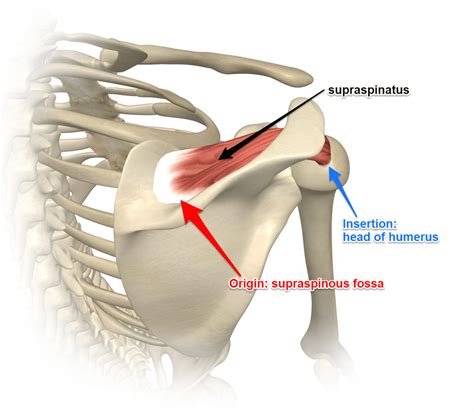
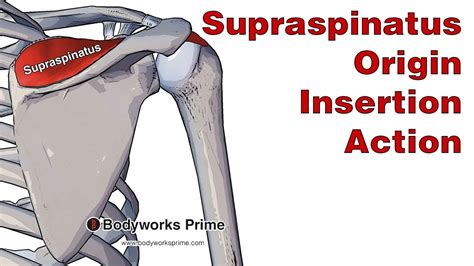
The supraspinatus muscle is one of the four muscles that comprise the rotator cuff, a group of muscles and tendons that surround the shoulder joint, providing stability and facilitating movement. Understanding the origin and insertion points of the supraspinatus muscle is crucial for diagnosing and treating shoulder injuries and conditions. The supraspinatus muscle originates from the supraspinous fossa, a depression in the scapula (shoulder blade) located above the spine of the scapula. This area serves as the anchor point for the muscle, providing a solid foundation for its contraction and relaxation.
The muscle fibers of the supraspinatus converge to form a tendon that passes under the acromion, a bony projection of the scapula that forms the highest point of the shoulder. The tendon then inserts into the greater tubercle of the humerus, the long bone of the upper arm. Specifically, the insertion point is on the superior facet of the greater tubercle, which is the uppermost aspect of the tubercle. This precise insertion point allows the supraspinatus muscle to play a critical role in shoulder abduction, the movement of the arm away from the body, and stabilization of the shoulder joint.
Key Points
- The supraspinatus muscle originates from the supraspinous fossa of the scapula.
- The muscle inserts into the superior facet of the greater tubercle of the humerus.
- The supraspinatus muscle is essential for shoulder abduction and stabilization.
- Understanding the origin and insertion points is crucial for diagnosing and treating shoulder injuries.
- The rotator cuff, including the supraspinatus muscle, is vital for maintaining shoulder joint integrity and facilitating movement.
Anatomical Considerations and Functional Significance
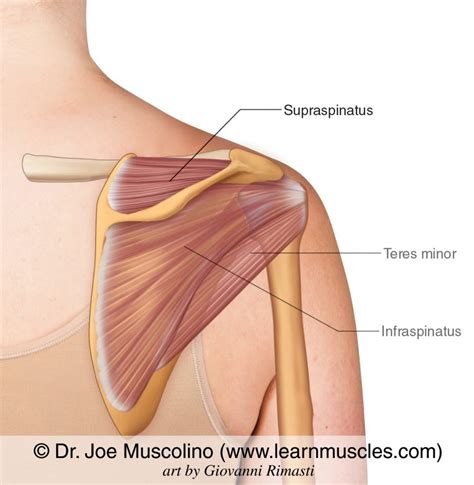
The anatomical relationship between the supraspinatus muscle and the surrounding structures of the shoulder joint is intricate. The muscle’s origin from the supraspinous fossa and its insertion into the greater tubercle of the humerus position it ideally to assist in the abduction of the arm, particularly in the initial stages of movement. The supraspinatus muscle works in concert with the other rotator cuff muscles, including the infraspinatus, teres minor, and subscapularis, to maintain the humeral head centered within the glenoid cavity of the scapula, thus ensuring smooth and efficient movement of the shoulder joint.
Biomechanical Aspects and Injury Risks
From a biomechanical perspective, the supraspinatus muscle is subjected to significant stress, particularly during repetitive overhead activities or sudden forceful movements. The tendon of the supraspinatus muscle is vulnerable to wear and tear, which can lead to conditions such as tendinitis or tears. The space through which the tendon passes under the acromion, known as the subacromial space, can also be a site of impingement, where the tendon is compressed against the acromion, leading to inflammation and pain. Understanding the biomechanical aspects of the supraspinatus muscle and its potential injury risks is essential for both prevention and treatment of shoulder injuries.
| Muscle Action | Movement Facilitated |
|---|---|
| Abduction | Movement of the arm away from the body |
| Stabilization | Maintenance of the humeral head within the glenoid cavity |
Clinical Relevance and Rehabilitation
Clinically, injuries to the supraspinatus muscle, such as tendinitis or tears, can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life, limiting their ability to perform daily activities and participate in sports. Accurate diagnosis, often involving imaging studies like MRI, is crucial for developing an effective treatment plan. Rehabilitation of the supraspinatus muscle and the rotator cuff as a whole typically involves a combination of physical therapy, including exercises to strengthen the muscles and improve flexibility, and potentially surgical intervention for more severe injuries. Understanding the origin and insertion points of the supraspinatus muscle is fundamental for the design of effective rehabilitation protocols.
Rehabilitation programs are tailored to address the specific needs of the individual, taking into account the extent of the injury, the patient's overall health, and their goals for recovery. Early stages of rehabilitation may focus on reducing pain and inflammation, followed by progressive strengthening exercises to restore muscle function and promote healing. The goal of rehabilitation is not only to restore function but also to prevent future injuries, emphasizing the importance of ongoing strengthening and flexibility exercises as part of a long-term maintenance program.
What is the primary function of the supraspinatus muscle?
+The primary function of the supraspinatus muscle is to assist in the abduction of the arm, particularly in the initial stages of movement, and to stabilize the shoulder joint.
Where does the supraspinatus muscle insert?
+The supraspinatus muscle inserts into the superior facet of the greater tubercle of the humerus.
What are common injuries affecting the supraspinatus muscle?
+Common injuries include tendinitis and tears, often resulting from repetitive strain, sudden forceful movements, or impingement under the acromion.
In conclusion, the supraspinatus muscle plays a vital role in the function and stability of the shoulder joint. Its precise origin from the supraspinous fossa and insertion into the greater tubercle of the humerus enable it to facilitate abduction and stabilize the joint. Understanding the anatomy, biomechanics, and clinical relevance of the supraspinatus muscle is essential for the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of shoulder injuries, as well as for the development of effective rehabilitation programs aimed at restoring function and promoting long-term shoulder health.



