When it comes to treating heartburn and acid reflux, two popular medications often come to mind: Pepcid and Prilosec. Both are effective in reducing stomach acid production, but they belong to different classes of drugs and have distinct mechanisms of action. Understanding the differences between Pepcid and Prilosec can help individuals make informed decisions about their treatment options. In this article, we will delve into the world of acid reducers, exploring the primary uses, benefits, and potential side effects of these two medications.
Key Points
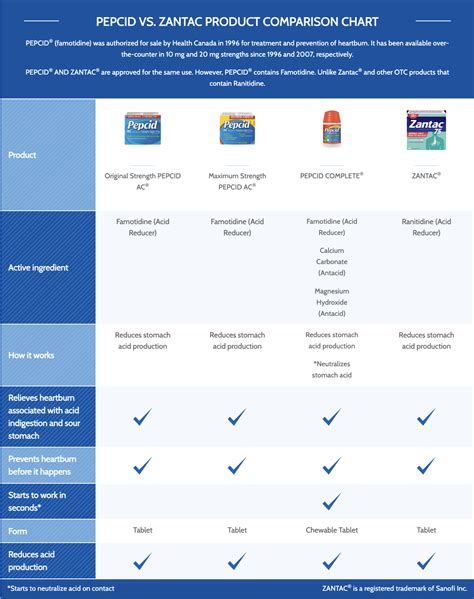
- Pepcid (famotidine) is an H2 blocker that reduces stomach acid production by blocking histamine receptors.
- Prilosec (omeprazole) is a proton pump inhibitor (PPI) that decreases acid production by inhibiting the proton pump in the stomach lining.
- Both medications are effective in treating heartburn, acid reflux, and ulcers, but PPIs like Prilosec are generally more potent.
- Pepcid has a faster onset of action, with effects visible within 1-2 hours, while Prilosec takes around 2-3 days to reach its full effect.
- Common side effects of both medications include headache, diarrhea, and nausea, but PPIs like Prilosec have been linked to increased risks of osteoporosis and vitamin B12 deficiency.
Primary Mechanisms of Action

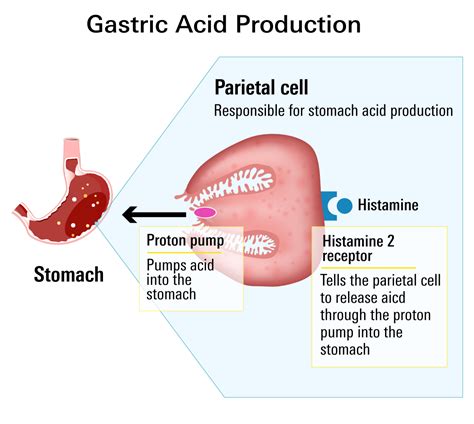
Pepcid, also known as famotidine, belongs to a class of medications called H2 blockers. It works by blocking the action of histamine, a chemical that stimulates the production of stomach acid. By reducing the amount of histamine that binds to receptors in the stomach lining, Pepcid decreases the production of stomach acid, thereby alleviating symptoms of heartburn and acid reflux.
Prilosec, on the other hand, is a proton pump inhibitor (PPI) that works by inhibiting the proton pump in the stomach lining. The proton pump is responsible for producing gastric acid, and by blocking its action, Prilosec significantly reduces the amount of acid produced in the stomach. This makes Prilosec a more potent acid reducer than Pepcid, especially for individuals with severe acid reflux or ulcers.
Comparing Efficacy and Onset of Action
Studies have shown that both Pepcid and Prilosec are effective in treating heartburn, acid reflux, and ulcers. However, PPIs like Prilosec tend to be more effective in reducing acid production and alleviating symptoms. A 2019 meta-analysis published in the Journal of Clinical Gastroenterology found that PPIs were significantly more effective than H2 blockers in healing esophagitis and reducing symptoms of acid reflux.
In terms of onset of action, Pepcid has a faster effect, with noticeable improvements in symptoms within 1-2 hours of administration. Prilosec, on the other hand, takes around 2-3 days to reach its full effect, as it needs time to accumulate in the body and inhibit the proton pump.
| Medication | Onset of Action | Peak Effect |
|---|---|---|
| Pepcid (famotidine) | 1-2 hours | 2-4 hours |
| Prilosec (omeprazole) | 2-3 days | 5-7 days |
Potential Side Effects and Interactions

Both Pepcid and Prilosec can cause side effects, although the severity and frequency of these effects vary. Common side effects of both medications include headache, diarrhea, and nausea. However, PPIs like Prilosec have been linked to increased risks of osteoporosis, vitamin B12 deficiency, and magnesium deficiency, especially with long-term use.
It's essential to note that both medications can interact with other drugs, including antacids, blood thinners, and certain antibiotics. Individuals taking Pepcid or Prilosec should inform their healthcare provider about all medications they are taking to minimize the risk of adverse interactions.
Special Considerations and Warnings
Pepcid and Prilosec are generally safe for most adults, but certain individuals may need to exercise caution when taking these medications. For example, pregnant or breastfeeding women should consult their healthcare provider before taking either medication, as the safety of these drugs during pregnancy and lactation has not been extensively studied.
Additionally, individuals with a history of kidney or liver disease should be monitored closely when taking Pepcid or Prilosec, as these medications can affect kidney and liver function. It's also essential to follow the recommended dosage and duration of treatment to minimize the risk of adverse effects.
What is the primary difference between Pepcid and Prilosec?
+Pepcid is an H2 blocker that reduces stomach acid production by blocking histamine receptors, while Prilosec is a proton pump inhibitor (PPI) that decreases acid production by inhibiting the proton pump in the stomach lining.
Which medication is more effective for severe acid reflux?
+Prilosec, as a PPI, is generally more effective than Pepcid for severe acid reflux, as it can reduce acid production more significantly.
Can I take Pepcid or Prilosec with other medications?
+It's essential to inform your healthcare provider about all medications you are taking, as both Pepcid and Prilosec can interact with other drugs, including antacids, blood thinners, and certain antibiotics.
In conclusion, while both Pepcid and Prilosec are effective in treating heartburn and acid reflux, they have distinct mechanisms of action and differing efficacy profiles. By understanding the primary differences between these medications, individuals can make informed decisions about their treatment options and work with their healthcare provider to find the best course of treatment for their specific needs.