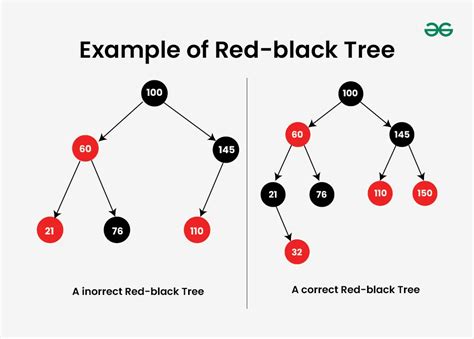
The Red-Black tree is a self-balancing binary search tree data structure with a guarantee of O(log n) time for search, insert, and delete operations. It is a variation of B-tree data structure and satisfies the following properties: each node is either red or black, the root node is black, all leaf nodes are black, if a node is red, both its children must be black, and for any node, all paths from the node to its leaf nodes contain the same number of black nodes. This ensures that the tree remains approximately balanced during insertions and deletions.
Key Points
- Red-Black trees maintain a balance between the height of the left and right subtrees, ensuring efficient search, insertion, and deletion operations.
- The tree properties, including node color and the number of black nodes, are crucial for maintaining balance and ensuring O(log n) time complexity.
- Insertion and deletion operations may require rotations and recoloring to maintain the balance and properties of the tree.
- Red-Black trees are widely used in databases, file systems, and other applications where efficient data retrieval and manipulation are critical.
- The tree's self-balancing mechanism allows it to adapt to changing data, making it a reliable choice for dynamic data structures.
How Red Black Tree Works
The Red-Black tree works by maintaining a set of properties that ensure the tree remains approximately balanced. When a new node is inserted or an existing node is deleted, the tree may become unbalanced. To restore balance, the tree performs rotations and recoloring operations. There are two primary types of rotations: left rotation and right rotation. A left rotation involves rotating a node to the left, while a right rotation involves rotating a node to the right. Recoloring involves changing the color of a node from red to black or vice versa.
Insertion Operation
When a new node is inserted into the tree, it is initially colored red. If the tree is empty, the new node becomes the root node and is colored black. If the tree is not empty, the new node is inserted as a leaf node, and its color is set to red. If the new node’s parent is black, the insertion operation is complete. However, if the new node’s parent is red, the tree may become unbalanced, and rotations and recoloring operations are necessary to restore balance.
| Operation | Description |
|---|---|
| Left Rotation | A node is rotated to the left to balance the tree. |
| Right Rotation | A node is rotated to the right to balance the tree. |
| Recoloring | A node's color is changed from red to black or vice versa to maintain tree properties. |
Deletion Operation
When a node is deleted from the tree, the tree may become unbalanced. To restore balance, the tree performs rotations and recoloring operations. If the deleted node has two children, its replacement node is found, and the tree is rebalanced. If the deleted node has one child, the child node replaces the deleted node, and the tree is rebalanced. If the deleted node has no children, the tree is rebalanced by rotating and recoloring nodes.
Advantages and Applications
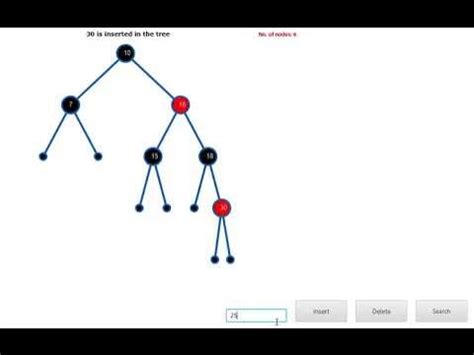
Red-Black trees have several advantages, including efficient search, insertion, and deletion operations, as well as the ability to maintain a balance between the height of the left and right subtrees. These advantages make Red-Black trees a popular choice for databases, file systems, and other applications where efficient data retrieval and manipulation are critical. Additionally, Red-Black trees are used in many programming languages, including C++, Java, and Python, to implement data structures such as maps, sets, and dictionaries.
What is the time complexity of search, insertion, and deletion operations in a Red-Black tree?
+The time complexity of search, insertion, and deletion operations in a Red-Black tree is O(log n), where n is the number of nodes in the tree.
How does a Red-Black tree maintain balance during insertion and deletion operations?
+A Red-Black tree maintains balance by performing rotations and recoloring operations to ensure that the number of black nodes on all paths from the root node to its leaf nodes remains the same.
What are the advantages of using a Red-Black tree in a database or file system?
+The advantages of using a Red-Black tree in a database or file system include efficient search, insertion, and deletion operations, as well as the ability to maintain a balance between the height of the left and right subtrees.
In conclusion, Red-Black trees are a powerful data structure that offers efficient search, insertion, and deletion operations, making them a popular choice for databases, file systems, and other applications. By understanding how Red-Black trees work and their advantages, developers can effectively utilize them to improve the performance and reliability of their applications.