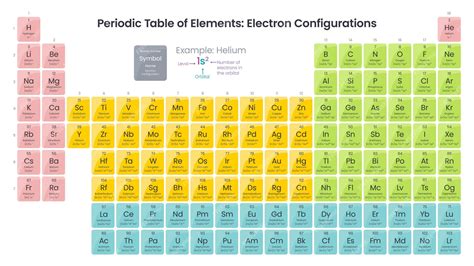
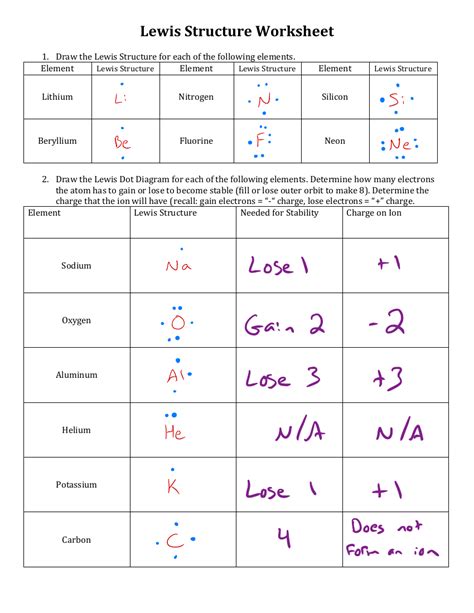
The periodic table is a fundamental tool in chemistry, providing a comprehensive framework for understanding the properties and behavior of elements. At its core, the periodic table is organized based on the electron configuration of atoms, which determines the chemical properties of an element. In this guide, we will delve into the world of electron configuration, exploring its significance, rules, and applications in understanding the periodic table.
Key Points
- Electron configuration is the arrangement of electrons in an atom, which determines its chemical properties.
- The Aufbau principle and the Pauli exclusion principle are fundamental rules governing electron configuration.
- Hund's rule of maximum multiplicity and the rule of lower energy levels also play crucial roles in determining electron configuration.
- Understanding electron configuration is essential for predicting the chemical behavior of elements and their positions in the periodic table.
- Electron configuration patterns can be used to identify periodic trends and relationships among elements.
Introduction to Electron Configuration

Electron configuration refers to the distribution of electrons in an atom, which is crucial for understanding its chemical reactivity and properties. The periodic table is arranged in a way that elements with similar electron configurations are placed in the same group or period, reflecting their shared chemical characteristics. Electron configuration is typically represented using a notation that indicates the energy level, orbital type, and number of electrons in each orbital.
Aufbau Principle and Pauli Exclusion Principle
The Aufbau principle states that electrons occupy the lowest available energy levels, while the Pauli exclusion principle asserts that no two electrons in an atom can have the same set of quantum numbers. These principles form the basis of electron configuration, guiding the arrangement of electrons in an atom. The Aufbau principle helps in understanding how electrons fill the orbitals, starting from the lowest energy level, while the Pauli exclusion principle ensures that each electron has a unique set of quantum numbers, thereby limiting the number of electrons in each orbital.
| Energy Level | Orbital Type | Electron Capacity |
|---|---|---|
| 1s | s-orbital | 2 electrons |
| 2s | s-orbital | 2 electrons |
| 2p | p-orbital | 6 electrons |
| 3s | s-orbital | 2 electrons |
| 3p | p-orbital | 6 electrons |
Applying Electron Configuration Rules
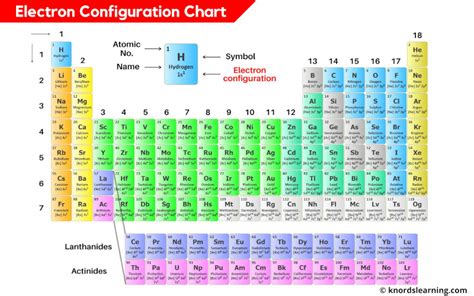
Beyond the Aufbau principle and the Pauli exclusion principle, other rules such as Hund’s rule of maximum multiplicity and the rule of lower energy levels play significant roles in determining the electron configuration of atoms. Hund’s rule states that when filling orbitals of equal energy, electrons will occupy each orbital singly before pairing up, maximizing the multiplicity. The rule of lower energy levels dictates that electrons will always occupy the lowest available energy levels, which is in line with the Aufbau principle. By applying these rules, chemists can predict the electron configuration of any element and understand its chemical behavior.
Electron Configuration Notation
Electron configuration is typically represented using a shorthand notation that indicates the energy level, orbital type, and the number of electrons in each orbital. For example, the electron configuration of carbon is 1s² 2s² 2p², indicating that carbon has two electrons in the 1s orbital, two electrons in the 2s orbital, and two electrons in the 2p orbitals. This notation provides a concise way to represent the electron configuration of an atom and is essential for understanding its chemical properties.
Periodic Trends and Electron Configuration
The periodic table exhibits several trends that are directly related to electron configuration. The atomic radius, electronegativity, and ionization energy are just a few properties that vary systematically across periods and groups, reflecting the underlying electron configuration. By understanding these trends, chemists can predict the chemical behavior of elements and their compounds, highlighting the importance of electron configuration in chemistry.
What is the significance of electron configuration in understanding the periodic table?
+Electron configuration is crucial for understanding the periodic table because it determines the chemical properties of elements. The arrangement of electrons in an atom influences its reactivity, which is why elements with similar electron configurations exhibit similar chemical behaviors.
How do the Aufbau principle and the Pauli exclusion principle contribute to electron configuration?
+The Aufbau principle ensures that electrons occupy the lowest available energy levels, while the Pauli exclusion principle prevents any two electrons from having the same set of quantum numbers. These principles are fundamental to determining the electron configuration of atoms.
What is the role of Hund's rule of maximum multiplicity in electron configuration?
+Hund's rule states that when filling orbitals of equal energy, electrons will occupy each orbital singly before pairing up, maximizing the multiplicity. This rule helps in predicting the electron configuration of atoms, especially when dealing with orbitals of equal energy.
Meta Description: Explore the fundamental principles of electron configuration and its role in understanding the periodic table. Discover how the Aufbau principle, Pauli exclusion principle, and Hund’s rule contribute to the arrangement of electrons in atoms and influence chemical properties.