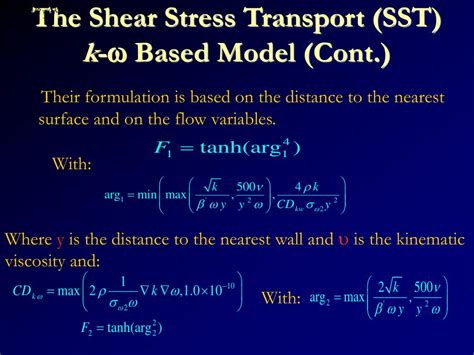
The concept of shear stress transport (SST) is a critical aspect of fluid dynamics, particularly in the context of turbulent flows. SST is a numerical method used to model the behavior of fluids under various conditions, including those with high levels of turbulence. The SST model is an extension of the k-ω (k-omega) model, which is a two-equation turbulence model that solves for the turbulent kinetic energy (k) and the specific dissipation rate (ω). The SST model improves upon the k-ω model by incorporating a blending function that combines the k-ω and k-ε (k-epsilon) models, allowing for a more accurate prediction of the flow behavior in different regions of the flow domain.
The SST model is widely used in computational fluid dynamics (CFD) to simulate complex flows, such as those encountered in aerospace, automotive, and chemical engineering applications. The model's ability to accurately predict the behavior of turbulent flows makes it an essential tool for designing and optimizing systems that involve fluid flow, such as pipes, channels, and turbomachinery. In addition to its applications in engineering, the SST model is also used in research to study the fundamental physics of turbulent flows and to develop new turbulence models.
Key Points
- The shear stress transport (SST) model is a numerical method used to model turbulent flows.
- The SST model is an extension of the k-ω model, which solves for the turbulent kinetic energy (k) and the specific dissipation rate (ω).
- The SST model combines the k-ω and k-ε models using a blending function, allowing for a more accurate prediction of the flow behavior.
- The SST model is widely used in computational fluid dynamics (CFD) to simulate complex flows in various engineering applications.
- The model's ability to accurately predict the behavior of turbulent flows makes it an essential tool for designing and optimizing systems that involve fluid flow.
Numerical Implementation of the SST Model
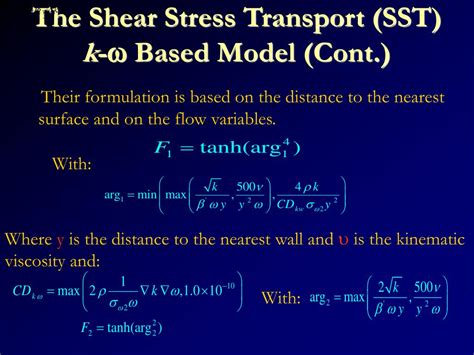
The numerical implementation of the SST model involves solving the governing equations of fluid motion, which include the continuity equation, the momentum equation, and the energy equation. The SST model is typically implemented using a finite volume method, which discretizes the flow domain into a set of control volumes and solves the governing equations using a numerical scheme. The numerical scheme used to solve the SST model can be either explicit or implicit, depending on the specific application and the desired level of accuracy.
The SST model requires the specification of several model parameters, including the turbulent kinetic energy (k), the specific dissipation rate (ω), and the blending function. The blending function is used to combine the k-ω and k-ε models, and its specification is critical to the accuracy of the SST model. The model parameters are typically specified using a set of boundary conditions, which define the flow behavior at the inlet, outlet, and walls of the flow domain.
Boundary Conditions for the SST Model
The boundary conditions for the SST model are critical to the accuracy of the simulation. The boundary conditions specify the flow behavior at the inlet, outlet, and walls of the flow domain, and they are used to define the model parameters. The boundary conditions can be either Dirichlet or Neumann, depending on the specific application and the desired level of accuracy. Dirichlet boundary conditions specify the value of the variable at the boundary, while Neumann boundary conditions specify the gradient of the variable at the boundary.
The SST model can be used to simulate a wide range of flows, including laminar and turbulent flows, and flows with complex geometries. The model's ability to accurately predict the behavior of turbulent flows makes it an essential tool for designing and optimizing systems that involve fluid flow. However, the SST model is not without its limitations, and it requires careful specification of the model parameters and boundary conditions to ensure accurate results.
| Model Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Turbulent kinetic energy (k) | 0.01 m^2/s^2 |
| Specific dissipation rate (ω) | 0.1 s^-1 |
| Blending function | 0.5 |
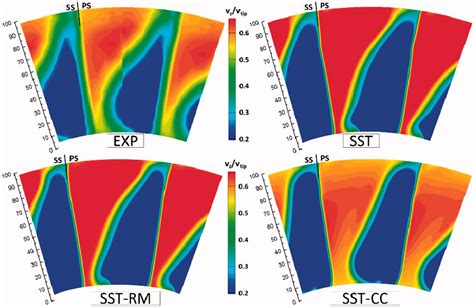
Applications of the SST Model
The SST model has a wide range of applications in engineering and research. The model is used to simulate complex flows in various fields, including aerospace, automotive, and chemical engineering. The SST model is also used to study the fundamental physics of turbulent flows and to develop new turbulence models. Some of the specific applications of the SST model include:
The simulation of turbulent flows in pipes and channels, which is critical to the design of piping systems and heat exchangers. The SST model is used to predict the behavior of the flow, including the velocity profile, pressure drop, and heat transfer coefficient. The model's ability to accurately predict the behavior of turbulent flows makes it an essential tool for designing and optimizing piping systems and heat exchangers.
The simulation of turbulent flows in turbomachinery, such as turbines and compressors. The SST model is used to predict the behavior of the flow, including the velocity profile, pressure drop, and efficiency. The model's ability to accurately predict the behavior of turbulent flows makes it an essential tool for designing and optimizing turbomachinery.
Limitations of the SST Model
The SST model is not without its limitations. The model is based on a set of assumptions and simplifications, which can limit its accuracy in certain situations. Some of the limitations of the SST model include:
The model's inability to accurately predict the behavior of flows with complex geometries, such as flows with multiple inlets and outlets. The model's assumption of a simple geometry can limit its accuracy in these situations.
The model's inability to accurately predict the behavior of flows with high levels of turbulence, such as flows with high Reynolds numbers. The model's assumption of a simple turbulence model can limit its accuracy in these situations.
Despite these limitations, the SST model is a powerful tool for simulating complex flows. The model's ability to accurately predict the behavior of turbulent flows makes it an essential tool for designing and optimizing systems that involve fluid flow.
What is the SST model used for?
+The SST model is used to simulate complex flows in various fields, including aerospace, automotive, and chemical engineering. The model is used to predict the behavior of the flow, including the velocity profile, pressure drop, and heat transfer coefficient.
What are the limitations of the SST model?
+The SST model has several limitations, including its inability to accurately predict the behavior of flows with complex geometries and high levels of turbulence. The model’s assumption of a simple geometry and turbulence model can limit its accuracy in these situations.
How is the SST model implemented?
+The SST model is typically implemented using a finite volume method, which discretizes the flow domain into a set of control volumes and solves the governing equations using a numerical scheme. The model parameters are specified using a set of boundary conditions, which define the flow behavior at the inlet, outlet, and walls of the flow domain.