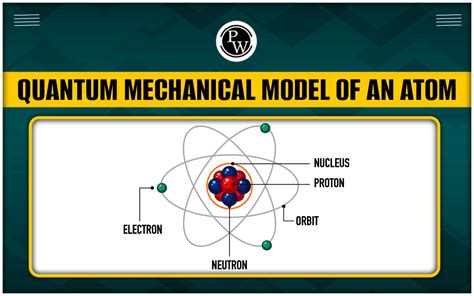
The quantum atom, a fundamental concept in physics, has fascinated scientists and researchers for decades. The behavior of atoms at the quantum level is a complex and intriguing topic, with various properties and characteristics that defy classical understanding. In this article, we will delve into five fascinating facts about quantum atoms, exploring their unique features and the implications of these properties on our understanding of the physical world.
Key Points
- Quantum atoms exhibit wave-particle duality, displaying both wave-like and particle-like behavior depending on the observation method.
- The principles of quantum superposition allow quantum atoms to exist in multiple energy states simultaneously, which has significant implications for quantum computing and cryptography.
- Quantum entanglement, a phenomenon where two or more atoms become connected and can affect each other even at vast distances, is a fundamental aspect of quantum mechanics.
- The Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle limits our ability to precisely measure certain properties of quantum atoms, such as position and momentum, due to the inherent uncertainty in quantum systems.
- Quantum atoms have unique spectral lines, which are used in various applications, including spectroscopy and the development of atomic clocks.
Wave-Particle Duality in Quantum Atoms
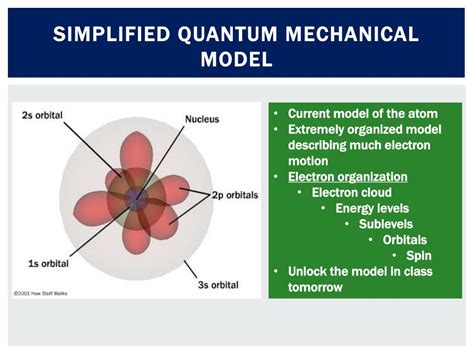
One of the most interesting aspects of quantum atoms is their ability to exhibit both wave-like and particle-like behavior. This property, known as wave-particle duality, is a fundamental concept in quantum mechanics. Depending on the observation method, quantum atoms can display characteristics of either waves or particles. For example, in a double-slit experiment, electrons (which are quantum particles) passing through two slits create an interference pattern on a screen, indicating wave-like behavior. However, when observed individually, electrons behave like particles, demonstrating the complex and context-dependent nature of quantum systems.
Quantum Superposition and Its Implications
Quantum superposition is another fascinating property of quantum atoms, where they can exist in multiple energy states simultaneously. This phenomenon has significant implications for quantum computing and cryptography, as it enables the creation of quantum bits (qubits) that can process multiple possibilities simultaneously. Quantum superposition is a critical component of quantum algorithms, such as Shor’s algorithm and Grover’s algorithm, which have the potential to solve complex problems more efficiently than classical computers.
| Quantum Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Wave-Particle Duality | Exhibits both wave-like and particle-like behavior depending on observation method |
| Quantum Superposition | Exists in multiple energy states simultaneously |
| Quantum Entanglement | Connected atoms can affect each other even at vast distances |
| Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle | Limits precise measurement of certain properties due to inherent uncertainty |
| Quantum Spectral Lines | Unique spectral lines used in spectroscopy and atomic clocks |
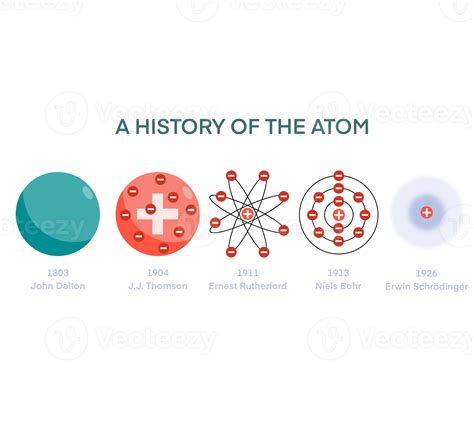
Quantum Entanglement and Its Applications
Quantum entanglement is a phenomenon where two or more atoms become connected and can affect each other even at vast distances. This property has been experimentally confirmed and is a fundamental aspect of quantum mechanics. Quantum entanglement has significant implications for quantum communication and cryptography, as it enables the creation of secure communication channels and quantum keys. Additionally, entanglement is being explored for its potential applications in quantum computing, quantum simulation, and quantum metrology.
The Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle and Quantum Measurements
The Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle is a fundamental concept in quantum mechanics that limits our ability to precisely measure certain properties of quantum atoms, such as position and momentum. This principle is a consequence of the inherent uncertainty in quantum systems, which arises from the wave-like nature of particles. The Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle has significant implications for quantum measurements, as it sets a fundamental limit on the precision with which we can measure certain properties. This principle is essential for understanding the behavior of quantum systems and has been experimentally confirmed in various contexts.
Quantum Spectral Lines and Their Applications
Quantum atoms have unique spectral lines, which are used in various applications, including spectroscopy and the development of atomic clocks. Spectral lines are a characteristic of the energy transitions within an atom, and they provide valuable information about the atomic structure and properties. The unique spectral lines of quantum atoms are used in spectroscopy to analyze the composition and properties of materials, while atomic clocks rely on the precise energy transitions of quantum atoms to maintain accurate timekeeping.
What is the significance of wave-particle duality in quantum atoms?
+Wave-particle duality is a fundamental property of quantum atoms, demonstrating their ability to exhibit both wave-like and particle-like behavior depending on the observation method. This property has significant implications for our understanding of quantum systems and is essential for the development of quantum technologies.
How does quantum superposition enable quantum computing?
+Quantum superposition enables quantum computing by allowing qubits to exist in multiple energy states simultaneously. This property enables quantum computers to process multiple possibilities simultaneously, making them potentially more efficient than classical computers for certain tasks.
What are the implications of quantum entanglement for quantum communication?
+Quantum entanglement has significant implications for quantum communication, as it enables the creation of secure communication channels and quantum keys. Entangled particles can be used to create secure communication channels, as any attempt to measure or eavesdrop on the communication would disrupt the entanglement and be detectable.
In conclusion, the properties of quantum atoms, including wave-particle duality, quantum superposition, quantum entanglement, the Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle, and quantum spectral lines, have far-reaching implications for our understanding of the physical world. As researchers continue to explore and apply these concepts, we can expect significant advancements in fields such as quantum computing, materials science, and optics. The unique properties of quantum atoms make them an exciting and fascinating area of study, with the potential to revolutionize our understanding of the world and enable the development of new technologies.