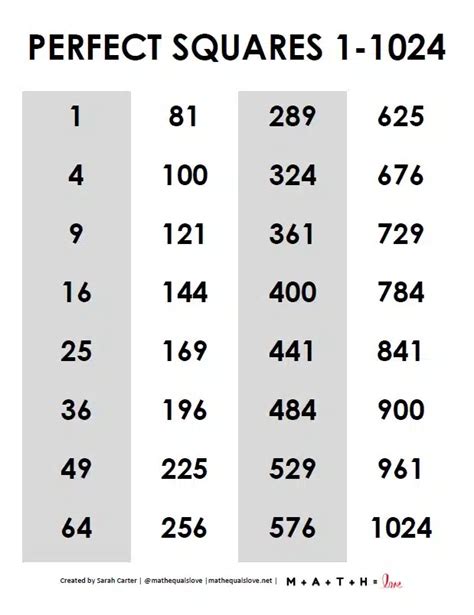
The concept of perfect squares is a fundamental aspect of number theory, and it has numerous applications in various fields, including mathematics, physics, and engineering. A perfect square is a number that can be expressed as the square of an integer, i.e., it is the result of multiplying an integer by itself. For instance, 16 is a perfect square because it can be expressed as 4^2, which equals 16. In this article, we will delve into the world of perfect squares, exploring their properties, applications, and a comprehensive list of perfect squares.
Introduction to Perfect Squares
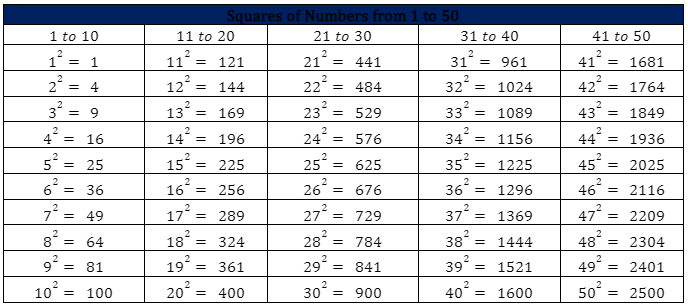
Perfect squares have been studied for centuries, and they play a crucial role in many mathematical concepts, such as algebra, geometry, and calculus. One of the key properties of perfect squares is that they can be expressed as the product of an integer with itself. This property makes perfect squares useful in various mathematical operations, such as factoring, solving equations, and calculating areas and volumes. For example, the area of a square with a side length of 5 units is 5^2 = 25 square units.
Properties of Perfect Squares
Perfect squares exhibit several interesting properties, including the fact that they are always non-negative, and the square root of a perfect square is an integer. Additionally, perfect squares can be expressed as the sum of two or more consecutive odd integers. For instance, 36 can be expressed as 6^2, which equals 36, and it can also be expressed as the sum of two consecutive odd integers: 17 + 19 = 36. Understanding these properties is essential for working with perfect squares and applying them to real-world problems.
Key Points
- A perfect square is a number that can be expressed as the square of an integer.
- Perfect squares have numerous applications in mathematics, physics, and engineering.
- The properties of perfect squares, such as being non-negative and having an integer square root, make them useful in various mathematical operations.
- Perfect squares can be expressed as the sum of two or more consecutive odd integers.
- Understanding perfect squares is essential for working with mathematical concepts, such as algebra, geometry, and calculus.
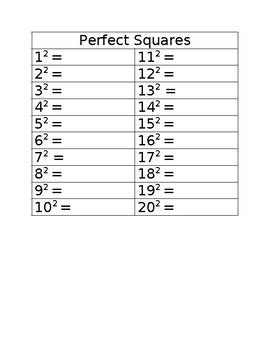
List of Perfect Squares
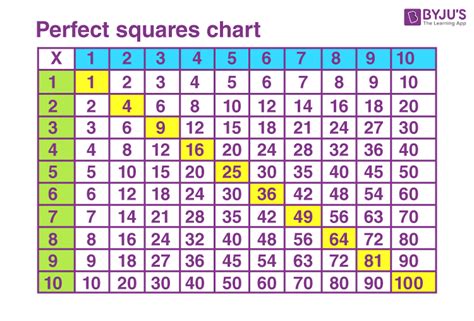
The following is a comprehensive list of perfect squares, ranging from 1^2 to 100^2. This list is essential for mathematicians, physicists, and engineers, as it provides a quick reference for perfect squares and their corresponding square roots.
