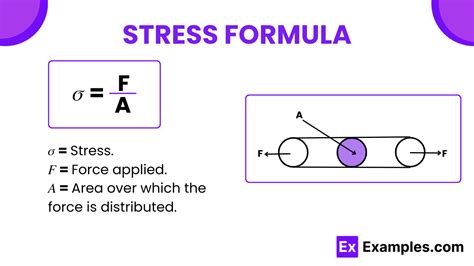
The stress formula, also known as the stress equation, is a mathematical expression used to calculate the stress on an object due to external forces. Stress is a measure of the internal forces that are distributed within an object, and it is typically measured in units of force per unit area, such as pascals (Pa) or pounds per square inch (psi). The stress formula is commonly used in engineering and physics to predict the behavior of materials under different types of loading conditions.
One of the most widely used stress formulas is the Hooke's law, which states that the stress (σ) on an object is proportional to the strain (ε) on the object, within the proportional limit of the material. The formula is expressed as: σ = E \* ε, where E is the modulus of elasticity of the material. This formula is useful for calculating the stress on an object that is subjected to tensile or compressive forces, such as a rod or a beam.
Key Points
- The stress formula is used to calculate the stress on an object due to external forces.
- Stress is a measure of the internal forces that are distributed within an object.
- The stress formula is commonly used in engineering and physics to predict the behavior of materials under different types of loading conditions.
- Hooke's law is a widely used stress formula that states that the stress on an object is proportional to the strain on the object.
- The modulus of elasticity is an important material property that is used in the stress formula to calculate the stress on an object.
Types of Stress
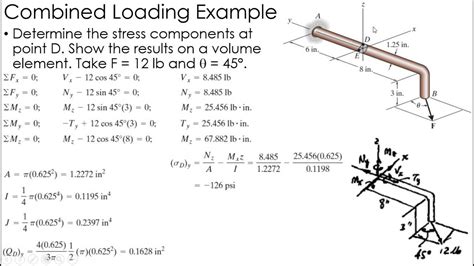
There are several types of stress that can occur in an object, including tensile stress, compressive stress, shear stress, and torsional stress. Tensile stress occurs when an object is subjected to a force that pulls it apart, such as a rope or a wire. Compressive stress occurs when an object is subjected to a force that squeezes it together, such as a column or a beam. Shear stress occurs when an object is subjected to a force that causes it to deform by sliding along a plane, such as a piece of paper or a metal sheet. Torsional stress occurs when an object is subjected to a force that causes it to twist, such as a screw or a bolt.
Tensile Stress
Tensile stress is a type of stress that occurs when an object is subjected to a force that pulls it apart. The formula for tensile stress is: σ = F / A, where F is the force applied to the object and A is the cross-sectional area of the object. Tensile stress is commonly used to calculate the stress on an object that is subjected to a tensile force, such as a rope or a wire.
| Type of Stress | Formula |
|---|---|
| Tensile Stress | σ = F / A |
| Compressive Stress | σ = F / A |
| Shear Stress | τ = F / A |
| Torsional Stress | τ = T / (π \* r^3) |
Applications of the Stress Formula
The stress formula has a wide range of applications in engineering and physics, including the design of buildings, bridges, and machines. It is used to calculate the stress on an object due to external forces, such as wind, water, or gravity. The stress formula is also used to predict the behavior of materials under different types of loading conditions, such as tensile, compressive, or shear loading.
Material Properties
The stress formula is closely related to the material properties of an object, such as its modulus of elasticity, yield strength, and ultimate strength. The modulus of elasticity is a measure of a material’s ability to resist deformation under stress, while the yield strength and ultimate strength are measures of a material’s ability to resist failure under stress. By understanding the material properties of an object, engineers can predict its behavior under different types of loading conditions and design safer and more efficient structures and machines.
In conclusion, the stress formula is a powerful tool for engineers and physicists to predict the behavior of materials under different types of loading conditions. By understanding the different types of stress and how to calculate them, engineers can design safer and more efficient structures and machines. The stress formula has a wide range of applications in engineering and physics, including the design of buildings, bridges, and machines.
What is the stress formula?
+The stress formula is a mathematical expression used to calculate the stress on an object due to external forces. It is commonly expressed as: σ = F / A, where F is the force applied to the object and A is the cross-sectional area of the object.
What are the different types of stress?
+There are several types of stress, including tensile stress, compressive stress, shear stress, and torsional stress. Each type of stress occurs when an object is subjected to a different type of external force.
How is the stress formula used in engineering and physics?
+The stress formula is used to predict the behavior of materials under different types of loading conditions. It is used to calculate the stress on an object due to external forces, such as wind, water, or gravity, and to design safer and more efficient structures and machines.