The relationship between the perimeter and area of a shape is a fundamental concept in geometry. While the area of a shape provides information about the amount of space inside the shape, the perimeter gives details about the distance around the shape. For certain shapes, it is possible to find the perimeter if the area is known, provided that the shape's dimensions or characteristics are also known. In this article, we will explore how to find the perimeter from the area for different geometric shapes, focusing on the most common ones: squares, rectangles, triangles, and circles.
Key Points
- The formula to find the perimeter of a shape from its area involves knowing the shape's specific characteristics or dimensions.
- For a square, the perimeter can be found by multiplying the square root of the area by 4.
- For a rectangle, knowing the area and one dimension allows us to find the other dimension and then calculate the perimeter.
- For a triangle, if we know the area and the base, we can find the height and then use the Pythagorean theorem to find the lengths of the sides and calculate the perimeter.
- For a circle, the perimeter (circumference) can be found from the area by first calculating the radius and then using the formula for the circumference.
Squares
A square is a special type of rectangle where all sides are equal. If we know the area of a square, we can easily find its side length by taking the square root of the area. The formula for the area of a square is A = s^2, where A is the area and s is the length of a side. To find the perimeter, we use the formula P = 4s, where P is the perimeter. Thus, if we know the area, we can find the side length and then calculate the perimeter as P = 4 * √A.
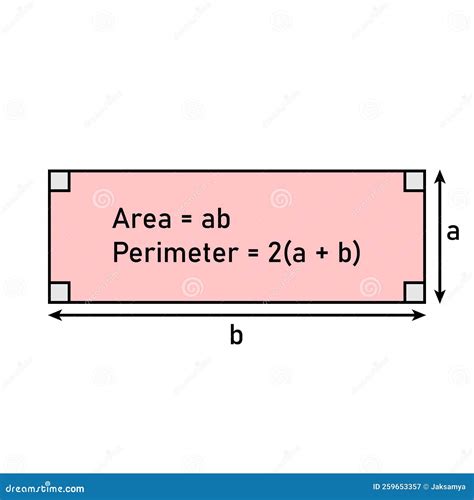
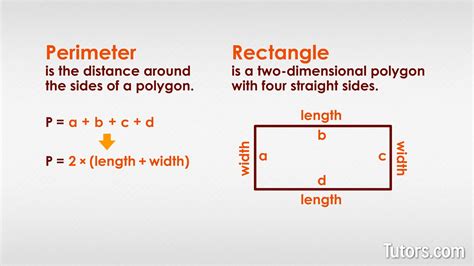
Rectangles
For a rectangle, the area is given by A = length * width. If we know the area and one dimension (either the length or the width), we can find the other dimension. For example, if we know the length and the area, we can find the width as width = A / length. Once we have both dimensions, we can calculate the perimeter using the formula P = 2 * (length + width).
Triangles
The area of a triangle can be found using the formula A = 0.5 * base * height. If we know the area and the base, we can rearrange this formula to find the height: height = 2 * A / base. However, finding the perimeter of a triangle from its area is more complex because it requires knowledge of at least one side or the relationship between the sides. If we know the lengths of two sides and the included angle, we can use the Law of Cosines to find the third side. Alternatively, if we have the height and the base, and the triangle is a right triangle, we can use the Pythagorean theorem to find the hypotenuse and then calculate the perimeter.
Circles
The area of a circle is given by A = π * r^2, where r is the radius. From the area, we can find the radius as r = √(A / π). The perimeter (circumference) of a circle is given by C = 2 * π * r. Substituting the expression for r from the area, we get C = 2 * π * √(A / π), which simplifies to C = 2 * √(π * A). This formula allows us to find the circumference of a circle directly from its area.
| Shape | Area Formula | Perimeter Formula from Area |
|---|---|---|
| Square | A = s^2 | P = 4 * √A |
| Rectangle | A = length * width | P = 2 * (length + width), given one dimension |
| Triangle | A = 0.5 * base * height | Complex, requires additional information |
| Circle | A = π * r^2 | C = 2 * √(π * A) |
Practical Applications
In real-world scenarios, finding the perimeter from the area is crucial in various fields such as architecture, engineering, and design. For instance, architects need to calculate the perimeter of rooms and buildings to determine the amount of materials needed for construction and decoration. Engineers use perimeter calculations to design efficient systems, such as pipelines and electrical circuits. In landscape design, understanding how to calculate perimeters from areas helps in planning gardens, parks, and other outdoor spaces effectively.
Challenges and Limitations
While the formulas for finding the perimeter from the area are well-established for regular shapes, challenges arise when dealing with irregular shapes or complex geometries. In such cases, approximate methods or numerical calculations may be necessary. Additionally, the precision of the calculations depends on the accuracy of the given area and the known dimensions of the shape. Therefore, it is essential to ensure that the input data are as accurate as possible to obtain reliable results.
Can I always find the perimeter of a shape from its area?
+No, finding the perimeter from the area is not always possible without additional information. For example, knowing the area of a triangle alone is not enough to calculate its perimeter without knowing at least one side or the relationship between the sides.
How does the shape's complexity affect the calculation of the perimeter from the area?
+The complexity of the shape significantly affects the calculation. Regular shapes like squares, rectangles, and circles have straightforward formulas, but irregular shapes may require approximation techniques or more complex geometric analysis.
What are some real-world applications of finding the perimeter from the area?
+Applications include architectural design, engineering, landscape planning, and any field requiring the calculation of material quantities or spatial arrangements based on known areas and dimensions.
In conclusion, finding the perimeter of a shape from its area is a geometric problem that can be solved for various shapes, provided that sufficient information about the shape’s dimensions or characteristics is available. Understanding these principles is essential for numerous practical applications across different fields. By applying the appropriate formulas and considering the specific properties of each shape, one can derive the perimeter, demonstrating the fundamental interplay between area, perimeter, and the geometric characteristics of shapes.