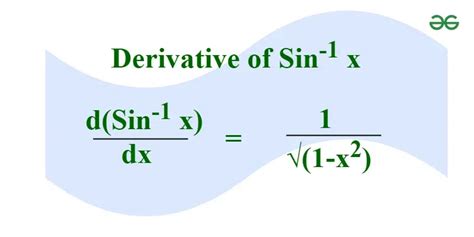The concept of the sine inverse derivative is a fundamental aspect of calculus, playing a crucial role in understanding various mathematical and real-world phenomena. The sine inverse function, denoted as arcsin(x) or sin^-1(x), is the inverse of the sine function and returns the angle whose sine is a given number. Understanding its derivative is essential for advanced calculus and applications in physics, engineering, and other fields. Here, we will delve into five tips for working with the sine inverse derivative, providing a comprehensive overview of its application, derivation, and practical implications.
Key Points
- The derivative of arcsin(x) is 1 / sqrt(1 - x^2), which is crucial for understanding rates of change in applications involving inverse sine functions.
- Derivation of the sine inverse derivative involves using the formula for the derivative of inverse functions, highlighting the importance of foundational calculus principles.
- Applications of the sine inverse derivative are found in optimization problems, particularly where the goal is to maximize or minimize a function involving the arcsin(x) term.
- Graphical analysis of the arcsin(x) function and its derivative provides insight into the behavior of these functions, including domains, ranges, and critical points.
- Practical problems involving the sine inverse derivative often require numerical methods or approximation techniques, especially when dealing with complex equations or real-world data.
Naturally Worded Primary Topic Section with Semantic Relevance
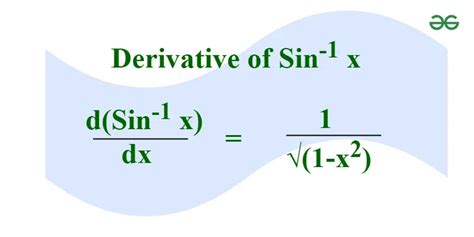
The sine inverse derivative, given by the formula d(arcsin(x))/dx = 1 / sqrt(1 - x^2), is a critical component in various mathematical derivations and applications. To derive this formula, one can start with the definition of the arcsin(x) function and apply the formula for the derivative of an inverse function, which involves the reciprocal of the derivative of the original function evaluated at the inverse function’s input. This process underscores the importance of understanding the relationships between functions and their inverses in calculus.
Derivation and Application of the Sine Inverse Derivative
The derivation of the sine inverse derivative begins with the sine function, y = sin(x), and its inverse, x = sin(y). By differentiating both sides implicitly with respect to x and solving for dy/dx, one can obtain the derivative of the arcsin(x) function. This derivative, 1 / sqrt(1 - x^2), indicates how the angle whose sine is x changes as x changes, within the domain -1 ≤ x ≤ 1. Applications of this derivative are seen in physics, where it can be used to model the motion of objects under certain constraints, and in engineering, particularly in the design of systems involving rotational motion.
| Mathematical Operation | Formula | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Derivative of arcsin(x) | 1 / sqrt(1 - x^2) | Rate of change of the angle whose sine is x |
| Domain of arcsin(x) | -1 ≤ x ≤ 1 | Range of valid inputs for the arcsin(x) function |
| Range of arcsin(x) | -π/2 ≤ arcsin(x) ≤ π/2 | Range of output values for the arcsin(x) function |
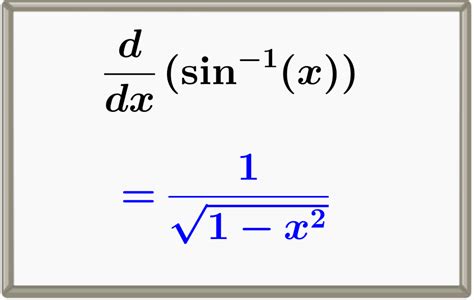
Practical Applications and Numerical Considerations
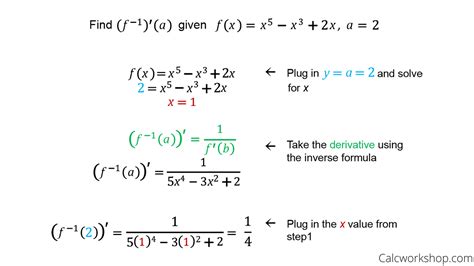
In practical problems, the sine inverse derivative may be used in conjunction with other calculus techniques, such as integration, to solve equations involving the arcsin(x) function. For instance, in optimizing a system’s design that involves rotational components, understanding how changes in the sine of an angle affect the overall system can be crucial. Numerical methods, such as the Newton-Raphson method, may be employed to find approximate solutions to equations involving the sine inverse derivative, especially when dealing with complex systems or experimental data.
Numerical Methods for Approximation
Numerical approximation techniques are invaluable when dealing with equations that involve the sine inverse derivative and cannot be solved analytically. These methods, including iterative techniques and polynomial approximations, allow for the estimation of solutions to a high degree of accuracy. In computational tools and programming languages, built-in functions for calculating the arcsin(x) and its derivative can facilitate the solution of complex problems involving these functions, making them accessible to a broader range of applications and users.
What is the primary application of the sine inverse derivative in calculus?
+The primary application of the sine inverse derivative is in solving optimization problems and modeling phenomena involving rotational motion or trigonometric relationships, particularly where the rate of change of an angle is critical.
How is the derivative of arcsin(x) derived?
+The derivative of arcsin(x) is derived by starting with the definition of the arcsin(x) function, differentiating implicitly with respect to x, and solving for dy/dx, which yields 1 / sqrt(1 - x^2).
What numerical methods can be used to approximate solutions involving the sine inverse derivative?
+Numerical methods such as the Newton-Raphson method, iterative techniques, and polynomial approximations can be used to approximate solutions to equations involving the sine inverse derivative, especially when analytical solutions are not feasible.
In conclusion, the sine inverse derivative is a powerful tool in calculus with a wide range of applications, from solving optimization problems to modeling complex systems. Its derivation and application underscore the importance of understanding the relationships between functions and their inverses, as well as the role of calculus in analyzing and solving problems involving rates of change and accumulation. By mastering the sine inverse derivative and its applications, one can gain a deeper insight into the mathematical principles that govern various phenomena and develop a more nuanced understanding of the interconnectedness of mathematical concepts.