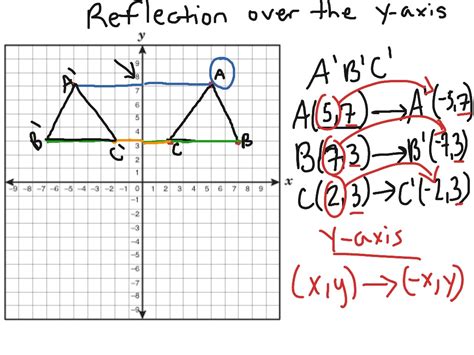
The concept of reflecting over the y-axis is a fundamental principle in mathematics, particularly in geometry and graphing. When a point or a graph is reflected over the y-axis, its x-coordinate changes sign, while the y-coordinate remains the same. This concept has numerous applications in various fields, including physics, engineering, and computer science. In this article, we will explore five ways to understand and apply the concept of reflection over the y-axis.
Understanding Reflection Over Y Axis

Reflection over the y-axis is a transformation that flips a point or a graph over the y-axis, creating a mirror image. This transformation can be represented mathematically as (x, y) → (-x, y), where (x, y) is the original point and (-x, y) is the reflected point. For example, if we have a point (3, 4), its reflection over the y-axis would be (-3, 4). This concept is essential in graphing functions, where reflecting a graph over the y-axis can help us visualize and analyze its properties.
Applications in Graphing
In graphing, reflection over the y-axis is used to create symmetric graphs, such as even and odd functions. An even function is symmetric with respect to the y-axis, meaning that f(x) = f(-x) for all x in the domain. On the other hand, an odd function is symmetric with respect to the origin, meaning that f(x) = -f(-x) for all x in the domain. Understanding reflection over the y-axis is crucial in identifying and graphing these types of functions.
| Function Type | Symmetry |
|---|---|
| Even Function | f(x) = f(-x) |
| Odd Function | f(x) = -f(-x) |
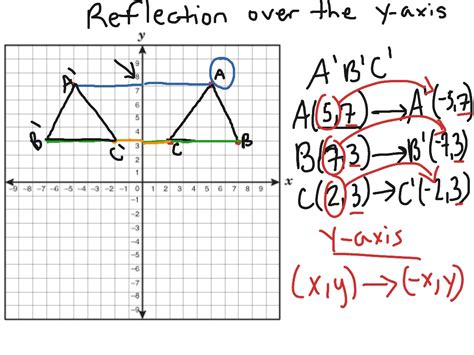
Geometric Interpretations

Reflection over the y-axis has geometric interpretations, particularly in the context of points and lines. When a point is reflected over the y-axis, its distance from the y-axis is preserved, but its position is flipped. Similarly, when a line is reflected over the y-axis, its slope and y-intercept change, but its x-intercept remains the same. Understanding these geometric interpretations is vital in solving problems involving reflections and symmetry.
Reflection in Physics and Engineering
In physics and engineering, reflection over the y-axis is used to model real-world phenomena, such as the reflection of light and sound waves. When a wave is reflected over a surface, its direction and amplitude change, but its frequency remains the same. This concept is essential in understanding and designing optical and acoustic systems, where reflection and refraction play critical roles.
Key Points
- Reflection over the y-axis changes the sign of the x-coordinate, but not the y-coordinate.
- Even functions are symmetric with respect to the y-axis, while odd functions are symmetric with respect to the origin.
- Geometric interpretations of reflection over the y-axis involve preserving distance and flipping position.
- Reflection over the y-axis is used to model real-world phenomena, such as the reflection of light and sound waves.
- Understanding reflection over the y-axis is essential in graphing, physics, and engineering.
Conclusion and Future Directions
In conclusion, reflection over the y-axis is a fundamental concept with far-reaching applications in mathematics, physics, and engineering. By understanding and applying this concept, we can gain insights into the properties of functions, geometric shapes, and real-world phenomena. As we continue to explore and develop new technologies, the concept of reflection over the y-axis will remain a vital tool in our arsenal, enabling us to model, analyze, and innovate with greater precision and accuracy.
What is the mathematical representation of reflection over the y-axis?
+The mathematical representation of reflection over the y-axis is (x, y) → (-x, y), where (x, y) is the original point and (-x, y) is the reflected point.
What is the difference between even and odd functions?
+Even functions are symmetric with respect to the y-axis, meaning that f(x) = f(-x) for all x in the domain. Odd functions, on the other hand, are symmetric with respect to the origin, meaning that f(x) = -f(-x) for all x in the domain.
How is reflection over the y-axis used in physics and engineering?
+Reflection over the y-axis is used to model real-world phenomena, such as the reflection of light and sound waves. This concept is essential in understanding and designing optical and acoustic systems, where reflection and refraction play critical roles.