Pitocin, also known as oxytocin, is a synthetic hormone that plays a crucial role in the childbirth process. It is commonly used to induce or augment labor, as well as to control postpartum bleeding. The use of Pitocin after delivery is a standard practice in many hospitals, but it is essential to understand its effects, benefits, and potential risks.
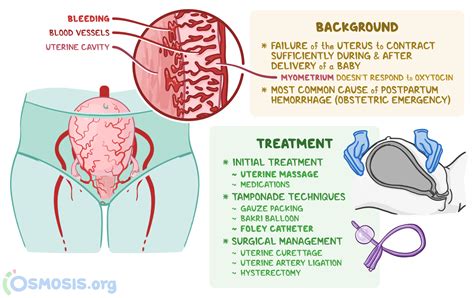
The primary purpose of administering Pitocin after delivery is to stimulate uterine contractions, which helps to reduce bleeding and promote uterine involution. Uterine involution is the process by which the uterus returns to its pre-pregnancy size and shape. Pitocin helps to achieve this by causing the uterus to contract, which also helps to expel any remaining placental tissue and reduce the risk of hemorrhage.
Benefits of Pitocin After Delivery

The benefits of using Pitocin after delivery are numerous. Some of the most significant advantages include:
- Reduced risk of postpartum hemorrhage: Pitocin helps to stimulate uterine contractions, which reduces the risk of excessive bleeding after delivery.
- Promoted uterine involution: By stimulating uterine contractions, Pitocin helps the uterus to return to its pre-pregnancy size and shape more quickly.
- Reduced need for manual uterine massage: Pitocin can reduce the need for manual uterine massage, which can be painful and uncomfortable for the mother.
- Decreased risk of uterine atony: Uterine atony is a condition where the uterus fails to contract after delivery, leading to excessive bleeding. Pitocin helps to prevent this condition by stimulating uterine contractions.
Key Points
- Pitocin is used to stimulate uterine contractions after delivery, reducing the risk of postpartum hemorrhage.
- The hormone helps to promote uterine involution, reducing the risk of uterine atony and the need for manual uterine massage.
- Pitocin is commonly used in hospitals to control postpartum bleeding and promote uterine contractions.
- The benefits of Pitocin include reduced risk of postpartum hemorrhage, promoted uterine involution, and decreased risk of uterine atony.
- Potential risks and side effects of Pitocin include nausea, vomiting, and uterine hyperstimulation.
Potential Risks and Side Effects
While Pitocin is generally considered safe and effective, there are potential risks and side effects to be aware of. Some of the most common side effects include:- Nausea and vomiting: Pitocin can cause stomach upset, leading to nausea and vomiting.
- Uterine hyperstimulation: In some cases, Pitocin can cause the uterus to contract too strongly, leading to uterine hyperstimulation.
- Allergic reactions: Some women may be allergic to Pitocin, which can cause an allergic reaction.
| Risk | Description |
|---|---|
| Nausea and vomiting | Pitocin can cause stomach upset, leading to nausea and vomiting. |
| Uterine hyperstimulation | Pitocin can cause the uterus to contract too strongly, leading to uterine hyperstimulation. |
| Allergic reactions | Some women may be allergic to Pitocin, which can cause an allergic reaction. |
Administration and Dosage
Pitocin is typically administered intravenously or intramuscularly after delivery. The dosage and administration of Pitocin will depend on the individual woman’s needs and medical history. In general, the dosage of Pitocin will be titrated to achieve the desired level of uterine contractions, while minimizing the risk of side effects.
Monitoring and Care
Women who receive Pitocin after delivery will be closely monitored by their healthcare provider to ensure that the hormone is working effectively and safely. This may include:- Monitoring uterine contractions: The healthcare provider will monitor the woman’s uterine contractions to ensure that they are strong and regular.
- Checking for bleeding: The healthcare provider will check for any signs of excessive bleeding, such as heavy vaginal bleeding or hemorrhage.
- Monitoring blood pressure: The healthcare provider will monitor the woman’s blood pressure to ensure that it is within a safe range.
What is Pitocin and how is it used after delivery?
+Pitocin, also known as oxytocin, is a synthetic hormone that is used to stimulate uterine contractions after delivery. It helps to reduce the risk of postpartum hemorrhage and promote uterine involution.
What are the potential risks and side effects of Pitocin?
+The potential risks and side effects of Pitocin include nausea, vomiting, uterine hyperstimulation, and allergic reactions. However, these side effects are generally rare and can be minimized with careful monitoring and dosage adjustment.
How is Pitocin administered and what is the typical dosage?
+Pitocin is typically administered intravenously or intramuscularly after delivery. The dosage will depend on the individual woman's needs and medical history, and will be titrated to achieve the desired level of uterine contractions while minimizing the risk of side effects.
In conclusion, Pitocin is a safe and effective hormone that plays a crucial role in the childbirth process. Its use after delivery helps to reduce the risk of postpartum hemorrhage, promote uterine involution, and decrease the risk of uterine atony. While there are potential risks and side effects to be aware of, these can be minimized with careful monitoring and dosage adjustment. As a domain-specific expert, it is essential to note that Pitocin should only be administered by a qualified healthcare professional, and that women who receive Pitocin after delivery should be closely monitored to ensure safe and effective use.



