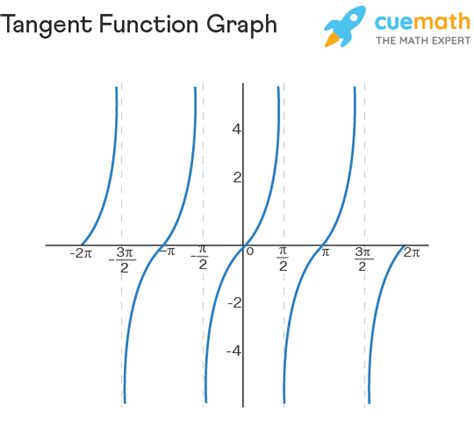
The tangent graph, a fundamental concept in trigonometry, represents the ratio of the sine and cosine functions. Understanding its properties and behavior is crucial for solving various mathematical problems, particularly in the fields of physics, engineering, and calculus. The following discussion provides an in-depth exploration of the tangent graph, focusing on key properties, applications, and practical tips for working with this essential trigonometric function.
Key Points
- The tangent function is periodic with a period of π, meaning its graph repeats every π units.
- The tangent graph has vertical asymptotes at odd multiples of π/2, where the function is undefined.
- The graph of the tangent function can be used to solve equations involving the tangent of an angle.
- Understanding the properties of the tangent graph is essential for applications in physics, engineering, and calculus.
- Graphing the tangent function can help visualize and analyze periodic phenomena in various fields.
Understanding the Tangent Graph
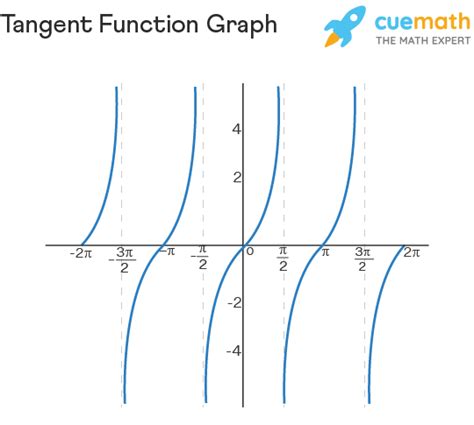
The tangent graph, denoted as y = tan(x), exhibits unique characteristics that distinguish it from other trigonometric functions. One of its primary features is its periodic nature, with a period of π. This means that the graph of the tangent function repeats itself every π units, both horizontally and vertically. The function’s range spans all real numbers, but its domain is restricted due to the presence of vertical asymptotes at odd multiples of π/2.
Identifying Vertical Asymptotes
Vertical asymptotes occur where the tangent function is undefined, which happens when the cosine of an angle is zero. These points are located at odd multiples of π/2, i.e., π/2, 3π/2, 5π/2, and so on. Recognizing these asymptotes is crucial for graphing the tangent function accurately and for solving equations that involve the tangent of an angle.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Period | π |
| Domain | All real numbers except odd multiples of π/2 |
| Range | All real numbers |
| Vertical Asymptotes | Odd multiples of π/2 |

Applications of the Tangent Graph
The tangent graph has numerous applications across various disciplines. In calculus, understanding the properties of the tangent function is vital for computing derivatives and integrals, particularly when dealing with trigonometric functions. In physics and engineering, the tangent graph can be used to model real-world phenomena, such as the motion of objects and the behavior of electrical circuits.
Graphing the Tangent Function
Graphing the tangent function involves understanding its periodic nature and the presence of vertical asymptotes. By recognizing these characteristics, one can accurately sketch the graph of the tangent function, which is essential for visualizing and analyzing periodic phenomena in various fields. Additionally, graphing software and calculators can be used to plot the tangent function, providing a more detailed and precise representation of its behavior.
In conclusion, the tangent graph is a fundamental concept in trigonometry with far-reaching applications in physics, engineering, and calculus. By understanding its properties, including its periodic nature and vertical asymptotes, one can effectively apply the tangent function to solve equations and model real-world phenomena.
What is the period of the tangent function?
+The period of the tangent function is π, meaning its graph repeats every π units.
Where are the vertical asymptotes of the tangent graph located?
+The vertical asymptotes of the tangent graph are located at odd multiples of π/2.
What are some applications of the tangent graph?
+The tangent graph has applications in physics, engineering, and calculus, including modeling the motion of objects and the behavior of electrical circuits.