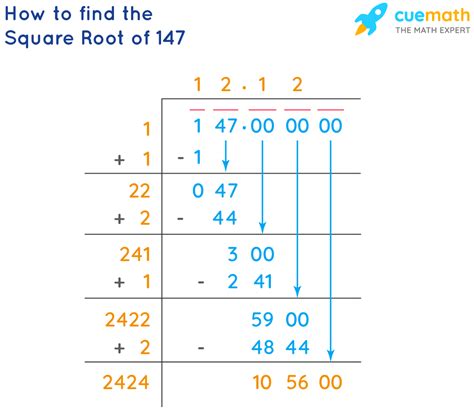
Calculating roots is a fundamental concept in mathematics, and there are several methods to achieve this, each with its own advantages and applications. The most common root calculations involve finding the square root, cube root, and nth root of a number. Here, we will explore five distinct ways to calculate roots, including traditional methods, algebraic approaches, and numerical techniques.
Key Points
- Understanding the concept of roots and their mathematical representation
- Traditional method of finding roots through factorization
- Algebraic approach using the quadratic formula for square roots
- Numerical method involving the Babylonian method for square roots
- Using calculus for finding roots, specifically the Newton-Raphson method
Understanding Roots and Traditional Methods
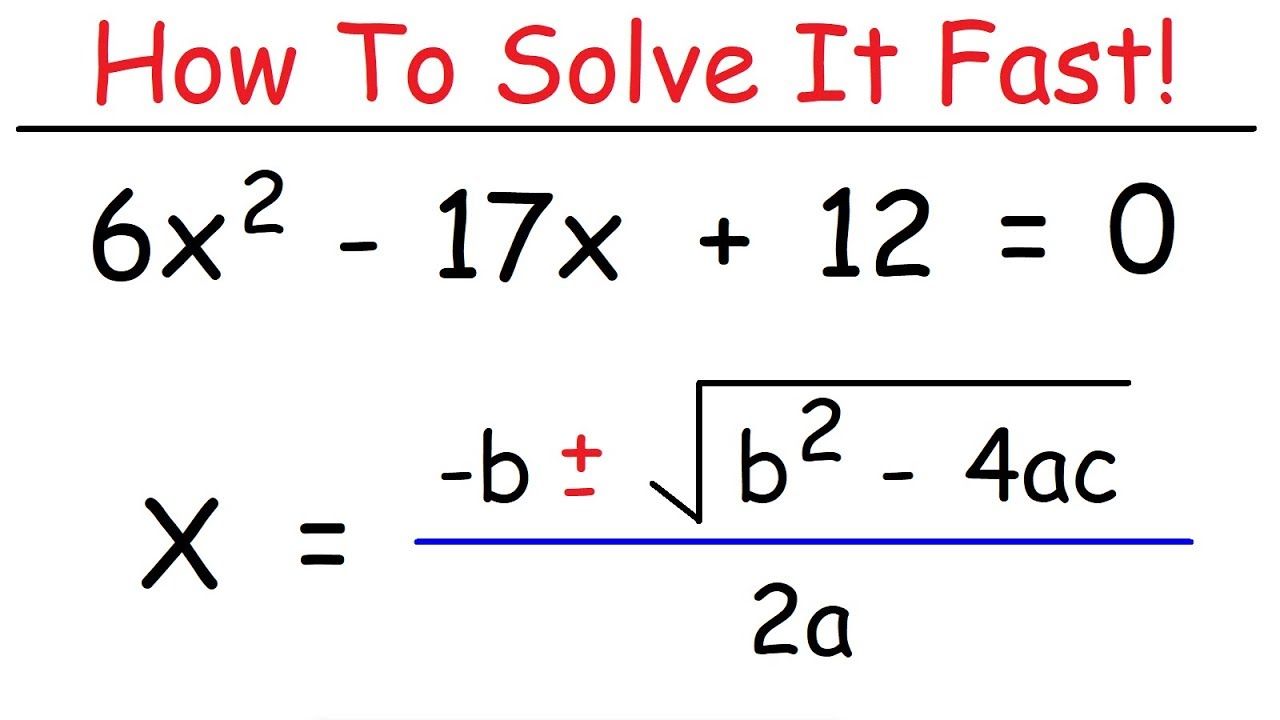
A root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself a certain number of times (the index of the root), gives the original number. For example, the square root of 16 is 4 because 4 multiplied by 4 equals 16. Traditionally, finding roots involved factoring the number into its prime factors and then grouping these factors in sets according to the index of the root. This method is straightforward for perfect squares, cubes, etc., but becomes impractical for larger numbers or when dealing with roots that are not perfect.
