The preterite tense is a fundamental concept in Spanish grammar, used to describe completed actions in the past. For verbs ending in -er, understanding the preterite tense is crucial for effective communication. The preterite ER verb endings guide is designed to provide a comprehensive overview of the conjugation patterns for regular -er verbs in the preterite tense, enabling learners to master this essential aspect of Spanish grammar.
Introduction to Preterite ER Verb Endings
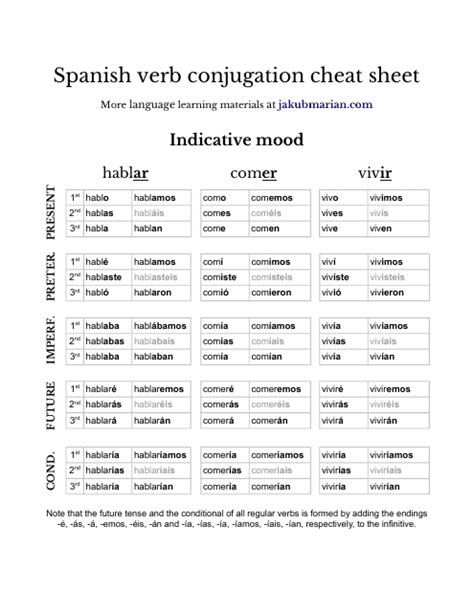
The preterite tense in Spanish is used to describe actions that started and finished in the past. Regular -er verbs follow a specific conjugation pattern in the preterite tense, which is essential for learners to understand. The conjugation of regular -er verbs in the preterite tense involves adding specific endings to the verb stem, depending on the subject pronoun. The verb endings for -er verbs in the preterite tense are as follows: -í, -iste, -ió, -imos, -isteis, and -ieron.
Key Points
- The preterite tense is used to describe completed actions in the past.
- Regular -er verbs follow a specific conjugation pattern in the preterite tense.
- The conjugation of regular -er verbs involves adding specific endings to the verb stem.
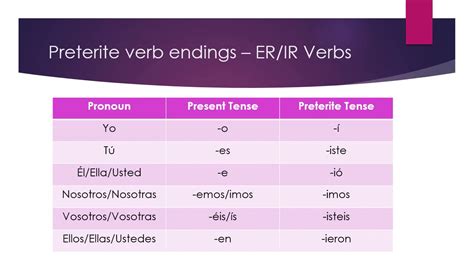
- The verb endings for -er verbs in the preterite tense are -í, -iste, -ió, -imos, -isteis, and -ieron.
- Mastering the preterite ER verb endings is essential for effective communication in Spanish.
Conjugation Patterns for Regular -er Verbs
The conjugation of regular -er verbs in the preterite tense is relatively straightforward. The verb stem is obtained by removing the -er ending from the infinitive form of the verb. The preterite tense endings are then added to the verb stem to form the conjugated verb. For example, the verb “comer” (to eat) is conjugated as follows: comí, comiste, comió, comimos, comisteis, and comieron.
| Subject Pronoun | Verb Ending | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | -í | comí |
| Tú | -iste | comiste |
| Él/ella/usted | -ió | comió |
| Nosotros/as | -imos | comimos |
| Vosotros/as | -isteis | comisteis |
| Ellos/as | -ieron | comieron |
Practical Applications of Preterite ER Verb Endings

Understanding the preterite ER verb endings is crucial for effective communication in Spanish. The preterite tense is used in a variety of contexts, including describing completed actions, expressing past habits, and narrating historical events. Mastering the conjugation of regular -er verbs in the preterite tense enables learners to express themselves more accurately and confidently in Spanish.
Common Irregularities and Exceptions
While regular -er verbs follow a predictable conjugation pattern, there are some irregularities and exceptions to be aware of. Some verbs, such as “ser” (to be) and “ir” (to go), have irregular conjugations in the preterite tense. Additionally, some verbs may have slight variations in their conjugation patterns, depending on the region or dialect. It’s essential to be aware of these irregularities and exceptions to ensure accurate and effective communication in Spanish.
What is the preterite tense used for in Spanish?
+The preterite tense is used to describe completed actions in the past. It is often used to describe actions that started and finished in the past, and is commonly used in combination with other tenses to provide a more detailed description of past events.
How do I conjugate regular -er verbs in the preterite tense?
+To conjugate regular -er verbs in the preterite tense, remove the -er ending from the infinitive form of the verb and add the preterite tense endings (-í, -iste, -ió, -imos, -isteis, and -ieron) to the verb stem.
Are there any irregularities or exceptions to the preterite ER verb endings?
+Yes, there are some irregularities and exceptions to the preterite ER verb endings. Some verbs, such as "ser" and "ir", have irregular conjugations in the preterite tense. Additionally, some verbs may have slight variations in their conjugation patterns, depending on the region or dialect.
In conclusion, mastering the preterite ER verb endings is essential for effective communication in Spanish. By understanding the conjugation patterns for regular -er verbs and being aware of irregularities and exceptions, learners can express themselves more accurately and confidently in Spanish. With practice and dedication, learners can develop a strong foundation in Spanish grammar and improve their overall language skills.