Within the realm of medical and aesthetic procedures, the term "plasty" refers to a surgical procedure that involves reshaping, repairing, or reconstructing a part of the body. This term is derived from the Greek word "plastikos," meaning "to mold" or "to form." Various types of plasty procedures exist, each designed to address specific needs or cosmetic concerns. Here, we'll delve into five key definitions of plasty procedures, exploring their purposes, techniques, and the benefits they offer to patients.
Introduction to Plasty Procedures
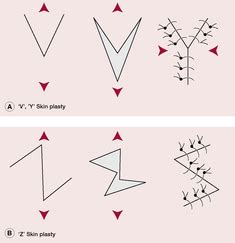
Plasty procedures encompass a broad spectrum of surgical interventions aimed at restoring form and function to different parts of the body. These can range from cosmetic surgeries intended to enhance aesthetic appeal to reconstructive surgeries that repair damaged tissues. The decision to undergo a plasty procedure is personal and can be motivated by a desire to correct congenital abnormalities, repair damage from injury or disease, or simply to improve one’s appearance. Understanding the different types of plasty and their applications is crucial for individuals considering such procedures.
1. Rhinoplasty
Rhinoplasty, commonly known as a nose job, is a plasty procedure focused on the nose. It can be performed for cosmetic reasons, to improve the appearance of the nose, or for functional reasons, such as to correct breathing difficulties caused by a deviated septum. This surgery involves reshaping the bone and cartilage of the nose to achieve the desired outcome. With advancements in surgical techniques, rhinoplasty can now offer more precise and less invasive options, such as closed rhinoplasty, which leaves no visible scars.
2. Mastopexy
Mastopexy, or breast lift surgery, is another form of plasty aimed at lifting and firming the breasts. This procedure is often sought by women whose breasts have sagged due to aging, pregnancy, or significant weight loss. Mastopexy involves removing excess skin and tightening the surrounding tissue to reshape and support the new breast contour. Sometimes, it is combined with breast augmentation for a more comprehensive aesthetic outcome. The technique used can vary depending on the degree of sagging and the patient’s overall body structure.
3. Blepharoplasty
Blepharoplasty is the medical term for eyelid surgery, designed to repair droopy eyelids by removing excess skin, muscle, and fat. As we age, the skin around our eyes can lose elasticity and firmness, leading to a tired appearance. This plasty procedure can be performed on the upper eyelids, lower eyelids, or both, to improve the function and appearance of the eyelids. By eliminating the excess tissue, blepharoplasty can not only enhance one’s cosmetic appeal but also improve vision that may be obstructed by drooping eyelids.
4. Otoplasty
Otoplasty, or ear surgery, is a plasty procedure intended to correct the shape, position, or size of the ears. It is often sought by individuals with protruding ears, a condition that can lead to self-consciousness, especially in children. The surgery involves reshaping the cartilage of the ears and repositioning them closer to the head. Otoplasty can significantly improve the aesthetic appearance of the ears and is usually performed on both children and adults. The procedure is tailored to the individual’s specific needs, ensuring a natural and proportionate result.
5. Abdominoplasty
Abdominoplasty, commonly referred to as a tummy tuck, is a plasty procedure focused on the abdomen. It is designed to flatten and firm the abdominal area by removing excess fat and skin and tightening the muscles of the abdominal wall. This surgery is particularly beneficial for individuals who have experienced significant weight loss or women after pregnancy, where the skin and muscles have been stretched beyond their elastic limit. Abdominoplasty can help restore a smoother, more youthful appearance to the abdomen, enhancing both the cosmetic and functional aspects of the abdominal area.
Key Points
- Plasty procedures offer a range of surgical interventions for aesthetic and functional improvements.
- Rhinoplasty, mastopexy, blepharoplasty, otoplasty, and abdominoplasty are examples of plasty procedures, each addressing specific needs.
- These procedures can significantly improve the quality of life and self-esteem of individuals by correcting congenital defects, repairing damage, or enhancing appearance.
- Each plasty procedure requires careful consideration and consultation with a medical professional to determine the best approach based on individual needs and health status.
- The decision to undergo a plasty procedure should be well-informed, taking into account the potential benefits, risks, and the importance of realistic expectations.
As with any surgical procedure, it's essential to approach plasty procedures with a thorough understanding of what they entail and the potential outcomes. By doing so, individuals can make informed decisions that align with their health goals and aesthetic aspirations. The evolution of plasty procedures has made them safer and more accessible, offering a viable option for those seeking to improve their quality of life and body image.
What is the primary purpose of undergoing a plasty procedure?
+The primary purpose of undergoing a plasty procedure can vary depending on the individual’s needs and the type of plasty. Generally, it is to improve the form and function of a body part, whether for aesthetic reasons, to correct a congenital defect, or to repair damage caused by injury or disease.
Are plasty procedures covered by insurance?
+Insurance coverage for plasty procedures depends on the nature of the procedure and the insurance policy. Reconstructive surgeries, such as those to repair damage from an injury or to correct a congenital defect, are more likely to be covered than purely cosmetic procedures.
What is the recovery process like for plasty procedures?
+The recovery process for plasty procedures varies significantly depending on the type of surgery, the individual’s health, and the surgical techniques used. Generally, patients can expect some degree of swelling, bruising, and discomfort, which can be managed with medication and rest. Full recovery times can range from a few weeks to several months.