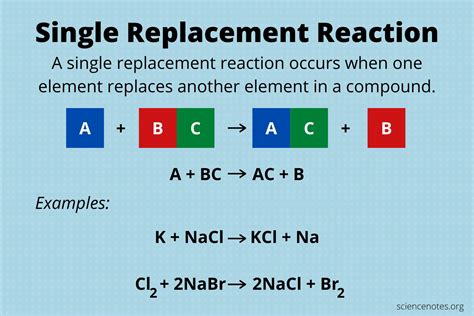
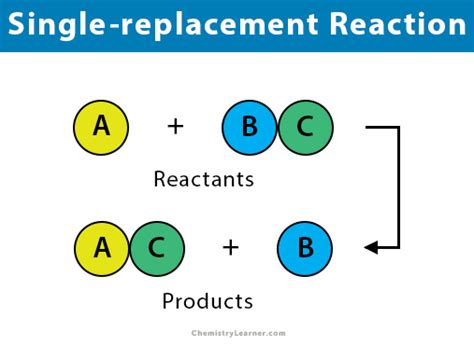
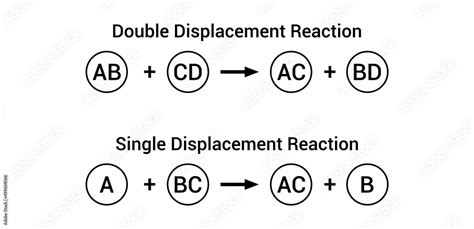
Single replacement reactions, also known as single displacement reactions, are a type of chemical reaction where one element replaces another element in a compound. This type of reaction is commonly observed in chemistry and is a fundamental concept in understanding the behavior of elements and their compounds. In a single replacement reaction, a more reactive element displaces a less reactive element from a compound, resulting in the formation of a new compound and the release of the displaced element.
Key Points
- Single replacement reactions involve the replacement of one element with another in a compound.
- These reactions are driven by the difference in reactivity between the elements involved.
- The more reactive element displaces the less reactive element from the compound.
- Single replacement reactions are commonly used in various industrial and laboratory applications.
- Understanding single replacement reactions is essential for predicting the behavior of elements and their compounds.
Characteristics of Single Replacement Reactions

Single replacement reactions have several characteristic features that distinguish them from other types of chemical reactions. One of the key characteristics is that they involve the replacement of one element with another in a compound. This means that the reactants and products of a single replacement reaction will have different chemical compositions. Another characteristic of single replacement reactions is that they are driven by the difference in reactivity between the elements involved. The more reactive element will displace the less reactive element from the compound, resulting in the formation of a new compound and the release of the displaced element.
Examples of Single Replacement Reactions
There are many examples of single replacement reactions that can be observed in everyday life and in industrial applications. One common example is the reaction between zinc and copper sulfate. In this reaction, zinc displaces copper from copper sulfate, resulting in the formation of zinc sulfate and the release of copper. This reaction can be represented by the equation: Zn + CuSO4 → ZnSO4 + Cu. Another example of a single replacement reaction is the reaction between magnesium and iron(III) oxide. In this reaction, magnesium displaces iron from iron(III) oxide, resulting in the formation of magnesium oxide and the release of iron. This reaction can be represented by the equation: 2Mg + Fe2O3 → 2MgO + 2Fe.
| Reaction | Equation |
|---|---|
| Zinc and copper sulfate | Zn + CuSO4 → ZnSO4 + Cu |
| Magnesium and iron(III) oxide | 2Mg + Fe2O3 → 2MgO + 2Fe |
| Sodium and water | 2Na + 2H2O → 2NaOH + H2 |
| Calcium and hydrochloric acid | Ca + 2HCl → CaCl2 + H2 |
Applications of Single Replacement Reactions
Single replacement reactions have many practical applications in various fields, including industry, medicine, and environmental science. One of the most significant applications of single replacement reactions is in the production of metals. Many metals, such as copper, zinc, and iron, are produced through single replacement reactions. For example, copper is produced through the reaction between copper ore and silicon dioxide, while zinc is produced through the reaction between zinc ore and carbon. Single replacement reactions are also used in the production of other chemicals, such as sodium hydroxide and calcium chloride.
Industrial Applications
Single replacement reactions are widely used in various industrial applications, including the production of metals, chemicals, and fuels. One of the most significant industrial applications of single replacement reactions is in the production of steel. Steel is produced through the reaction between iron ore and carbon, which involves a series of single replacement reactions. Another important industrial application of single replacement reactions is in the production of fertilizers, such as ammonia and nitric acid. These fertilizers are produced through single replacement reactions involving nitrogen and hydrogen.
Single replacement reactions are also used in the production of fuels, such as hydrogen and methane. Hydrogen is produced through the reaction between water and a metal, such as zinc or magnesium, while methane is produced through the reaction between carbon dioxide and hydrogen. These reactions involve single replacement reactions and are important for the production of clean energy.
What is a single replacement reaction?
+A single replacement reaction is a type of chemical reaction where one element replaces another element in a compound.
What are some examples of single replacement reactions?
+Some examples of single replacement reactions include the reaction between zinc and copper sulfate, the reaction between magnesium and iron(III) oxide, and the reaction between sodium and water.
What are the applications of single replacement reactions?
+Single replacement reactions have many practical applications in various fields, including industry, medicine, and environmental science. They are used in the production of metals, chemicals, and fuels, and are important for the production of clean energy.
In conclusion, single replacement reactions are an important concept in chemistry, with many practical applications in various fields. By understanding single replacement reactions, we can gain insights into the behavior of elements and their compounds, and develop new technologies and industrial processes. The examples of single replacement reactions discussed in this article demonstrate the significance of this concept in chemistry and its importance in various industrial and laboratory applications.