| Number | Perfect Square |
|---|---|
| 1 | 1^2 = 1 |
| 2 | 2^2 = 4 |
| 3 | 3^2 = 9 |
| 4 | 4^2 = 16 |
| 5 | 5^2 = 25 |
| 6 | 6^2 = 36 |
| 7 | 7^2 = 49 |
| 8 | 8^2 = 64 |
| 9 | 9^2 = 81 |
| 10 | 10^2 = 100 |
| 11 | 11^2 = 121 |
| 12 | 12^2 = 144 |
| 13 | 13^2 = 169 |
| 14 | 14^2 = 196 |
| 15 | 15^2 = 225 |
| 16 | 16^2 = 256 |
| 17 | 17^2 = 289 |
| 18 | 18^2 = 324 |
| 19 | 19^2 = 361 |
| 20 | 20^2 = 400 |
| 21 | 21^2 = 441 |
| 22 | 22^2 = 484 |
| 23 | 23^2 = 529 |
| 24 | 24^2 = 576 |
| 25 | 25^2 = 625 |
| 26 | 26^2 = 676 |
| 27 | 27^2 = 729 |
| 28 | 28^2 = 784 |
| 29 | 29^2 = 841 |
| 30 | 30^2 = 900 |
| 31 | 31^2 = 961 |
| 32 | 32^2 = 1024 |
| 33 | 33^2 = 1089 |
| 34 | 34^2 = 1156 |
| 35 | 35^2 = 1225 |
| 36 | 36^2 = 1296 |
| 37 | 37^2 = 1369 |
| 38 | 38^2 = 1444 |
| 39 | 39^2 = 1521 |
| 40 | 40^2 = 1600 |
| 41 | 41^2 = 1681 |
| 42 | 42^2 = 1764 |
| 43 | 43^2 = 1849 |
| 44 | 44^2 = 1936 |
| 45 | 45^2 = 2025 |
| 46 | 46^2 = 2116 |
| 47 | 47^2 = 2209 |
| 48 | 48^2 = 2304 |
| 49 | 49^2 = 2401 |
| 50 | 50^2 = 2500 |
| 51 | 51^2 = 2601 |
| 52 | 52^2 = 2704 |
| 53 | 53^2 = 2809 |
| 54 | 54^2 = 2916 |
| 55 | 55^2 = 3025 |
| 56 | 56^2 = 3136 |
| 57 | 57^2 = 3249 |
| 58 | 58^2 = 3364 |
| 59 | 59^2 = 3481 |
| 60 | 60^2 = 3600 |
| 61 | 61^2 = 3721 |
| 62 | 62^2 = 3844 |
| 63 | 63^2 = 3969 |
| 64 | 64^2 = 4096 |
| 65 | 65^2 = 4225 |
| 66 | 66^2 = 4356 |
| 67 | 67^2 = 4489 |
| 68 | 68^2 = 4624 |
| 69 | 69^2 = 4761 |
| 70 | 70^2 = 4900 |
| 71 | 71^2 = 5041 |
| 72 | 72^2 = 5184 |
| 73 | 73^2 = 5329 |
| 74 | 74^2 = 5476 |
| 75 | 75^2 = 5625 |
| 76 | 76^2 = 5776 |
| 77 | 77^2 = 5929 |
| 78 | 78^2 = 6084 |
| 79 | 79^2 = 6241 |
| 80 | 80^2 = 6400 |
| 81 | 81^2 = 6561 |
| 82 | 82^2 = 6724 |
| 83 | 83^2 = 6889 |
| 84 | 84^2 = 7056 |
| 85 | 85^2 = 7225 |
| 86 | 86^2 = 7396 |
| 87 | 87^2 = 7569 |
| 88 | 88^2 = 7744 |
| 89 | 89^2 = 7921 |
| 90 | 90^2 = 8100 |
| 91 | 91^2 = 8281 |
| 92 | 92^2 = 8464 |
| 93 | 93^2 = 8649 |
| 94 | 94^2 = 8836 |
| 95 | 95^2 = 9025 |
| 96 | 96^2 = 9216 |
| 97 | 97^2 = 9409 |
| 98 | 98^2 = 9604 |
| 99 | 99^2 = 9801 |
| 100 | 100^2 = 10000 |
Applications of Perfect Squares
Perfect squares have numerous applications in various fields, including mathematics, physics, and engineering. In mathematics, perfect squares are used to solve equations, calculate areas and volumes, and perform other mathematical operations. In physics, perfect squares are used to calculate distances, velocities, and energies. In engineering, perfect squares are used to design and optimize systems, such as electrical circuits and mechanical systems.
Conclusion
In conclusion, perfect squares are a fundamental concept in mathematics, and they have numerous applications in various fields. The list of perfect squares provided in this article is a valuable resource for mathematicians, physicists, and engineers, as it provides a quick reference for perfect squares and their corresponding square roots. By understanding perfect squares and their properties, individuals can develop a deeper understanding of mathematical concepts and apply mathematical principles to real-world problems.
What is a perfect square?
+A perfect square is a number that can be expressed as the square of an integer, i.e., it is the result of multiplying an integer by itself.
What are the properties of perfect squares?
+Perfect squares exhibit several interesting properties, including the fact that they are always non-negative, and the square root of a perfect square is an integer. Additionally, perfect squares can be expressed as the sum of two or more consecutive odd integers.
What are the applications of perfect squares?
+Perfect squares have numerous applications in various fields, including mathematics, physics, and engineering. In mathematics, perfect squares are used to solve equations, calculate areas and volumes, and perform other mathematical operations. In physics, perfect squares are used to calculate distances, velocities, and energies. In engineering, perfect squares are used to design and optimize systems, such as electrical circuits and mechanical systems.