Rope, a fundamental tool with a rich history, has been a cornerstone of various industries and activities for centuries. From sailing and climbing to rescue operations and even decorative purposes, the versatility of rope is undeniable. The evolution of rope, from natural fibers like hemp and cotton to synthetic materials such as nylon and polyester, has significantly expanded its applications and durability. This article will delve into five distinct ways rope is utilized, highlighting its importance and the innovation surrounding its use.
Key Points
- Historical significance and evolution of rope
- Industrial applications, including construction and manufacturing
- Sports and recreational uses, such as climbing and sailing
- Decorative and aesthetic applications in interior design
- Innovative materials and technologies enhancing rope durability and functionality
Industrial and Manufacturing Applications
Rope plays a crucial role in various industrial settings, including construction, manufacturing, and logistics. Its strength, durability, and versatility make it an essential tool for lifting, pulling, and securing heavy loads. The construction industry, for example, relies heavily on ropes for crane operations, scaffolding, and safety netting. In manufacturing, ropes are used in pulley systems, conveyor belts, and as a component in the production of other goods. The development of synthetic fibers has enhanced the performance and lifespan of industrial ropes, making them more resistant to abrasion, chemicals, and extreme temperatures.
Advancements in Materials and Technologies
The advancement in materials science has led to the development of high-performance ropes with improved strength-to-weight ratios, UV resistance, and reduced stretch. These innovations have expanded the potential applications of rope, allowing for its use in more demanding environments and conditions. For instance, aramid fibers like Kevlar offer exceptional strength and heat resistance, making them ideal for high-risk applications such as firefighting and rescue operations. Similarly, the integration of smart technologies, such as sensors and monitoring systems, into rope design can provide real-time feedback on tension, wear, and potential failures, enhancing safety and efficiency.
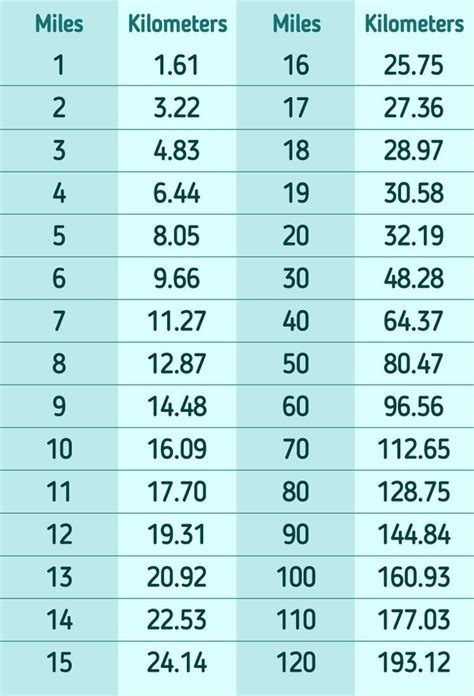
| Material Type | Strength (MPa) | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Natural Fibers (Hemp, Cotton) | Up to 400 | Traditional sailing, decorative |
| Nylon | Up to 900 | Industrial, climbing, sailing |
| Polyester | Up to 1100 | Marine, industrial, heavy-duty applications |
| Aramid (Kevlar) | Up to 3600 | High-performance, rescue, firefighting |

Sports and Recreational Activities

Rope is an integral part of many sports and recreational activities, offering a challenging and engaging way to stay active. Rock climbing, for example, relies on ropes for safety and ascent, with different types of ropes (such as dynamic and static ropes) suited to various climbing styles and terrains. Sailing also utilizes ropes extensively, from the rigging that supports the mast to the sheets that control the sails. The development of lightweight, high-strength ropes has improved performance in these sports, enabling athletes to push their limits while ensuring safety.
Decorative and Aesthetic Uses
Beyond its functional applications, rope is also used for decorative purposes, adding a rustic or nautical touch to interior and exterior designs. In home decor, ropes can be used as unique lighting fixtures, wall hangings, or even as a material for crafting furniture. The versatility of rope in design is vast, with its texture, color, and pattern offering a wide range of creative possibilities. From macrame wall hangings to rope-wrapped furniture, the aesthetic appeal of rope continues to inspire designers and homeowners alike.
Innovative Applications and Future Directions
As technology advances and new materials are developed, the potential applications of rope continue to expand. Innovations such as fiber-optic ropes, which can transmit data through light, and ropes integrated with sensors for real-time condition monitoring, are opening new avenues for rope use in telecommunications, smart infrastructure, and more. The challenge of sustainability is also driving innovation, with researchers exploring the use of recycled materials and biodegradable fibers in rope production. As the world seeks more efficient, durable, and environmentally friendly solutions, the humble rope is poised to play an increasingly significant role.
What are the primary materials used in rope production today?
+The primary materials include natural fibers like hemp and cotton, and synthetic fibers such as nylon, polyester, and aramid (Kevlar), each offering unique properties suited to different applications.
How has the development of synthetic fibers impacted the use of rope in industrial settings?
+Synthetic fibers have significantly enhanced the durability, strength, and resistance of ropes to environmental factors, making them more reliable and efficient for industrial use.
What role does rope play in sports and recreational activities?
+Rope is crucial for safety and performance in many sports, such as rock climbing and sailing, providing a means of ascent, descent, and control.
In conclusion, the significance of rope extends far beyond its basic function as a tool for lifting, pulling, and securing. Its evolution, applications, and the innovations surrounding its use have made it an indispensable component of various industries, sports, and even decorative arts. As research and development continue to push the boundaries of what rope can do, its importance in our daily lives and its potential to address future challenges will only continue to grow.