Converting radians to revolutions is a fundamental concept in mathematics and physics, particularly in the fields of trigonometry and rotational motion. Radians are a unit of measurement for angles, defined as the ratio of the length of an arc to the radius of a circle. On the other hand, revolutions are a unit of measurement for the number of complete rotations or turns made by an object. Understanding the relationship between radians and revolutions is crucial for solving problems in various fields, including engineering, astronomy, and navigation.
Key Points
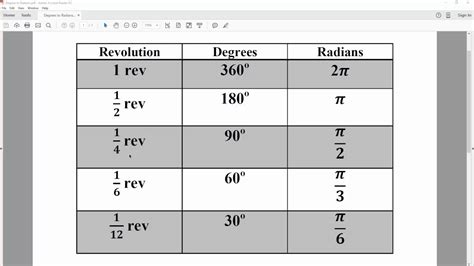
- The conversion factor between radians and revolutions is based on the fact that one revolution is equal to 2π radians.
- To convert radians to revolutions, we divide the number of radians by 2π.
- This conversion is essential in calculating the number of rotations made by an object, given its angular displacement in radians.
- Revolutions can be further converted into other units such as degrees, with 1 revolution being equal to 360 degrees.
- Understanding the conversion between radians and revolutions facilitates the calculation of rotational speeds and angular velocities in various applications.
Conversion Formula

The formula to convert radians to revolutions is straightforward and involves dividing the number of radians by 2π (approximately 6.2832). This formula stems from the definition of a radian and the fact that a full circle (or one revolution) corresponds to 2π radians.
Calculation Example
For instance, if an object rotates through an angle of 4π radians, to find out how many revolutions it has made, we would use the conversion formula: revolutions = radians / 2π. Substituting the given value, we get revolutions = 4π / 2π = 2. This means the object has completed 2 full revolutions.
| Unit of Measurement | Conversion Factor |
|---|---|
| Radians to Revolutions | 1 radian = 1 / (2π) revolutions |
| Revolutions to Radians | 1 revolution = 2π radians |
Practical Applications

The conversion between radians and revolutions has numerous practical applications. In mechanical engineering, it’s used to design and optimize rotational systems such as gears and motors. In astronomy, understanding the rotational motion of celestial bodies in terms of both radians and revolutions is crucial for predicting orbits and calculating positions. Moreover, in navigation, converting between these units helps in determining the distance traveled and the direction of travel based on the angular displacement of a vehicle.
Technical Specifications
In technical contexts, the precision of the conversion between radians and revolutions can significantly impact the performance and efficiency of systems. For example, in the design of a robotic arm, the accuracy of its rotational movement is critical for tasks that require precision, such as assembly or surgery. The conversion formula provides a basis for calculating the necessary rotational adjustments to achieve the desired position and orientation.
In conclusion, the conversion from radians to revolutions is a fundamental process that underlies many aspects of rotational motion and is essential for a wide range of applications. By understanding and applying this conversion, professionals and researchers can solve complex problems in fields such as engineering, physics, and astronomy, leading to innovations and advancements in technology and our understanding of the universe.
What is the conversion factor between radians and revolutions?
+The conversion factor is based on the fact that 1 revolution equals 2π radians. To convert radians to revolutions, divide the number of radians by 2π.
Why is it important to convert between radians and revolutions?
+Converting between these units is crucial for calculating rotational speeds, angular velocities, and the number of rotations in various applications, including engineering, astronomy, and navigation.
How does the conversion between radians and revolutions apply to real-world problems?
+This conversion is applied in designing rotational systems, predicting celestial orbits, and determining the distance and direction traveled by a vehicle based on its angular displacement. It’s essential for precision and efficiency in these applications.