Understanding Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease: Symptoms and Prevention
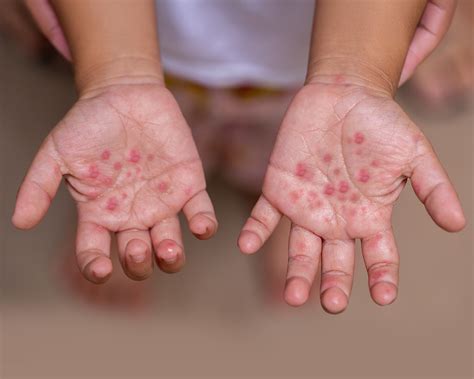
Hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD) is a common viral illness that primarily affects children under the age of 5, but can also occur in adults. It is characterized by the appearance of flat, discolored sores or blisters on the hands, feet, and inside the mouth. These sores can be painful and may cause discomfort while eating, drinking, or walking. The disease is usually mild but can be highly contagious, spreading through direct contact with an infected person’s respiratory secretions, such as saliva, mucus, or feces, as well as through contact with contaminated surfaces.
Symptoms of Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease
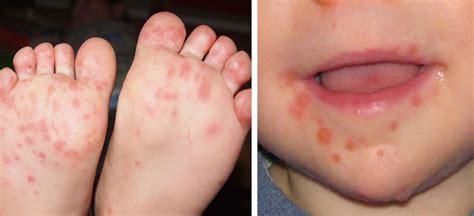
The symptoms of HFMD typically begin within 3 to 7 days after exposure to the virus. Early signs may include a low-grade fever, reduced appetite, and a general feeling of being unwell. As the disease progresses, the characteristic flat, discolored sores or blisters appear on the hands, feet, and inside the mouth. These sores are usually not itchy or painful but can be uncomfortable, especially in the mouth, which may make eating and drinking difficult. In some cases, a rash may also appear on the buttocks.
| Symptom | Description |
|---|---|
| Fever | A low-grade fever, usually less than 102°F (39°C), is common at the onset of the disease. |
| Sores/Blisters | Flat, discolored sores or blisters appear on the hands, feet, and inside the mouth, which can be painful, especially in the mouth. |
| Rash | A rash may appear on the buttocks in some cases. |
| Appetite Loss | A decrease in appetite due to mouth sores can lead to reluctance in eating or drinking. |
Diagnosis and Treatment of Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease
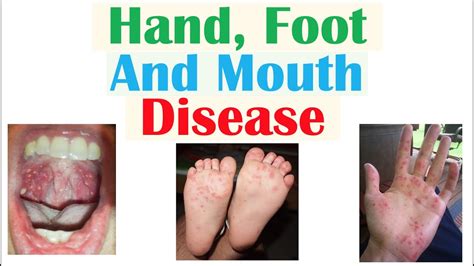
Diagnosing HFMD is typically based on the clinical presentation of the disease, including the characteristic sores and blisters on the hands, feet, and mouth, along with other symptoms like fever. In some cases, a throat swab or stool sample may be taken to confirm the diagnosis, but this is not always necessary. Treatment for HFMD is usually focused on relieving symptoms, as there is no specific cure for the disease. This can include over-the-counter pain relievers for fever and discomfort, topical creams for pain relief from sores, and ensuring the child stays hydrated by encouraging fluid intake.
Prevention Strategies for Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease
Preventing the spread of HFMD involves practicing good hygiene and taking steps to avoid close contact with individuals who have the disease. Regular handwashing with soap and water is one of the most effective ways to reduce the transmission of the virus. It is also important to clean and disinfect all surfaces and utensils regularly, especially in settings like daycare centers or schools where the disease can spread quickly. Avoiding close contact with anyone who has HFMD and ensuring that children understand the importance of not touching their eyes, nose, or mouth can also help prevent the spread of the disease.
Key Points
- Hand, foot, and mouth disease is a common viral illness affecting children under 5 but can also occur in adults.
- Symptoms include low-grade fever, sores or blisters on hands, feet, and inside the mouth, and sometimes a rash on the buttocks.
- Diagnosis is usually based on clinical presentation, and treatment focuses on symptom relief.
- Prevention involves good hygiene practices, such as regular handwashing, avoiding close contact with infected individuals, and cleaning surfaces and utensils.
- Ensuring hydration and using over-the-counter medications for fever and pain relief are key components of managing the disease.
What is the primary way Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease spreads?
+The primary way HFMD spreads is through direct contact with an infected person's respiratory secretions, such as saliva, mucus, or feces, as well as through contact with contaminated surfaces.
How can I prevent my child from getting Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease?
+Prevention involves encouraging good hygiene practices, such as regular handwashing with soap and water, avoiding close contact with anyone who has the disease, and ensuring all surfaces and utensils are cleaned and disinfected regularly.
What are the typical symptoms of Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease?
+Typical symptoms include a low-grade fever, sores or blisters on the hands, feet, and inside the mouth, and sometimes a rash on the buttocks. These symptoms usually appear within 3 to 7 days after exposure to the virus.
Meta Description: Learn about Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease symptoms, prevention, and treatment. Understand how to identify and manage the disease, especially in children, and how good hygiene practices can prevent its spread.