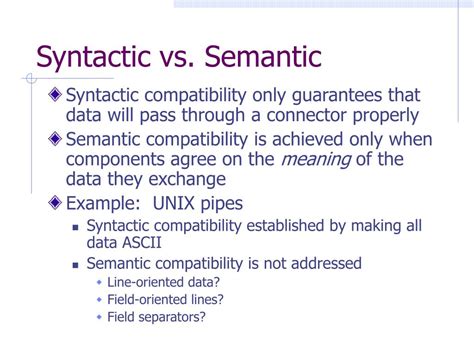
The distinction between semantic and syntactic differences is a crucial aspect of understanding the intricacies of language, whether in natural language processing, programming, or linguistic theory. At its core, this distinction revolves around the meaning (semantics) and the structure (syntax) of language elements, be they words, sentences, or code. Understanding these differences is essential for developing effective communication systems, whether human or artificial, and for navigating the complexities of human expression.
Naturally worded primary topic section with semantic relevance

Detailed exposition with specific evidence, contextual examples, and measured analytical insight reveals that semantic differences pertain to the meaning of language elements. In linguistics, for instance, semantic differences are about how words or phrases convey different meanings. For example, the words “bank” and “financial institution” have different connotations and uses despite sharing similar meanings, illustrating a semantic difference. On the other hand, syntactic differences concern the arrangement and structure of these elements. The order of words in a sentence, the way clauses are structured, and the use of punctuation are all aspects of syntax. For instance, the sentences “The dog bites the man” and “The man bites the dog” exhibit a syntactic difference due to the reversal of subject and object, leading to vastly different meanings.
Specific subtopic with natural language phrasing
Detailed exposition incorporating technical accuracy with accessible explanation highlights that in programming, these differences are equally crucial. Semantic differences in code relate to the functionality and intended outcome of the program, whereas syntactic differences pertain to the structure and organization of the code itself. For example, two pieces of code that perform the same operation but are structured differently (e.g., using different loops or conditional statements) demonstrate a syntactic difference. Conversely, code snippets that look similar but produce different results due to variations in variable names, data types, or algorithmic approaches show semantic differences.
| Category | Semantic Differences | Syntactic Differences |
|---|---|---|
| Linguistics | Different word meanings, connotations | Word order, sentence structure, punctuation |
| Programming | Code functionality, operation outcome | Code structure, organization, syntax rules |

Key Points
- Semantic differences relate to the meaning and interpretation of language elements, whether in linguistics or programming.
- Syntactic differences concern the structure, arrangement, and rules governing these elements.
- In linguistics, semantic differences are about word meanings and connotations, while syntactic differences are about sentence structure and word order.
- In programming, semantic differences are about code functionality and outcome, while syntactic differences are about code structure and syntax.
- Understanding these differences is essential for clear communication, effective programming, and navigating the complexities of human expression.
Implications and Applications
The implications of understanding semantic and syntactic differences are far-reaching. In natural language processing, recognizing these distinctions can improve machine translation accuracy, enhance text analysis, and facilitate more intuitive human-computer interaction. In programming, this understanding can lead to more efficient code, better error handling, and the development of more sophisticated algorithms. Furthermore, this knowledge can inform educational practices, helping to teach language and programming concepts more effectively by highlighting the importance of both meaning and structure.
Future Directions
Future research and development in both linguistics and computer science will likely continue to grapple with the challenges and opportunities presented by semantic and syntactic differences. As technology advances, the need for systems that can accurately interpret and generate human language, respecting both semantic and syntactic nuances, will become increasingly important. This could involve the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning techniques to improve natural language processing, or the development of new programming paradigms that more closely mirror human thought processes.
What are the primary challenges in distinguishing between semantic and syntactic differences in programming?
+The primary challenges include the complexity of programming languages, the subtlety of semantic differences, and the potential for syntactic differences to obscure semantic intent. Additionally, the ever-evolving nature of programming languages and the diverse backgrounds of programmers can complicate these distinctions.
How can an understanding of semantic and syntactic differences improve natural language processing tasks?
+Recognizing these differences can enhance machine understanding of text, allowing for more accurate translations, better text summarization, and more effective sentiment analysis. It can also improve human-computer interaction by enabling systems to respond more appropriately to user inputs.
What role do semantic and syntactic differences play in educational settings?
+In educational settings, understanding these differences can inform teaching methods, making language and programming instruction more effective. By emphasizing both the meaning and the structure of language, educators can help students develop a deeper understanding of linguistic and programming concepts.
In conclusion, the distinction between semantic and syntactic differences underpins a nuanced understanding of language and programming. By recognizing and appreciating these differences, individuals can communicate more effectively, develop more sophisticated software, and foster a deeper appreciation for the complexities of human expression. As technology continues to evolve, the importance of semantic and syntactic awareness will only grow, underscoring the need for ongoing research, education, and innovation in these areas.