Tadalafil and sildenafil are two of the most widely recognized and prescribed medications for the treatment of erectile dysfunction (ED), a condition that affects millions of men worldwide. Both drugs belong to a class of medications known as phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE5) inhibitors, which work by increasing blood flow to the penis to help achieve and maintain an erection. Despite sharing a common mechanism of action, tadalafil and sildenafil have distinct differences in terms of their pharmacokinetics, efficacy, and side effect profiles, making one more suitable for certain individuals than the other.
Key Points
- Tadalafil and sildenafil are both PDE5 inhibitors used to treat erectile dysfunction but have different durations of action.
- Tadalafil has a longer half-life, allowing for greater spontaneity in sexual activity compared to sildenafil.
- Sildenafil has a faster onset of action but a shorter duration, typically lasting around 4-6 hours.
- Both medications are effective, but the choice between them may depend on individual preferences, lifestyle, and specific health conditions.
- Common side effects include headache, flushing, and dyspepsia, but the incidence can vary between the two drugs.
Pharmacological Comparison

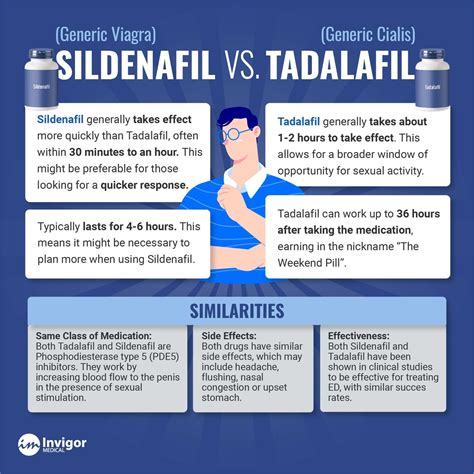
From a pharmacological standpoint, the primary difference between tadalafil and sildenafil lies in their pharmacokinetic profiles. Tadalafil has a significantly longer half-life of approximately 17.5 hours compared to sildenafil’s half-life of about 3-4 hours. This longer half-life translates into a longer duration of action for tadalafil, allowing men to engage in sexual activity at any time within a 36-hour window after taking the medication, provided they are sexually stimulated. In contrast, sildenafil’s shorter duration of action means that sexual activity is generally confined to a 4-6 hour window after dosing.
Onset of Action and Efficacy
The onset of action for sildenafil is typically faster than for tadalafil, with some men experiencing the effects of sildenafil within 30 minutes of taking the medication. Tadalafil, while taking slightly longer to become effective, offers the advantage of a longer window of opportunity for sexual activity. Both medications have been shown to be highly effective in clinical trials, with significant improvements in erectile function scores compared to placebo. However, individual responses can vary, and factors such as dosage, timing, and individual health conditions can influence the efficacy of these medications.
| Medication | Half-life | Onset of Action | Duration of Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tadalafil | 17.5 hours | 30 minutes to 2 hours | Up to 36 hours |
| Sildenafil | 3-4 hours | 30 minutes to 1 hour | 4-6 hours |

Side Effects and Safety
Both tadalafil and sildenafil are generally well-tolerated, with most men experiencing few or no side effects. Common side effects associated with PDE5 inhibitors include headache, flushing, dyspepsia, and nasal congestion. The incidence of these side effects can vary between tadalafil and sildenafil, with some studies suggesting that tadalafil may have a slightly more favorable side effect profile due to its longer half-life and lower peak plasma concentrations. However, the difference in side effect incidence between the two medications is generally small, and individual experiences can vary widely.
Contraindications and Interactions
Both tadalafil and sildenafil are contraindicated in men who take nitrates or guanylate cyclase stimulators, as the combination of these medications can lead to a significant drop in blood pressure. Additionally, caution is advised when prescribing these medications to men with certain cardiovascular conditions, as well as those with severe hepatic or renal impairment. The potential for drug interactions, particularly with medications that inhibit or induce the cytochrome P450 enzyme system, should also be carefully considered to minimize the risk of adverse effects.
What is the primary difference between tadalafil and sildenafil in terms of their effect on erectile dysfunction?
+The primary difference lies in their duration of action, with tadalafil lasting up to 36 hours and sildenafil typically lasting 4-6 hours.
Which medication has a faster onset of action?
+Sildenafil generally has a faster onset of action, with effects experienced within 30 minutes to 1 hour after dosing.
Are there any significant differences in the side effect profiles of tadalafil and sildenafil?
+While both medications share similar common side effects, the incidence can vary slightly between them, with some studies suggesting a more favorable profile for tadalafil.
In conclusion, the choice between tadalafil and sildenafil for the treatment of erectile dysfunction should be based on a comprehensive assessment of individual patient needs, preferences, and health status. By understanding the pharmacological differences, efficacy, and potential side effects of these medications, healthcare providers can offer personalized treatment recommendations that enhance the quality of life for men affected by ED.