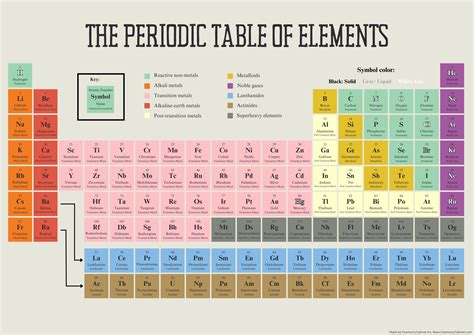
Periodic chemistry, a fundamental aspect of chemistry, deals with the study of elements and their periodic trends. Understanding the periodic table is crucial for any student or professional in the field of chemistry. The periodic table is a tabular display of the known chemical elements, organized by their atomic number (number of protons in the nucleus), electron configuration, and recurring chemical properties. In this article, we will delve into five periodic chemistry tips that can help deepen your understanding of the subject.
Key Points
- Understanding the structure of the periodic table and how elements are classified.
- Recognizing periodic trends, such as atomic radius, electronegativity, and ionization energy.
- Identifying the relationships between elements in the same group and period.
- Applying knowledge of the periodic table to predict chemical properties and reactions.
- Using the periodic table as a tool for identifying and understanding the properties of unknown elements.
Navigating the Periodic Table
The periodic table is structured in a way that elements with similar chemical properties recur at regular intervals. It is divided into rows called periods and columns called groups or families. Elements in the same group exhibit similar chemical properties due to the same number of electrons in their outermost shell. The periodic table can be broadly classified into metals, nonmetals, and metalloids. Metals are typically found on the left side and center of the periodic table, while nonmetals are found on the right side. Metalloids, which exhibit some properties of metals and some of nonmetals, are found along the metal-nonmetal dividing line.
Periodic Trends
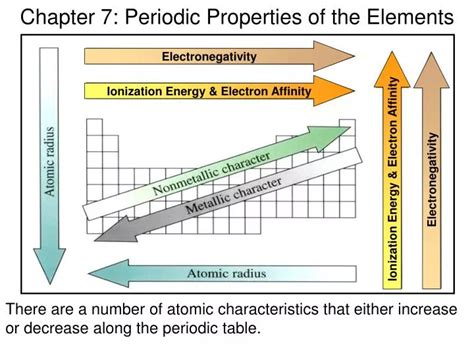
One of the most powerful tools in periodic chemistry is the recognition of periodic trends. These trends refer to the variations in chemical properties as you move across a period or down a group in the periodic table. Key trends include atomic radius, electronegativity, and ionization energy. Atomic radius generally decreases from left to right across a period due to the increasing effective nuclear charge, and increases down a group due to the addition of new electron shells. Electronegativity, which measures an atom’s ability to attract electrons in a covalent bond, increases from left to right across a period and decreases down a group. Ionization energy, the energy required to remove an electron from an atom, follows a similar trend to electronegativity, increasing across a period and decreasing down a group.
| Periodic Trend | Description | Periodic Variation |
|---|---|---|
| Atomic Radius | Size of the atom | Decreases across a period, increases down a group |
| Electronegativity | Ability to attract electrons | Increases across a period, decreases down a group |
| Ioniization Energy | Energy to remove an electron | Increases across a period, decreases down a group |
Practical Applications of Periodic Chemistry
The knowledge of periodic chemistry has numerous practical applications. It helps in predicting the chemical properties of elements and their compounds, which is essential in fields like materials science, pharmaceuticals, and environmental science. For instance, understanding the electronegativity trend can help in designing molecules with specific properties, such as the development of new drugs or materials. Furthermore, the periodic table is used in the discovery of new elements and in understanding their properties, contributing to advancements in technology and science.
Using the Periodic Table for Element Identification
The periodic table can also serve as a valuable tool for identifying unknown elements. By analyzing the chemical properties of an unknown substance, such as its reactivity with air or water, its conductivity, or its magnetic properties, one can narrow down the possible identities of the element based on its position in the periodic table. This method, combined with more sophisticated analytical techniques like spectroscopy, can lead to the identification of the element and deepen our understanding of its properties and potential applications.
What is the primary function of the periodic table in chemistry?
+The primary function of the periodic table is to organize elements based on their atomic number, electron configuration, and recurring chemical properties, allowing for the prediction of chemical behavior and the identification of relationships between elements.
How do periodic trends help in understanding chemistry?
+Periodic trends, such as atomic radius, electronegativity, and ionization energy, help in understanding how the properties of elements change across periods and down groups, enabling the prediction of chemical properties and reactions based on an element's position in the periodic table.
What are some practical applications of periodic chemistry?
+Practical applications include predicting chemical properties for the development of new materials and drugs, identifying unknown elements, and contributing to advancements in technology and science through the discovery of new elements and understanding their properties.
In conclusion, periodic chemistry provides a foundational framework for understanding the elements and their properties. By mastering the structure of the periodic table, recognizing periodic trends, and applying this knowledge to predict chemical behavior, individuals can deepen their understanding of chemistry and contribute to advancements in various fields. The periodic table, a tool that has evolved over centuries, continues to be a cornerstone of chemical research and education, offering insights into the properties of elements and their potential applications.