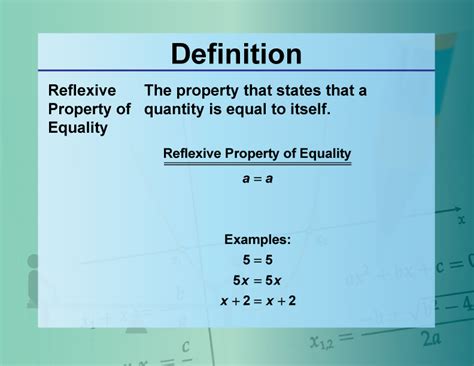
The reflexive property of equality is a fundamental concept in mathematics that states that every element is equal to itself. This property may seem trivial at first glance, but it serves as a cornerstone for various mathematical operations and proofs. In this article, we will delve into the details of the reflexive property, its significance, and its applications in different areas of mathematics.
The reflexive property of equality is often denoted as $a = a$, where $a$ can be any element from a set. This property asserts that every element is identical to itself, which may seem like a straightforward and obvious statement. However, its implications and applications are far-reaching and have significant consequences in various mathematical contexts.
Definition and Explanation

To understand the reflexive property, let's consider a simple example. Suppose we have a set of integers, and we want to determine if the number 5 is equal to itself. Using the reflexive property, we can confidently state that $5 = 5$, as it satisfies the definition of equality. This property holds true for all elements in the set, regardless of their values or properties.
The reflexive property is one of the three fundamental properties of equality, along with the symmetric and transitive properties. These properties together form the foundation of equality and are essential for performing various mathematical operations, such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division.
Significance in Mathematics
The reflexive property has significant implications in various areas of mathematics, including algebra, geometry, and calculus. In algebra, the reflexive property is used to simplify equations and expressions by allowing us to substitute equal elements with each other. For instance, if we have an equation $x = 2$, we can use the reflexive property to rewrite it as $x = x$, which may seem trivial but is essential for further manipulations.
In geometry, the reflexive property is used to define congruence and similarity between shapes. For example, if we have two triangles with equal corresponding sides and angles, we can use the reflexive property to conclude that they are congruent. This property is also essential in calculus, where it is used to define limits and continuity of functions.
| Mathematical Operation | Reflexive Property Application |
|---|---|
| Algebraic Equations | Simplification and substitution of equal elements |
| Geometric Congruence | Definition of congruence and similarity between shapes |
| Calculus | Definition of limits and continuity of functions |
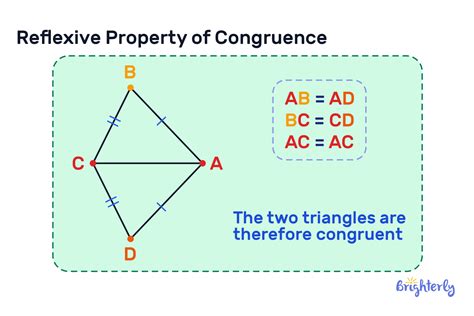
Real-World Applications

The reflexive property has numerous real-world applications, ranging from physics and engineering to computer science and data analysis. In physics, the reflexive property is used to describe the conservation of energy and momentum. For instance, if an object is at rest, its energy and momentum are equal to themselves, which is a direct application of the reflexive property.
In computer science, the reflexive property is used in programming languages to define the equality of variables and data structures. For example, if we have a variable $x$ with a value of 5, we can use the reflexive property to conclude that $x = x$, which is essential for performing various operations and comparisons.
Implications and Future Directions
The reflexive property has far-reaching implications for the development of new mathematical concepts and theorems. By acknowledging the equality of an element with itself, we can build upon this foundation to explore more complex mathematical structures and relationships. Future research directions may include the application of the reflexive property to emerging areas, such as quantum computing and artificial intelligence.
Key Points
- The reflexive property states that every element is equal to itself.
- This property is fundamental to various mathematical operations and proofs.
- The reflexive property has significant implications in algebra, geometry, and calculus.
- It has numerous real-world applications, ranging from physics and engineering to computer science and data analysis.
- Future research directions may include the application of the reflexive property to emerging areas, such as quantum computing and artificial intelligence.
In conclusion, the reflexive property of equality is a fundamental concept in mathematics that has significant implications and applications in various areas. By acknowledging the equality of an element with itself, we can build upon this foundation to develop more complex mathematical concepts and theorems. As we continue to explore and apply the reflexive property, we may uncover new insights and discoveries that can shape the future of mathematics and its applications.
What is the reflexive property of equality?
+The reflexive property of equality states that every element is equal to itself, denoted as $a = a$.
What are the implications of the reflexive property in mathematics?
+The reflexive property has significant implications in algebra, geometry, and calculus, and is used to simplify equations, define congruence and similarity between shapes, and define limits and continuity of functions.
What are some real-world applications of the reflexive property?
+The reflexive property has numerous real-world applications, ranging from physics and engineering to computer science and data analysis, including the description of conservation of energy and momentum, and the definition of equality of variables and data structures in programming languages.
Meta description suggestion: “Discover the reflexive property of equality and its significance in mathematics, including its implications in algebra, geometry, and calculus, and its real-world applications in physics, engineering, and computer science.” (149 characters)