Algebraic Approach: The Quadratic Formula
For square roots, an algebraic approach can be employed using the quadratic formula. The quadratic formula, (x = \frac{-b \pm \sqrt{b^2 - 4ac}}{2a}), is primarily used to solve quadratic equations of the form (ax^2 + bx + c = 0). However, it can also be used to find the square root of a number by setting the equation to (x^2 - n = 0), where (n) is the number for which you want to find the square root. This method involves solving for (x), which gives the square root of (n).
Numerical Methods: The Babylonian Method
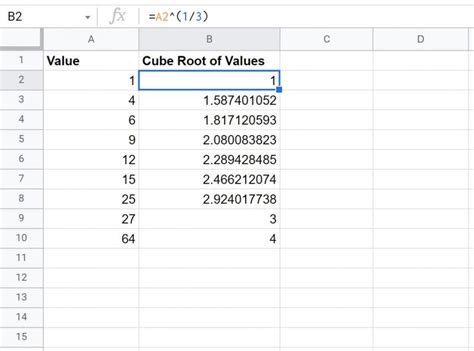
The Babylonian method is an ancient algorithm for computing the square root of a number. It starts with an initial guess, then repeatedly replaces that guess with the average of the guess and the number divided by the guess. Mathematically, if (x) is the guess for the square root of (n), the next guess is (\frac{1}{2}(x + \frac{n}{x})). This method converges quickly to the actual square root and can be extended to find other roots through modifications.
Calculus Approach: The Newton-Raphson Method
The Newton-Raphson method is a powerful numerical technique for finding roots of real-valued functions. It starts with an initial guess for the root and iteratively improves this guess using the formula (x_{n+1} = x_n - \frac{f(x_n)}{f’(x_n)}), where (x_n) is the current guess, (f(x_n)) is the value of the function at (x_n), and (f’(x_n)) is the derivative of the function at (x_n). This method can be used to find square roots, cube roots, and roots of any order by defining (f(x) = x^n - a), where (a) is the number for which you want to find the nth root.
| Method | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Traditional | Factoring into prime factors | Finding square root of 16 by factoring into 2*2*2*2 |
| Algebraic | Using the quadratic formula | Finding square root of 16 using x = \frac{-0 \pm \sqrt{0^2 - 4*1*(-16)}}{2*1} |
| Numerical (Babylonian) | Iterative averaging for square roots | Finding square root of 2 using the Babylonian method with an initial guess of 1 |
| Calculus (Newton-Raphson) | Iterative method for roots using derivatives | Finding square root of 2 using the Newton-Raphson method with f(x) = x^2 - 2 |

Conclusion and Future Directions
In conclusion, calculating roots is a fundamental operation in mathematics that can be approached through various methods, each with its strengths and applications. From traditional factoring to advanced numerical techniques like the Newton-Raphson method, the choice of method depends on the context and requirements of the calculation. As computational power increases and new algorithms are developed, the efficiency and accuracy of root calculations will continue to improve, enabling deeper explorations into mathematical sciences and their applications.
What is the most efficient method for calculating square roots?
+The efficiency of a method for calculating square roots can depend on the context, including the size of the numbers and the available computational resources. However, the Babylonian method and the Newton-Raphson method are generally considered efficient for numerical computations.
Can the Newton-Raphson method be used for finding roots of any order?
+Yes, the Newton-Raphson method can be adapted to find roots of any order by appropriately defining the function (f(x)). For example, to find the nth root of a number (a), one can use (f(x) = x^n - a).
What are the limitations of traditional methods for finding roots?
+Traditional methods, such as factoring, are limited by the size and complexity of the numbers involved. They can become impractical for large numbers or when dealing with roots that are not perfect.