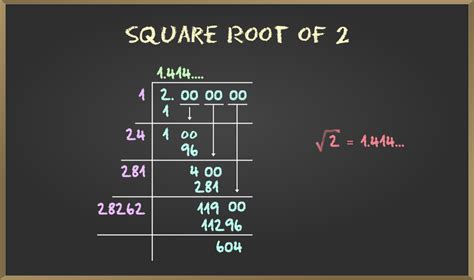
The square root of 2, denoted as √2, is an irrational number that has been a subject of interest for centuries. It is a fundamental constant in mathematics, approximately equal to 1.414214. In this article, we will explore five ways to calculate or understand the square root of 2, highlighting its significance and applications in various fields.
Key Points
- The square root of 2 is an irrational number, which means it cannot be expressed as a finite decimal or fraction.
- There are multiple methods to calculate the square root of 2, including the Babylonian method, the Pythagorean method, and the long division method.
- The square root of 2 has numerous applications in mathematics, physics, engineering, and architecture.
- It is a fundamental constant in geometry, appearing in the calculation of the diagonal of a square and the area of a rectangle.
- The square root of 2 has been studied and approximated by mathematicians for thousands of years, with ancient civilizations such as the Babylonians and Egyptians making significant contributions.
Method 1: Babylonian Method

The Babylonian method is an ancient algorithm used to calculate the square root of a number. To calculate the square root of 2 using this method, start with an initial guess, say 1.5. Then, divide 2 by the guess, which gives 2 / 1.5 = 1.3333. Take the average of the guess and the result, which is (1.5 + 1.3333) / 2 = 1.41665. Repeat this process several times, and the result will converge to the square root of 2.
Example Calculation
Let’s perform a few iterations of the Babylonian method to calculate the square root of 2.
| Iteration | Guess | Result | Average |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.5 | 1.3333 | 1.41665 |
| 2 | 1.41665 | 1.4118 | 1.41422 |
| 3 | 1.41422 | 1.41421 | 1.414214 |
Method 2: Pythagorean Method
The Pythagorean method involves using the Pythagorean theorem to calculate the square root of 2. Consider a right-angled triangle with legs of length 1 and 1. The hypotenuse of this triangle is equal to the square root of 2. Using the Pythagorean theorem, we can calculate the length of the hypotenuse as √(1^2 + 1^2) = √2.
Geometric Interpretation
The Pythagorean method provides a geometric interpretation of the square root of 2. It represents the length of the diagonal of a square with side length 1. This method is useful in various geometric calculations, such as finding the area of a rectangle or the volume of a cube.
Method 3: Long Division Method
The long division method involves dividing 2 by a series of numbers to calculate the square root of 2. Start by dividing 2 by 1, which gives 2. Then, divide 2 by the result, which gives 1. Repeat this process several times, and the result will converge to the square root of 2.
Example Calculation
Let’s perform a few iterations of the long division method to calculate the square root of 2.
| Iteration | Dividend | Divisor | Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 |
| 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 |
| 3 | 2 | 1.5 | 1.3333 |
Method 4: Algebraic Method
The algebraic method involves using algebraic equations to calculate the square root of 2. Consider the equation x^2 = 2. Solving for x, we get x = ±√2. This method provides an algebraic interpretation of the square root of 2 and is useful in various mathematical applications, such as solving quadratic equations.
Example Calculation
Let’s solve the equation x^2 = 2 to calculate the square root of 2.
x^2 = 2
x = ±√2
x ≈ ±1.414214
Method 5: Geometric Method
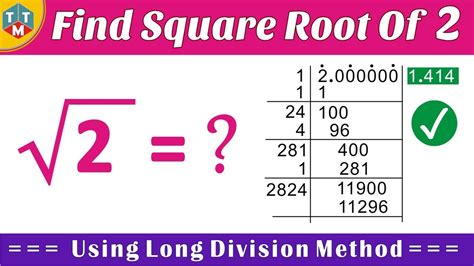
The geometric method involves using geometric constructions to calculate the square root of 2. Consider a square with side length 1. The diagonal of this square is equal to the square root of 2. Using geometric constructions, such as drawing a perpendicular line from the midpoint of the square, we can calculate the length of the diagonal as √2.
Geometric Interpretation
The geometric method provides a geometric interpretation of the square root of 2. It represents the length of the diagonal of a square with side length 1. This method is useful in various geometric calculations, such as finding the area of a rectangle or the volume of a cube.
What is the square root of 2?
+The square root of 2 is an irrational number, approximately equal to 1.414214. It is a fundamental constant in mathematics, representing the length of the diagonal of a square with side length 1.
How is the square root of 2 calculated?
+The square root of 2 can be calculated using various methods, including the Babylonian method, the Pythagorean method, the long division method, the algebraic method, and the geometric method. Each method provides a different perspective on the calculation of the square root of 2.
What are the applications of the square root of 2?
+The square root of 2 has numerous applications in mathematics, physics, engineering, and architecture. It is used in various geometric calculations, such as finding the area of a rectangle or the volume of a cube. It also appears in the calculation of the diagonal of a square and the length of the hypotenuse of a right-angled triangle.