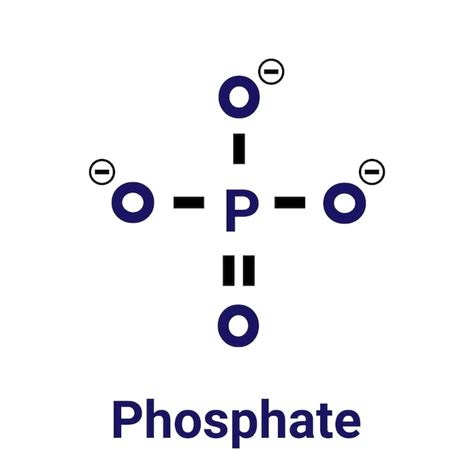
Phosphates are a class of compounds that play a crucial role in various biological and chemical processes. Understanding the Lewis structure of phosphates is essential for comprehending their properties and reactivity. In this article, we will delve into the world of phosphate Lewis structures, exploring the key concepts, rules, and tips for constructing these vital molecular representations.
Introduction to Phosphate Lewis Structures
Phosphates are a type of oxyanion, consisting of a phosphorus atom bonded to four oxygen atoms. The Lewis structure of a phosphate ion (PO43-) is a fundamental concept in chemistry, as it helps predict the molecule’s shape, polarity, and chemical behavior. The phosphate Lewis structure is typically represented as a tetrahedral arrangement of oxygen atoms around a central phosphorus atom, with a double bond between the phosphorus and one of the oxygen atoms.
Key Points
- Phosphates have a tetrahedral molecular geometry
- The phosphate Lewis structure features a double bond between phosphorus and oxygen
- Phosphates are highly reactive due to their charged nature
- Lewis structures are essential for predicting phosphate reactivity and properties
- Understanding phosphate Lewis structures is crucial for various biological and chemical applications
Tip 1: Determine the Central Atom
When constructing a Lewis structure, it is essential to identify the central atom. In the case of phosphates, the phosphorus atom is the central atom, as it is the least electronegative atom in the molecule. The oxygen atoms, being more electronegative, will surround the phosphorus atom, forming a tetrahedral arrangement.
| Atom | Electronegativity |
|---|---|
| Phosphorus (P) | 2.19 |
| Oxygen (O) | 3.44 |
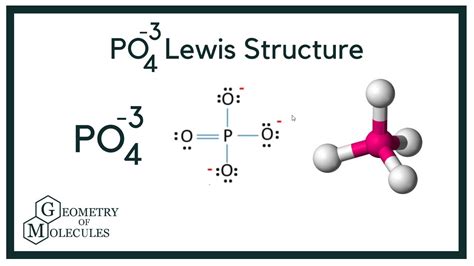
Tip 2: Calculate the Total Valence Electrons
To construct a Lewis structure, we need to calculate the total valence electrons available. For a phosphate ion, we have one phosphorus atom and four oxygen atoms. The total valence electrons can be calculated as follows: 5 (phosphorus) + 4 x 6 (oxygen) + 3 (charge) = 32. This means we have 32 valence electrons to distribute among the atoms in the Lewis structure.
Tip 3: Draw the Skeleton Structure
With the central atom and total valence electrons determined, we can start drawing the skeleton structure of the phosphate ion. The phosphorus atom will be surrounded by four oxygen atoms, forming a tetrahedral arrangement. We can then distribute the valence electrons among the atoms, ensuring that each oxygen atom has a full outer shell (8 electrons) and the phosphorus atom has a full outer shell (8 electrons) as well.
Tip 4: Add Formal Charges
Once the skeleton structure is complete, we need to add formal charges to the atoms. In the case of the phosphate ion, the phosphorus atom will have a formal charge of +1, while the oxygen atoms will have formal charges of -1, -1, -1, and 0 (for the double-bonded oxygen). The formal charges help us understand the molecule’s reactivity and properties.
Tip 5: Verify the Octet Rule
Finally, we need to verify that the Lewis structure satisfies the octet rule. The octet rule states that each atom in the molecule should have a full outer shell (8 electrons). In the case of the phosphate ion, the phosphorus atom has 8 electrons (5 valence electrons + 3 electrons from the double bond), and each oxygen atom has 8 electrons (6 valence electrons + 2 electrons from the single bond or 4 electrons from the double bond). This ensures that the Lewis structure is stable and accurate.
In conclusion, constructing a phosphate Lewis structure requires attention to detail and a thorough understanding of the underlying principles. By following these five tips, chemists and researchers can create accurate and informative Lewis structures that help predict the properties and reactivity of phosphate compounds.
What is the molecular geometry of a phosphate ion?
+The molecular geometry of a phosphate ion is tetrahedral, with the phosphorus atom at the center and the four oxygen atoms surrounding it.
Why is it essential to determine the central atom in a Lewis structure?
+Determining the central atom is crucial because it helps predict the molecular geometry and reactivity of the compound. The central atom is typically the least electronegative atom in the molecule.
How do formal charges affect the properties of a phosphate compound?
+Formal charges can significantly impact the properties of a phosphate compound. The formal charges help predict the molecule’s reactivity, polarity, and chemical behavior.