The Spanish language is known for its complex grammar rules, and one of the most challenging aspects for learners is the conjugation of verbs. The ser preterite conjugation is a fundamental concept in Spanish grammar, and mastering it is essential for effective communication. In this article, we will delve into the world of ser preterite conjugation, exploring its rules, exceptions, and practical applications.
Understanding the Ser Preterite Conjugation

The verb “ser” is one of the most commonly used verbs in Spanish, and it has several conjugations, including the preterite tense. The preterite tense is used to describe completed actions in the past, and it is essential to understand its conjugation to communicate effectively. The ser preterite conjugation is used to describe permanent or inherent characteristics of a person or thing in the past, such as their nationality, occupation, or physical appearance.
Conjugation Rules
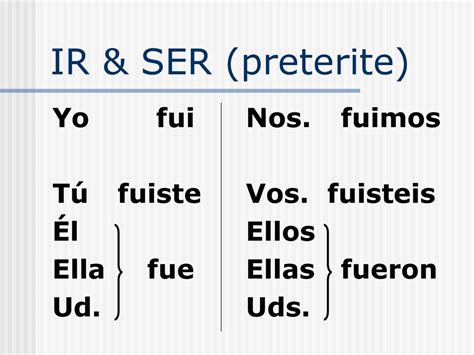
The ser preterite conjugation follows a specific pattern, which is similar to the present tense conjugation. The verb “ser” is conjugated as follows:
| Subject | Conjugation |
|---|---|
| Yo | Fui |
| Tú | Fuiste |
| Él/Ella/Usted | Fue |
| Nosotros/Nosotras | Fuimos |
| Vosotros/Vosotras | Fuisteis |
| Ellos/Ellas/Ustedes | Fueron |

As you can see, the conjugation pattern is relatively simple, and it is essential to practice it to become proficient. It's also important to note that the ser preterite conjugation is used in combination with other verbs to form the passive voice, which is a crucial aspect of Spanish grammar.
Key Points
- The ser preterite conjugation is used to describe permanent or inherent characteristics of a person or thing in the past.
- The conjugation pattern is similar to the present tense conjugation.
- The verb "ser" is conjugated as fui, fuiste, fue, fuimos, fuisteis, and fueron.
- The ser preterite conjugation is used in combination with other verbs to form the passive voice.
- Practice is essential to become proficient in the ser preterite conjugation.
Practical Applications
The ser preterite conjugation has several practical applications in everyday conversation. For example, you can use it to describe someone’s nationality, occupation, or physical appearance in the past. You can also use it to describe the characteristics of a place or thing in the past.
For instance, you can say "Yo fui estudiante en la Universidad de Madrid" (I was a student at the University of Madrid), or "Ella fue médica en un hospital de Nueva York" (She was a doctor at a hospital in New York). You can also use the ser preterite conjugation to describe the characteristics of a place or thing, such as "La casa fue construida en el siglo XIX" (The house was built in the 19th century).
Exceptions and Irregularities
While the ser preterite conjugation follows a specific pattern, there are some exceptions and irregularities that you need to be aware of. For example, the verb “ser” has several irregularities in the preterite tense, such as the use of the auxiliary verb “haber” to form the passive voice.
Additionally, some verbs have irregular conjugations in the preterite tense, such as the verb "ir" (to go), which is conjugated as fui, fuiste, fue, fuimos, fuisteis, and fueron. It's essential to practice these irregularities to become proficient in the ser preterite conjugation.
In conclusion, the ser preterite conjugation is a fundamental concept in Spanish grammar, and mastering it is essential for effective communication. By understanding the conjugation rules, exceptions, and practical applications, you can become proficient in Spanish and improve your language skills.
What is the ser preterite conjugation used for?
+The ser preterite conjugation is used to describe permanent or inherent characteristics of a person or thing in the past.
What are the conjugation rules for the ser preterite conjugation?
+The verb "ser" is conjugated as fui, fuiste, fue, fuimos, fuisteis, and fueron.
Are there any exceptions or irregularities in the ser preterite conjugation?
+Yes, there are some exceptions and irregularities in the ser preterite conjugation, such as the use of the auxiliary verb "haber" to form the passive voice.
By following these guidelines and practicing the ser preterite conjugation, you can improve your Spanish language skills and become more confident in your ability to communicate effectively. ¡Buena suerte!
Meta description suggestion: “Learn the ser preterite conjugation in Spanish with our comprehensive guide, including conjugation rules, exceptions, and practical applications.” (149 characters)