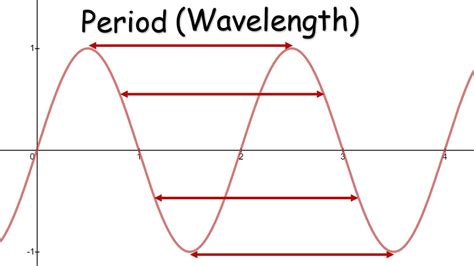
The relationship between period and waves is a fundamental concept in physics, particularly in the study of oscillations and wave dynamics. The period of a wave is the time it takes for one complete cycle of the wave to pass a given point, and it plays a crucial role in determining the characteristics of the wave. In this article, we will explore five ways in which the period affects waves, delving into the intricacies of wave behavior and the underlying physical principles.
Key Points
- The period of a wave is inversely proportional to its frequency, with a shorter period resulting in a higher frequency.
- A change in period affects the wavelength of a wave, with a shorter period resulting in a shorter wavelength.
- The period of a wave influences its speed, with a shorter period resulting in a faster speed in certain types of waves.
- The period of a wave affects its energy, with a shorter period generally resulting in higher energy.
- The period of a wave can impact its interaction with other waves and objects, leading to phenomena such as interference and diffraction.
Understanding Wave Period and Frequency
The period (T) of a wave is related to its frequency (f) by the equation T = 1/f. This means that as the period of a wave decreases, its frequency increases, and vice versa. This relationship is fundamental to understanding how the period affects the behavior of waves. For example, in the context of sound waves, a shorter period corresponds to a higher pitch, while a longer period corresponds to a lower pitch.
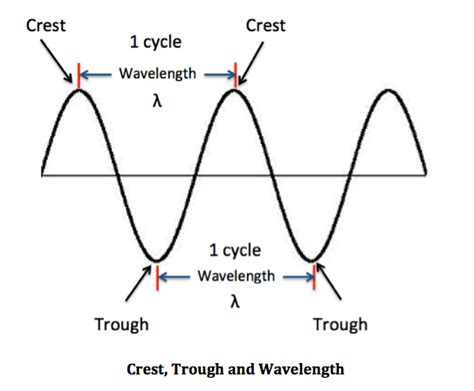
Period and Wavelength Relationship
The period of a wave also affects its wavelength (λ). The speed (v) of a wave is given by the equation v = λ/T, which shows that the wavelength is directly proportional to the period. For waves traveling at a constant speed, a shorter period results in a shorter wavelength. This relationship is crucial in understanding various wave phenomena, such as diffraction and interference, where the wavelength plays a significant role. In the context of light waves, for instance, the period affects the color of the light, with shorter periods corresponding to shorter wavelengths and thus to higher energy photons.
| Wave Type | Period | Wavelength | Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|
| Radio Waves | Long | Long | Low |
| Visible Light | Short | Short | High |
| Gamma Rays | Very Short | Very Short | Very High |
Impact of Period on Wave Speed
The speed of a wave can be influenced by its period, although this relationship depends on the type of wave and the medium in which it travels. For certain types of waves, such as water waves in deep water, the speed is independent of the period. However, for waves in shallow water or for other types of waves like seismic waves, the speed can be affected by the period. Understanding this relationship is crucial for predicting the behavior of waves in various environments.
Period and Wave Energy
The energy of a wave is often related to its period, although the exact nature of this relationship can depend on the context. Generally, a shorter period corresponds to higher energy, as the wave cycles through its peaks and troughs more rapidly. This is evident in the context of seismic waves, where shorter period waves (higher frequency waves) tend to carry less energy than longer period waves but can still cause significant damage due to their higher frequency content.
Interaction with Other Waves and Objects
The period of a wave also affects its interaction with other waves and objects. Phenomena such as interference and diffraction are heavily influenced by the period (and thus the wavelength) of the waves involved. When waves with different periods interact, they can produce complex patterns of interference, leading to enhancements or cancellations of the wave amplitude at different points in space. Similarly, the diffraction of waves around obstacles or through openings is dependent on the wavelength (and thus the period) of the wave, with shorter period waves being less affected by small obstacles.
How does the period of a wave affect its frequency?
+The period of a wave is inversely proportional to its frequency. This means that as the period decreases, the frequency increases, and vice versa.
What is the relationship between the period of a wave and its wavelength?
+The wavelength of a wave is directly proportional to its period when the wave is traveling at a constant speed. This means that a shorter period results in a shorter wavelength.
How does the period of a wave influence its interaction with other waves?
+The period of a wave affects its interaction with other waves through phenomena such as interference and diffraction. The period (and thus the wavelength) determines how waves will interact with each other and with objects they encounter.
In conclusion, the period of a wave has a profound impact on its characteristics and behavior. From influencing frequency and wavelength to affecting speed, energy, and interaction with other waves and objects, the period is a fundamental property that underlies many aspects of wave dynamics. Understanding these relationships is essential for a deep appreciation of the complex and fascinating world of waves and their role in our universe.