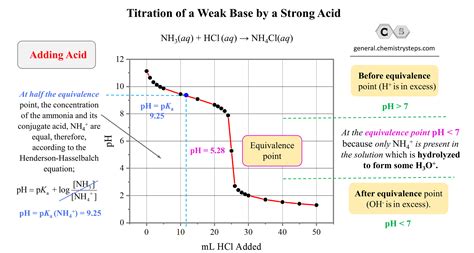
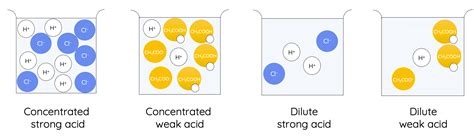
The reaction between a strong acid and a weak base is a fundamental concept in chemistry, particularly in the realm of acid-base reactions. Strong acids are those that completely dissociate in water, producing a high concentration of hydrogen ions (H+), while weak bases are those that only partially dissociate, resulting in a lower concentration of hydroxide ions (OH-). The reaction between these two species is characterized by the transfer of a proton (H+) from the strong acid to the weak base, forming a conjugate acid and a conjugate base.
Key Points
- The reaction between a strong acid and a weak base results in the formation of a conjugate acid and a conjugate base.
- The strong acid completely dissociates in water, producing a high concentration of hydrogen ions (H+).
- The weak base only partially dissociates, resulting in a lower concentration of hydroxide ions (OH-).
- The reaction is characterized by the transfer of a proton (H+) from the strong acid to the weak base.
- The equilibrium constant (Kb) for the reaction can be used to determine the strength of the weak base.
Reaction Mechanism
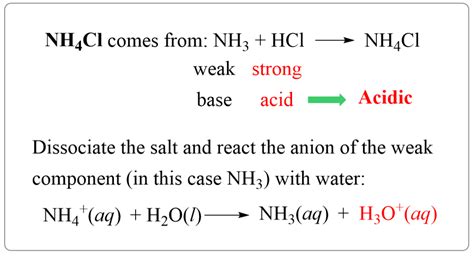
The reaction between a strong acid, such as hydrochloric acid (HCl), and a weak base, such as ammonia (NH3), can be represented by the following equation: HCl + NH3 → NH4+ + Cl-. In this reaction, the hydrogen ion (H+) from the hydrochloric acid transfers to the ammonia molecule, forming an ammonium ion (NH4+). The chloride ion (Cl-) is the conjugate base of the hydrochloric acid, while the ammonium ion is the conjugate acid of the ammonia.
Equilibrium Constant
The equilibrium constant (Kb) for the reaction between a strong acid and a weak base can be used to determine the strength of the weak base. The Kb value represents the ratio of the concentrations of the conjugate acid and the weak base to the concentration of the strong acid. A higher Kb value indicates a stronger weak base. For example, the Kb value for ammonia is approximately 1.8 x 10^-5, indicating that it is a relatively weak base.
| Weak Base | Kb Value |
|---|---|
| Ammonia (NH3) | 1.8 x 10^-5 |
| Methylamine (CH3NH2) | 4.4 x 10^-4 |
| Dimethylamine (CH3)2NH | 5.9 x 10^-4 |
Applications
The reaction between a strong acid and a weak base has several practical applications in various fields, including chemistry, biology, and environmental science. For example, in the production of fertilizers, ammonia is often reacted with strong acids, such as sulfuric acid, to produce ammonium sulfate. This reaction is an important step in the manufacture of fertilizers, as it allows for the production of a stable and water-soluble form of nitrogen.
Buffer Solutions
Buffer solutions are mixtures of a weak acid and its conjugate base, or a weak base and its conjugate acid. These solutions are used to maintain a stable pH in a variety of applications, including laboratory experiments and industrial processes. The reaction between a strong acid and a weak base can be used to prepare buffer solutions, as it allows for the formation of a conjugate acid and a conjugate base. For example, a buffer solution can be prepared by mixing ammonia with hydrochloric acid, resulting in the formation of ammonium chloride.
In conclusion, the reaction between a strong acid and a weak base is an important concept in chemistry, with several practical applications in various fields. By understanding the reaction mechanism and the equilibrium constant (Kb) for the reaction, we can predict the behavior of different acid-base systems and prepare buffer solutions with specific pH values.
What is the difference between a strong acid and a weak base?
+A strong acid is a molecule that completely dissociates in water, producing a high concentration of hydrogen ions (H+), while a weak base is a molecule that only partially dissociates, resulting in a lower concentration of hydroxide ions (OH-).
What is the equilibrium constant (Kb) for the reaction between a strong acid and a weak base?
+The equilibrium constant (Kb) for the reaction between a strong acid and a weak base represents the ratio of the concentrations of the conjugate acid and the weak base to the concentration of the strong acid. A higher Kb value indicates a stronger weak base.
What are some practical applications of the reaction between a strong acid and a weak base?
+The reaction between a strong acid and a weak base has several practical applications, including the production of fertilizers, the preparation of buffer solutions, and the maintenance of a stable pH in various industrial processes.