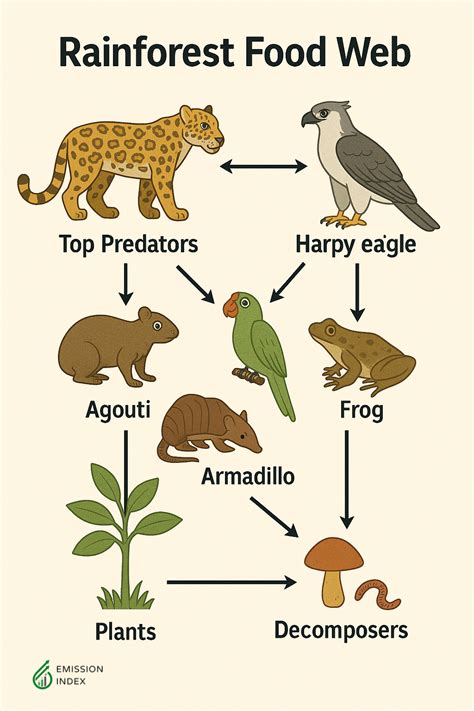
The rainforest, often referred to as the lungs of the Earth, is a complex and vibrant ecosystem that supports a wide variety of plant and animal life. One of the most fascinating aspects of the rainforest is its food web, which is comprised of numerous species that interact with one another in a delicate balance of predation, symbiosis, and competition. In this article, we will delve into five key facts about the rainforest food web, exploring the intricate relationships between the species that call this ecosystem home.
Introduction to Rainforest Food Webs
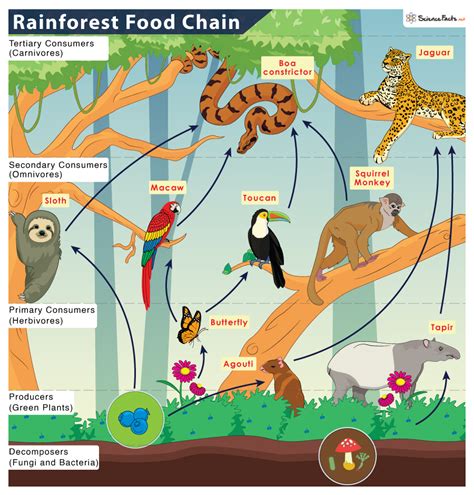
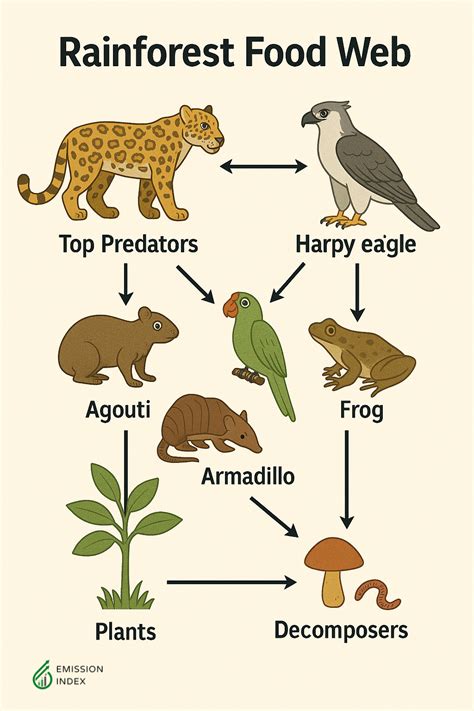
Rainforest food webs are characterized by their diversity and complexity, with numerous species playing unique roles in the ecosystem. From the towering canopy to the forest floor, each layer of the rainforest supports a distinct community of organisms that are interconnected through their feeding relationships. The food web in a rainforest is often depicted as a pyramid, with producers such as plants and algae forming the base, followed by primary consumers like herbivores, and then secondary consumers including carnivores and omnivores. At the apex of the pyramid are the top predators, which play a crucial role in regulating the populations of other species in the ecosystem.
Key Points
- The rainforest food web is characterized by its diversity and complexity, with numerous species interacting in a delicate balance.
- Producers like plants and algae form the base of the food web, followed by primary consumers, secondary consumers, and top predators.
- The relationships between species in the rainforest food web are not limited to predation, but also include symbiotic and competitive interactions.
- Human activities such as deforestation and habitat fragmentation pose significant threats to the integrity of rainforest food webs.
- Conservation efforts aimed at protecting and restoring rainforest ecosystems are crucial for maintaining the balance and diversity of their food webs.
Fact 1: Diversity of Species

The rainforest is home to an estimated 10% of all known plant and animal species, despite covering only about 6% of the Earth’s surface. This diversity is a key component of the rainforest food web, as it allows for a wide range of feeding relationships and interactions between species. For example, a single species of tree in the rainforest can support hundreds of species of insects, which in turn are preyed upon by birds, bats, and other animals. This complex network of relationships is essential for maintaining the balance and resilience of the ecosystem.
