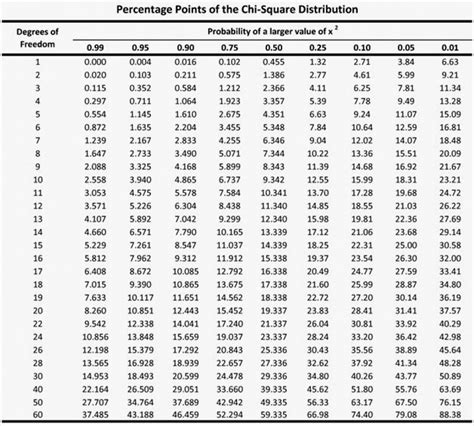
The chi-square test is a statistical method used to determine whether there is a significant association between two categorical variables. The chi-square table, also known as a contingency table, is a fundamental tool in this analysis. In this article, we will delve into the world of chi-square table analysis, exploring its applications, interpretations, and best practices.
Introduction to Chi-Square Table Analysis

Chi-square table analysis is a widely used technique in statistics, particularly in hypothesis testing. The chi-square test is used to examine the relationship between two categorical variables, such as gender and smoking status, or education level and income. The test calculates the probability that any observed difference between the variables is due to chance. The chi-square table is a crucial component of this analysis, as it displays the frequency of observations in each category.
Constructing a Chi-Square Table
A chi-square table is a simple, yet powerful tool for analyzing categorical data. The table consists of rows and columns, each representing a category of the two variables being analyzed. The cells in the table contain the observed frequencies, which are the number of observations in each category. For example, if we are analyzing the relationship between gender (male, female) and smoking status (smoker, non-smoker), the chi-square table might look like this:
| Smoking Status | Male | Female | Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| Smoker | 20 | 15 | 35 |
| Non-Smoker | 30 | 40 | 70 |
| Total | 50 | 55 | 105 |
In this example, the table shows that there are 20 males who are smokers, 15 females who are smokers, and so on. The total number of observations is 105.
Interpreting Chi-Square Test Results

Once the chi-square table has been constructed, the next step is to perform the chi-square test. The test calculates the chi-square statistic, which is a measure of the difference between the observed frequencies and the expected frequencies under the null hypothesis. The null hypothesis states that there is no significant association between the two variables. The alternative hypothesis states that there is a significant association.
Calculating the Chi-Square Statistic
The chi-square statistic is calculated using the following formula:
χ² = Σ [(observed frequency - expected frequency)² / expected frequency]
Where Σ denotes the sum of the squared differences between the observed and expected frequencies, divided by the expected frequency.
The expected frequencies are calculated under the assumption of independence between the two variables. The expected frequency for each cell is calculated as the product of the row total and the column total, divided by the total number of observations.
For example, in the previous table, the expected frequency for the cell "male smoker" would be:
Expected frequency = (50 x 35) / 105 = 16.67
The observed frequency for this cell is 20, so the contribution to the chi-square statistic would be:
(20 - 16.67)² / 16.67 = 0.51
The chi-square statistic is the sum of these contributions for all cells in the table.
Key Points
- The chi-square test is used to determine whether there is a significant association between two categorical variables.
- The chi-square table is a crucial component of the analysis, displaying the frequency of observations in each category.
- The expected frequencies are calculated under the assumption of independence between the two variables.
- The chi-square statistic is calculated using the formula: χ² = Σ [(observed frequency - expected frequency)² / expected frequency].
- The null hypothesis states that there is no significant association between the two variables, while the alternative hypothesis states that there is a significant association.
Common Applications of Chi-Square Table Analysis
Chi-square table analysis has a wide range of applications in various fields, including medicine, social sciences, and marketing. Some common applications include:
Medical Research
Chi-square table analysis is often used in medical research to examine the relationship between disease outcomes and various factors, such as age, gender, and treatment. For example, a study might use chi-square table analysis to investigate the association between smoking status and lung cancer risk.
Market Research
Chi-square table analysis is also used in market research to analyze the relationship between consumer behavior and demographic characteristics, such as age, income, and education level. For example, a company might use chi-square table analysis to examine the association between customer satisfaction and product features.
What is the purpose of chi-square table analysis?
+The purpose of chi-square table analysis is to determine whether there is a significant association between two categorical variables.
How is the chi-square statistic calculated?
+The chi-square statistic is calculated using the formula: χ² = Σ [(observed frequency - expected frequency)² / expected frequency].
What is the null hypothesis in chi-square table analysis?
+The null hypothesis states that there is no significant association between the two variables.
In conclusion, chi-square table analysis is a powerful tool for examining the relationship between two categorical variables. By constructing a chi-square table and performing the chi-square test, researchers can determine whether there is a significant association between the variables. The applications of chi-square table analysis are diverse, ranging from medical research to market research. By understanding the principles and applications of chi-square table analysis, researchers can make informed decisions and draw meaningful conclusions from their data.