The noble gases are a group of elements in the periodic table that are known for their unreactive nature. They are located in the far right column of the periodic table and include helium (He), neon (Ne), argon (Ar), krypton (Kr), xenon (Xe), and radon (Rn). These elements are characterized by their full outer energy level, which makes them stable and unreactive. In this article, we will explore the properties and characteristics of the noble gases, including their history, uses, and interesting facts.
Key Points
- The noble gases are a group of six elements that are known for their unreactive nature.
- They are located in the far right column of the periodic table.
- The noble gases have a full outer energy level, which makes them stable and unreactive.
- They have a range of uses, including lighting, lasers, and medical applications.
- The noble gases are also used in scientific research, including the study of superconductivity and superfluidity.
History of the Noble Gases
The discovery of the noble gases dates back to the late 19th century, when scientists such as William Ramsay and Lord Rayleigh discovered the elements argon, helium, and neon. The name “noble gas” was coined because of their unreactive nature, which was thought to be similar to the nobility, who were considered to be above the common people. Over time, the other noble gases were discovered, and today we know that there are six elements in this group.
Properties of the Noble Gases
The noble gases have a number of unique properties that set them apart from other elements. They are all colorless, odorless, and tasteless, and they are all monatomic, meaning that they exist as single atoms rather than molecules. They also have a range of physical properties, including melting and boiling points, that are unique to each element. The following table shows some of the key properties of the noble gases:
| Element | Symbol | Atomic Number | Melting Point (K) | Boiling Point (K) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Helium | He | 2 | 0.95 | 4.22 |
| Neon | Ne | 10 | 24.56 | 27.07 |
| Argon | Ar | 18 | 83.81 | 87.30 |
| Krypton | Kr | 36 | 115.79 | 119.93 |
| Xenon | Xe | 54 | 161.36 | 165.03 |
| Radon | Rn | 86 | 202.15 | 211.30 |

Uses of the Noble Gases
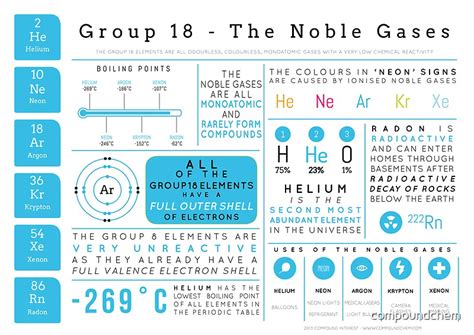
The noble gases have a range of uses, including lighting, lasers, and medical applications. For example, neon is used in neon signs, while argon is used in light bulbs. Xenon is used in high-intensity lamps, such as those used in movie projectors, while krypton is used in fluorescent lamps. Radon is used in cancer treatment, where it is used to kill cancer cells.
Medical Applications
The noble gases also have a range of medical applications. For example, xenon is used as an anesthetic, while argon is used in medical imaging. Helium is used in respiratory therapy, where it is used to help patients breathe. The following are some of the medical applications of the noble gases:
- Xenon: anesthetic, medical imaging
- Argon: medical imaging, wound healing
- Helium: respiratory therapy, medical imaging
- Neon: medical imaging, cancer treatment
- Krypton: medical imaging, cancer treatment
- Radon: cancer treatment
Interesting Facts About the Noble Gases
There are many interesting facts about the noble gases. For example, helium is the lightest noble gas, while radon is the heaviest. Xenon is the most expensive noble gas, while argon is the most abundant. The following are some interesting facts about the noble gases:
- Helium is the lightest noble gas, with an atomic mass of 4.003 u.
- Radon is the heaviest noble gas, with an atomic mass of 222.0176 u.
- Xenon is the most expensive noble gas, with a price of around $10 per liter.
- Argon is the most abundant noble gas, making up around 0.934% of the Earth's atmosphere.
- Neon is used in neon signs, which are made by electrifying a gas mixture that contains neon.
- Krypton is used in fluorescent lamps, which are made by electrifying a gas mixture that contains krypton.
What are the noble gases?
+The noble gases are a group of six elements that are known for their unreactive nature. They are located in the far right column of the periodic table and include helium (He), neon (Ne), argon (Ar), krypton (Kr), xenon (Xe), and radon (Rn).
What are the properties of the noble gases?
+The noble gases have a number of unique properties that set them apart from other elements. They are all colorless, odorless, and tasteless, and they are all monatomic, meaning that they exist as single atoms rather than molecules.
What are the uses of the noble gases?
+The noble gases have a range of uses, including lighting, lasers, and medical applications. For example, neon is used in neon signs, while argon is used in light bulbs. Xenon is used in high-intensity lamps, such as those used in movie projectors, while krypton is used in fluorescent lamps.
What are the medical applications of the noble gases?
+The noble gases have a range of medical applications. For example, xenon is used as an anesthetic, while argon is used in medical imaging. Helium is used in respiratory therapy, where it is used to help patients breathe.
What are some interesting facts about the noble gases?
+There are many interesting facts about the noble gases. For example, helium is the lightest noble gas, while radon is the heaviest. Xenon is the most expensive noble gas, while argon is the most abundant.