Sinus infections, also known as sinusitis, are a common health issue affecting millions of people worldwide. The condition occurs when the sinuses, which are air-filled cavities in the skull, become inflamed or infected. This can be caused by a variety of factors, including viral or bacterial infections, allergies, and environmental factors. In this article, we will delve into five essential facts about sinus infections, exploring their causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and prevention strategies.
Understanding Sinus Infections: Causes and Risk Factors
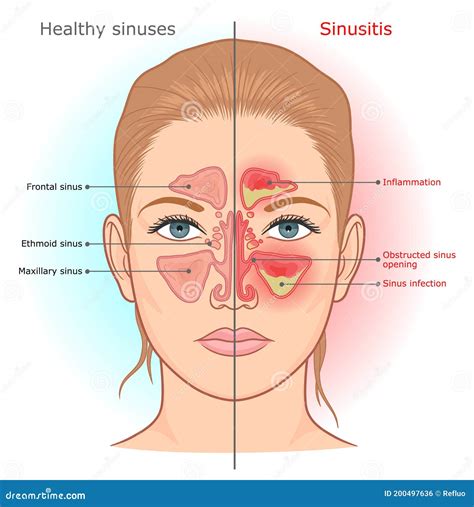
Sinus infections can be acute or chronic, with the former lasting less than four weeks and the latter persisting for more than 12 weeks. Acute sinusitis is often caused by a viral upper respiratory infection, such as the common cold, while chronic sinusitis may be linked to allergies, asthma, or anatomical issues like a deviated septum. Understanding the causes and risk factors is crucial for effective management and prevention. For instance, people with weakened immune systems, such as those with diabetes or HIV/AIDS, are more susceptible to sinus infections. Additionally, exposure to air pollutants, cigarette smoke, and certain chemicals can increase the risk of developing sinusitis.
Symptoms and Diagnosis of Sinus Infections
The symptoms of a sinus infection can vary depending on the severity and duration of the condition. Common symptoms include nasal congestion, yellow or green nasal discharge, facial pain or pressure, headache, and a reduced sense of smell. In some cases, fever, fatigue, and cough may also be present. Diagnosis typically involves a physical examination, medical history, and imaging tests like CT scans or X-rays to visualize the sinuses. A healthcare provider may also perform an endoscopy to directly observe the sinuses and collect tissue samples for further analysis. It’s worth noting that chronic sinusitis often requires more comprehensive diagnostic approaches to identify underlying causes and rule out other conditions.
| Symptom | Description |
|---|---|
| Nasal Congestion | Blockage of the nasal passages, making it difficult to breathe |
| Facial Pain | Pain or pressure in the cheeks, forehead, or nose |
| Nasal Discharge | Yellow or green discharge from the nose, which may be thick and pus-like |

Treatment and Management of Sinus Infections
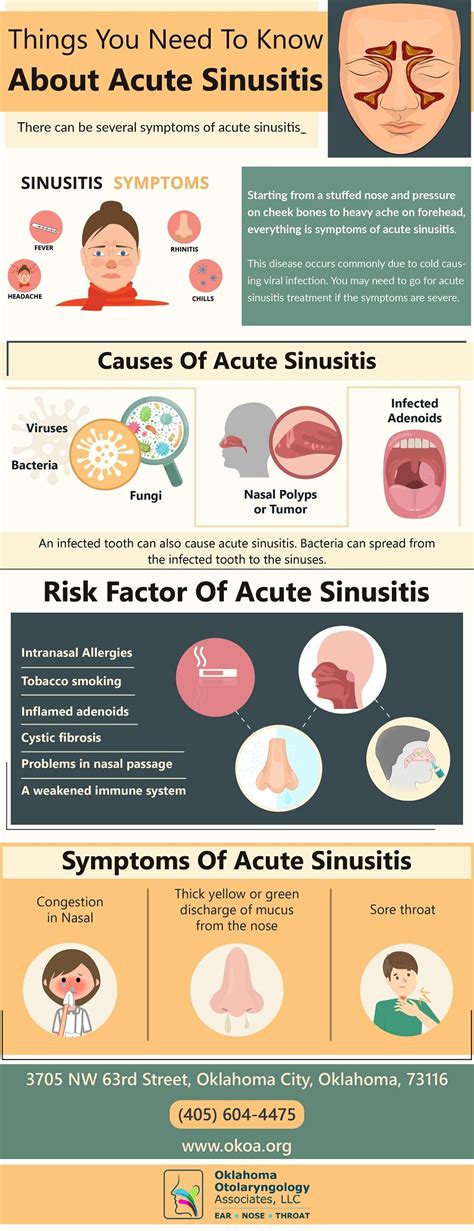
Treatment for sinus infections depends on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. For acute viral sinusitis, symptom relief and supportive care, such as over-the-counter pain medications, nasal decongestants, and saline nasal sprays, are often recommended. In cases of bacterial sinusitis, antibiotics may be prescribed. Chronic sinusitis may require more aggressive treatment, including long-term antibiotics, nasal corticosteroids, or surgery to correct anatomical issues or remove blockages. Additionally, lifestyle changes, such as quitting smoking, using a humidifier to moisten the air, and avoiding allergens, can help manage symptoms and prevent recurrence.
Prevention Strategies for Sinus Infections
Preventing sinus infections involves maintaining a healthy lifestyle and taking steps to reduce exposure to potential triggers. Practicing good hygiene, such as washing hands regularly, especially during cold and flu seasons, can help prevent the spread of viral infections. Avoiding close contact with people who have colds or other upper respiratory infections, getting enough sleep, and staying physically active can also boost the immune system. Furthermore, managing allergies through medication or immunotherapy and avoiding environmental irritants can reduce the risk of developing sinusitis.
Key Points
- Sinus infections can be acute or chronic, with different causes and treatment approaches.
- Understanding symptoms and seeking early medical attention is crucial for effective management and preventing complications.
- Treatment options vary from symptom relief and supportive care for viral infections to antibiotics for bacterial causes and surgical interventions for chronic conditions.
- Lifestyle modifications, including quitting smoking and avoiding allergens, play a significant role in managing chronic sinusitis and preventing recurrence.
- Preventive measures, such as maintaining good hygiene, practicing a healthy lifestyle, and managing allergies, can significantly reduce the risk of developing sinus infections.
In conclusion, sinus infections are complex conditions that require a comprehensive approach for effective management and prevention. By understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and prevention strategies, individuals can better navigate their healthcare journey and work towards achieving sinus health. Remember, early intervention and a proactive approach to health can make a significant difference in outcomes and quality of life.
What are the most common causes of sinus infections?
+The most common causes of sinus infections include viral upper respiratory infections, such as the common cold, bacterial infections, allergies, and environmental factors like air pollution and cigarette smoke.
How can I prevent sinus infections?
+Preventing sinus infections involves practicing good hygiene, managing allergies, avoiding environmental irritants, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and getting enough rest. Quitting smoking and avoiding close contact with people who have colds or other upper respiratory infections can also help.
What are the symptoms of chronic sinusitis?
+The symptoms of chronic sinusitis can include persistent nasal congestion, facial pain, headache, reduced sense of smell, and nasal discharge. These symptoms can vary in severity and may be accompanied by fever, fatigue, and cough in some cases.



