The concept of spring constant is a fundamental aspect of physics and engineering, particularly in the study of elastic potential energy and the behavior of springs under various conditions. A spring constant, denoted by the symbol k, is a measure of the stiffness of a spring. It quantifies the amount of force required to stretch or compress a spring by a unit distance. The unit of measurement for spring constant is a critical factor in understanding and applying the principles of springs in real-world applications.
Understanding Spring Constant Units
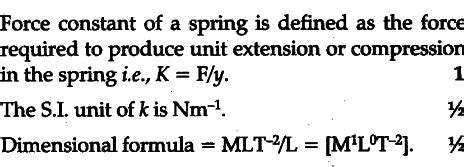
The spring constant unit is derived from Hooke’s Law, which states that the force (F) exerted by a spring is directly proportional to its displacement (x) from its equilibrium position. The formula is F = kx, where k is the spring constant. Given that force is measured in Newtons (N) and displacement in meters (m), the unit of spring constant can be deduced as Newtons per meter (N/m). This unit reflects the force required to stretch or compress a spring by one meter.
Conversion and Context
In some contexts, especially in the United States, spring constants might be expressed in pounds per inch (lb/in), reflecting a different system of measurement. To convert between these units, one must consider the conversion factors for both force (1 pound = 4.448 Newtons) and length (1 inch = 0.0254 meters). This conversion is essential for ensuring that calculations are accurate and consistent, regardless of the system of measurement being used.
| Unit System | Spring Constant Unit |
|---|---|
| SI (International System of Units) | Newtons per meter (N/m) |
| Imperial System | Pounds per inch (lb/in) |
| Other | Kilograms per meter (kg/m), though less common and typically not preferred for expressing spring constants |
Practical Applications and Considerations

In real-world applications, understanding the spring constant is vital for designing and predicting the behavior of mechanical systems that involve springs, such as suspension systems in vehicles, clocks and watches, and medical devices. The selection of springs with appropriate spring constants is critical to ensure that these systems function as intended, providing the necessary support, precision, or force.
Design and Calculation
When designing a system that incorporates springs, engineers must carefully calculate the required spring constant based on the expected load, available space, and desired performance characteristics. This calculation involves considering the material properties of the spring, its geometry, and how it will be used within the system. The use of incorrect spring constants can lead to system failures, inefficiencies, or undesirable behaviors.
Key Points
- The spring constant is a measure of a spring's stiffness, quantifying the force required to stretch or compress it by a unit distance.
- The standard unit for spring constant is Newtons per meter (N/m), derived from Hooke's Law.
- Conversions between different units, such as from N/m to pounds per inch (lb/in), are necessary for compatibility in diverse applications.
- Understanding and correctly applying spring constants is crucial for the design and functionality of mechanical systems involving springs.
- Material properties, geometry, and the intended use of a spring are key factors in determining its spring constant and selecting appropriate springs for applications.
Conclusion and Future Perspectives
In conclusion, the concept of spring constant and its unit of measurement are fundamental to the understanding and application of springs in physics and engineering. As technology advances and mechanical systems become more complex, the importance of accurately calculating and applying spring constants will only continue to grow. Whether in the development of more efficient vehicles, precise medical devices, or innovative consumer products, the principle of spring constant will remain a cornerstone of design and innovation.
What is the standard unit of measurement for spring constant?
+The standard unit of measurement for spring constant is Newtons per meter (N/m), as derived from Hooke’s Law, which relates the force exerted by a spring to its displacement.
Why is understanding spring constant important in engineering and physics?
+Understanding spring constant is crucial for designing and predicting the behavior of mechanical systems that involve springs, ensuring that these systems function as intended and providing the necessary support, precision, or force.
How do you convert spring constant units from N/m to lb/in?
+To convert spring constant units from N/m to lb/in, you must consider the conversion factors for both force (1 pound = 4.448 Newtons) and length (1 inch = 0.0254 meters), and apply these factors to the spring constant value in N/m to obtain the equivalent value in lb/in.