Severe mental illness (SMI) is a term used to describe a range of mental health conditions that significantly impact an individual's daily life, social relationships, and overall well-being. These conditions, which include schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and severe depression, affect millions of people worldwide, causing substantial distress, impairment, and disability. The complexities of SMI require a comprehensive understanding, encompassing not only the clinical manifestations but also the social, economic, and cultural factors that influence its development, treatment, and management.
The prevalence of SMI varies globally, with estimates suggesting that approximately 1 in 4 people will experience a mental health disorder each year. However, the lifetime prevalence of SMI is significantly lower, affecting around 1 in 50 individuals. Despite its relatively lower prevalence compared to other mental health conditions, SMI accounts for a disproportionate share of the global mental health burden, primarily due to its chronic nature, severity of symptoms, and the significant impact on quality of life. The economic burden of SMI is also substantial, with estimates indicating that mental health disorders cost the global economy trillions of dollars annually in lost productivity, healthcare expenditures, and social services.
Key Points
- Severe mental illness (SMI) includes conditions like schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and severe depression, significantly impacting daily life and well-being.
- The global prevalence of SMI is estimated to affect approximately 1 in 50 individuals, with a substantial economic burden on the healthcare system and economy.
- Early intervention, comprehensive treatment, and social support are critical in managing SMI and improving outcomes.
- Cultural, social, and economic factors play a significant role in the development, treatment, and management of SMI.
- Stigma surrounding mental health remains a barrier to seeking help, underscoring the need for public awareness campaigns and education.
Understanding Severe Mental Illness
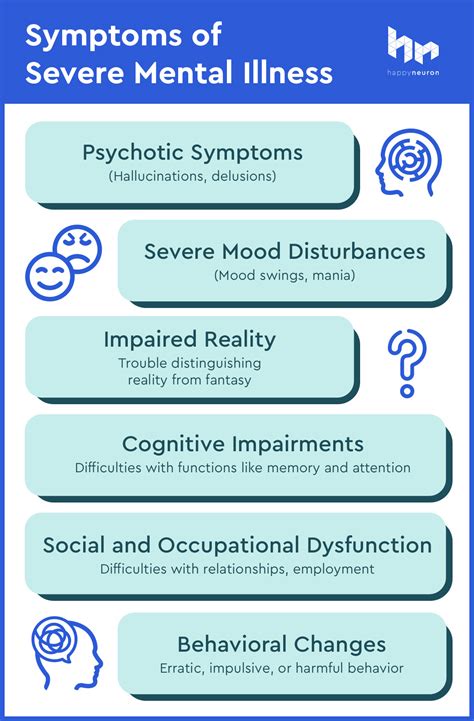
SMI is characterized by severe symptoms that interfere with an individual’s ability to function in daily life. These symptoms can include hallucinations, delusions, disorganized thinking, and extreme mood swings. The diagnosis of SMI is based on a comprehensive clinical evaluation, incorporating detailed patient history, physical examination, and psychological assessments. Diagnostic criteria, as outlined in classification systems like the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5) or the International Classification of Diseases (ICD-11), guide clinicians in making accurate diagnoses.
Clinical Manifestations and Diagnosis
The clinical presentation of SMI can vary significantly between individuals, with symptoms often fluctuating in severity over time. For instance, schizophrenia is typically characterized by a combination of positive symptoms (such as hallucinations and delusions) and negative symptoms (such as social withdrawal and lack of motivation). Bipolar disorder, on the other hand, is marked by extreme mood swings, ranging from manic highs to depressive lows. Severe depression is distinguished by persistent feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and a loss of interest in activities once enjoyed. Accurate diagnosis is crucial, as it informs treatment decisions and predicts long-term outcomes.
| Condition | Key Symptoms | Treatment Approaches |
|---|---|---|
| Schizophrenia | Hallucinations, delusions, disorganized thinking | Antipsychotic medications, cognitive-behavioral therapy |
| Bipolar Disorder | Extreme mood swings, manic and depressive episodes | Mood stabilizers, antipsychotics, psychotherapy |
| Severe Depression | Persistent sadness, hopelessness, loss of interest in activities | Antidepressants, psychotherapy, lifestyle modifications |
Treatment and Management of Severe Mental Illness

The treatment of SMI is tailored to the individual’s specific needs, taking into account the nature and severity of their symptoms, as well as their personal preferences and circumstances. Pharmacological interventions, such as antipsychotics for schizophrenia and mood stabilizers for bipolar disorder, are often the first line of treatment. However, psychological therapies, including cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and family therapy, play a crucial role in helping individuals cope with their symptoms, manage their condition, and improve their quality of life.
Psychological Therapies and Social Support
Psychological therapies aim to address the cognitive, emotional, and behavioral aspects of SMI. CBT, for example, helps individuals identify and challenge negative thought patterns and behaviors that contribute to their symptoms. Family therapy is also beneficial, as it educates family members about the condition, improves communication, and enhances support networks. Social support, whether from family, friends, or support groups, is vital in helping individuals with SMI cope with the challenges of their condition and maintain a sense of connection and belonging.
The importance of addressing social determinants of health, such as housing, employment, and access to healthcare, cannot be overstated. Individuals with SMI often face significant barriers in these areas, which can exacerbate their symptoms and worsen their overall well-being. Therefore, comprehensive care models that integrate mental health services with social services are essential in providing holistic support and improving outcomes.
What are the primary symptoms of severe mental illness?
+The primary symptoms of SMI vary by condition but can include hallucinations, delusions, disorganized thinking, extreme mood swings, and persistent feelings of sadness or hopelessness.
How is severe mental illness diagnosed?
+Diagnosis of SMI is based on a comprehensive clinical evaluation, incorporating patient history, physical examination, psychological assessments, and diagnostic criteria from classification systems like the DSM-5 or ICD-11.
What are the treatment options for severe mental illness?
+Treatment options for SMI include pharmacological interventions, psychological therapies like CBT and family therapy, and social support. The approach is tailored to the individual's specific needs and circumstances.
In conclusion, severe mental illness presents a complex challenge that requires a comprehensive and multifaceted approach to diagnosis, treatment, and management. By understanding the clinical manifestations, incorporating evidence-based treatments, and addressing the social determinants of health, we can improve outcomes for individuals with SMI and work towards reducing the stigma and barriers that prevent many from seeking the help they need.