Understanding reciprocal math concepts is essential for tackling various mathematical problems, especially those involving fractions, ratios, and algebraic equations. Reciprocal math tips can significantly simplify complex calculations and provide a deeper understanding of mathematical relationships. Here, we'll delve into five reciprocal math tips that can enhance your mathematical prowess and problem-solving skills.
Introduction to Reciprocal Math Concepts

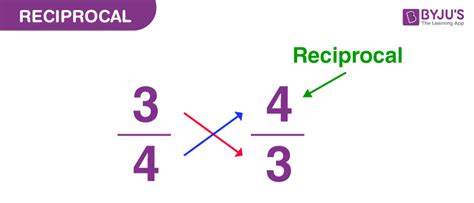
Reciprocal math involves the concept of reciprocals, which are numbers that, when multiplied together, result in 1. For any non-zero number x, its reciprocal is 1/x. This concept is fundamental in understanding fractions, where the numerator and denominator can be seen as a ratio, and the reciprocal of a fraction is obtained by swapping its numerator and denominator. Mastering reciprocal math is crucial for simplifying fractions, solving equations, and manipulating algebraic expressions.
Key Points
- Understanding the concept of reciprocals and their role in simplifying fractions and solving equations.
- Applying reciprocal math to simplify complex fractions and ratios.
- Utilizing reciprocal identities in algebra to solve equations and manipulate expressions.
- Recognizing the relationship between reciprocals and proportions in real-world applications.
- Developing problem-solving strategies that incorporate reciprocal math concepts for efficient calculation and analysis.
Tip 1: Simplifying Complex Fractions
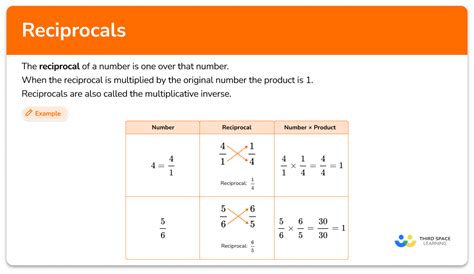
Simplifying complex fractions is one of the most straightforward applications of reciprocal math. When dealing with fractions that contain other fractions in their numerators or denominators, finding the reciprocal of the denominator and then multiplying can significantly simplify the calculation. For instance, to simplify a complex fraction like (3⁄4) / (2⁄3), we first find the reciprocal of the denominator (2⁄3), which is (3⁄2), and then multiply it by the numerator (3⁄4), resulting in (3⁄4) * (3⁄2) = 9⁄8.
Calculating with Reciprocals
Calculating with reciprocals involves understanding that the reciprocal of a number is its multiplicative inverse. This concept is crucial for solving equations and simplifying expressions. For example, if we need to solve for x in the equation x * (1⁄4) = 3, we multiply both sides by the reciprocal of (1⁄4), which is 4, to isolate x. This results in x = 3 * 4 = 12. Understanding how to use reciprocals in calculations can streamline the process of solving linear equations and simplifying algebraic expressions.
| Operation | Reciprocal Application |
|---|---|
| Division by a Fraction | Multiply by the Reciprocal of the Fraction |
| Simplifying Complex Fractions | Multiply by the Reciprocal of the Denominator |
| Solving Linear Equations | Multiply Both Sides by the Reciprocal of the Coefficient |

Tip 2: Utilizing Reciprocal Identities in Algebra
In algebra, reciprocal identities play a vital role in simplifying expressions and solving equations. The reciprocal identity states that for any non-zero numbers a and b, (a/b) = (b/a)^-1. This identity is crucial for manipulating algebraic expressions that involve exponents and fractions. For example, to simplify the expression (x^2 / y^3), we can apply the reciprocal identity to rewrite it as (y^3 / x^2)^-1, which simplifies to y^-3 * x^2.
Applying Reciprocal Math in Real-World Scenarios
Reciprocal math has numerous applications in real-world scenarios, including physics, engineering, and economics. Understanding how to apply reciprocal concepts can help in solving problems related to ratios, proportions, and inverse relationships. For instance, in physics, the concept of reciprocal math is used to understand the relationship between force and distance in the context of work done. Recognizing these applications can deepen one’s appreciation for the practicality of reciprocal math concepts.
Tip 3: Recognizing Inverse Relationships
Recognizing inverse relationships is a critical aspect of reciprocal math. Inverse relationships occur when an increase in one quantity results in a proportional decrease in another quantity, and vice versa. Understanding these relationships is essential in modeling real-world phenomena, such as the relationship between the pressure and volume of a gas. The inverse relationship can be represented mathematically using the formula P1 * V1 = P2 * V2, where P represents pressure, and V represents volume. This formula illustrates how changes in pressure are inversely related to changes in volume.
Tip 4: Manipulating Algebraic Expressions
Manipulating algebraic expressions often involves using reciprocal math to simplify or solve equations. By recognizing opportunities to apply reciprocal identities, one can efficiently simplify complex expressions. For example, the expression (2x + 3) / (x - 2) can be simplified by finding a common denominator and then applying reciprocal math principles to manipulate the expression into a more manageable form. This might involve multiplying by the conjugate of the denominator over itself to eliminate the fraction.
Strategic Problem-Solving with Reciprocal Math
Developing strategic problem-solving skills that incorporate reciprocal math concepts is crucial for tackling complex mathematical problems. This involves recognizing patterns, identifying opportunities to apply reciprocal identities, and efficiently manipulating expressions to solve equations. By mastering these strategies, individuals can improve their ability to analyze and solve problems in mathematics and related fields.
Tip 5: Mastering Proportional Reasoning
Mastering proportional reasoning is a key aspect of reciprocal math, as it involves understanding the relationships between quantities that are in proportion. Proportional reasoning is essential in solving problems related to ratios, scaling, and similar figures. By applying reciprocal math concepts, individuals can efficiently solve proportional reasoning problems. For example, if a recipe for making cookies requires a ratio of 2 cups of flour to 1 cup of sugar and you want to make half the recipe, applying proportional reasoning with reciprocal math helps in determining the exact amounts of flour and sugar needed.
What is the definition of a reciprocal in mathematics?
+The reciprocal of a number is its multiplicative inverse, which means that when the number is multiplied by its reciprocal, the result is 1. For example, the reciprocal of 4 is 1/4, because 4 * (1/4) = 1.
How are reciprocals used in simplifying complex fractions?
+To simplify a complex fraction, we multiply the fraction by the reciprocal of its denominator. This process effectively simplifies the fraction into a more manageable form. For instance, to simplify (3/4) / (2/3), we multiply (3/4) by the reciprocal of (2/3), which is (3/2), resulting in (3/4) * (3/2) = 9/8.
What are some real-world applications of reciprocal math?
+Reciprocal math has numerous real-world applications, including physics, where it's used to describe the relationship between force and distance, and economics, where it models the relationship between quantities of goods and their prices. Understanding reciprocal relationships is crucial in these fields for predictive modeling and problem-solving.
In conclusion, mastering reciprocal math concepts is essential for efficient problem-solving in mathematics and its applications. By understanding and applying the five reciprocal math tips outlined above, individuals can enhance their mathematical skills, deepen their understanding of algebraic and fractional relationships, and develop strategic approaches to solving complex problems. Whether in academic pursuits or real-world applications, the principles of reciprocal math offer a powerful tool for analysis and calculation, making them an indispensable part of any mathematician’s or problem-solver’s toolkit.