Role of Keystone Species
Keystone species, which are species that have a disproportionate impact on the environment and play a unique role in the ecosystem, are particularly important in the rainforest food web. Examples of keystone species in the rainforest include jaguars, which prey on herbivores and help to regulate their populations, and leafcutter ants, which are important seed dispersers and help to maintain the diversity of plant species. The loss of keystone species can have significant cascading effects on the ecosystem, highlighting the importance of conservation efforts aimed at protecting these species and their habitats.
| Species | Role in Ecosystem |
|---|---|
| Jaguar | Top predator, regulates herbivore populations |
| Leafcutter Ant | Seed disperser, maintains plant diversity |
| Howler Monkey | Seed disperser, contributes to forest regeneration |
Fact 2: Symbiotic Relationships
Symbiotic relationships, in which two or more species interact in a mutually beneficial way, are common in the rainforest food web. For example, certain species of fungi form symbiotic relationships with the roots of trees, providing essential nutrients in exchange for carbohydrates. Similarly, some species of birds and monkeys have been observed following army ants, which flush out insects and small animals as they forage, allowing the birds and monkeys to feed on these prey items. These symbiotic relationships highlight the complex and interconnected nature of the rainforest ecosystem.
Fact 3: Nutrient Cycling
Nutrient cycling, which refers to the process by which nutrients are transferred from one species to another through the food web, is an essential component of the rainforest ecosystem. In the rainforest, nutrients are often limiting, and species have evolved a range of strategies to acquire and conserve these resources. For example, certain species of plants have developed relationships with mycorrhizal fungi, which help to solubilize nutrients in the soil, making them available to the plants. Similarly, decomposer organisms such as bacteria and fungi play a critical role in breaking down organic matter and releasing nutrients back into the ecosystem.
Importance of Decomposers
Decomposers, which include organisms such as bacteria, fungi, and insects, are essential for the functioning of the rainforest ecosystem. These organisms help to break down organic matter, releasing nutrients back into the soil and making them available to other species. Without decomposers, the rainforest ecosystem would quickly become nutrient-limited, leading to a decline in productivity and diversity. The importance of decomposers highlights the need to conserve and protect these organisms, as well as the ecosystems in which they live.
Fact 4: Human Impact
Human activities such as deforestation, habitat fragmentation, and climate change pose significant threats to the integrity of rainforest food webs. The loss of habitat and the fragmentation of populations can disrupt the delicate balance of the ecosystem, leading to the loss of species and the degradation of ecosystem function. For example, the loss of top predators can lead to an increase in herbivore populations, which can in turn lead to the overgrazing of vegetation and the degradation of habitat. The impacts of human activities on rainforest food webs highlight the need for conservation efforts aimed at protecting and restoring these ecosystems.
Fact 5: Conservation Efforts
Conservation efforts aimed at protecting and restoring rainforest ecosystems are crucial for maintaining the balance and diversity of their food webs. These efforts can include the establishment of protected areas, such as national parks and wildlife reserves, as well as the restoration of degraded habitats and the reintroduction of native species. Additionally, sustainable land-use practices, such as agroforestry and permaculture, can help to reduce the impact of human activities on the ecosystem and promote the conservation of biodiversity. By working to protect and restore rainforest ecosystems, we can help to maintain the integrity of their food webs and ensure the long-term health and resilience of these ecosystems.
What is the importance of keystone species in the rainforest food web?
+Keystone species play a unique and crucial role in the rainforest ecosystem, and their loss can have significant cascading effects on the food web. They help to maintain the balance and diversity of the ecosystem, and their conservation is essential for protecting the integrity of the food web.
How do human activities impact the rainforest food web?
+Human activities such as deforestation, habitat fragmentation, and climate change pose significant threats to the integrity of rainforest food webs. These activities can disrupt the delicate balance of the ecosystem, leading to the loss of species and the degradation of ecosystem function.
What can be done to conserve and protect rainforest food webs?
+Conservation efforts aimed at protecting and restoring rainforest ecosystems are crucial for maintaining the balance and diversity of their food webs. These efforts can include the establishment of protected areas, the restoration of degraded habitats, and the reintroduction of native species. Additionally, sustainable land-use practices can help to reduce the impact of human activities on the ecosystem and promote the conservation of biodiversity.
In conclusion, the rainforest food web is a complex and fascinating ecosystem that is essential for maintaining the balance and diversity of life on Earth. By understanding the intricate relationships between species in the rainforest, we can gain insights into the fundamental principles that govern the structure and function of ecosystems. The conservation of rainforest food webs is crucial for protecting the integrity of these ecosystems, and efforts aimed at protecting and restoring these ecosystems are essential for ensuring the long-term health and resilience of our planet.